
Concept explainers
Insect-Assisted Fertilization in Moss Moss sperm can swim, but plant ecologist Nils Cronberg suspected that they sometimes hitch a ride on crawling insects or mites (tiny animals related to spiders). To test this hypothesis he carried out an experiment. He placed patches of male and female moss gametophytes in dishes, either next to one another or with water-absorbing plaster between them. The plaster prevented sperm from Swimming between plants. He then looked at how the presence or absence of insects affected the number of sporophytes formed. FIGURE 22.8 shows his results.
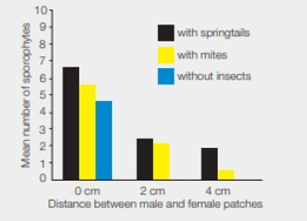
FIGURE 22.8 Sporophyte production in female moss patches with and without either crawling insects (springtails) or mites. No Sporophytes formed in the animal-free dishes when moss patches were 2 or 4 centimeters apart
Why is sporophyte formation a good way to determine if fertilization occurred?
To determine: The chemical that was produced in the greatest amount and its stimulus.
Concept introduction: Secondary metabolites are produced as metabolic intermediate or product but they are not essential for growth. They play a role in reinforcement of tissues for example cellulose, suberin, lignin; protection, and serve as attractants for pollinators. They contribute in plant’s ability to compete and survive. Volatile compounds are such secondary metabolites produced by plants. They attract insects for pollination as well as provide defensive signaling systems against pests and diseases.
Answer to Problem 1DAA
Correct answer: The chemical β-Caryophyllene was produced in greatest amount in response to the treatment with budworms and thrips.
Explanation of Solution
As given in the problem statement, the researchers studied the production of different volatile chemicals by tobacco plants in response to predation by insects- western flower thrips and tobacco budworms.
Refer Fig. 30.19, “Volatile (airborne) compounds produced by tobacco plants in response to predation by different insects” in the textbook. It shows the results of volatile compounds produced (ng/ day) in untreated plants (C), plants that are mechanically wounded (W), attacked by thrips (T), mechanically wounded and attacked by thrips (WT), attacked by budworms (HV), or attacked by budworms and thrips (HVT). When tobacco plants were treated with budworms and thrips (HVT), the chemical β-Caryophyllene was produced that was measured as 6,166 ng/ day. This was the highest amount of chemical produced among all the treatments.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- 9 S es Read the section "Investigating Life: In (Extremely) Cold Blood." Then, drag and drop the terms on the left to complete the concept map. Red blood cells Genes Icefishes -have mutated have colorless Oxygen have few lack encode Blood Cellular respiration consists of- contain carries is a Platelets White blood cells carries low amounts of Hemoglobin is necessary for Plasma Protein Reset.arrow_forwardPlating 50 microliters of a sample diluted by a factor of 10-6 produced 91 colonies. What was the originalcell density (CFU/ml) in the sample?arrow_forwardEvery tutor here has got this wrong, don't copy off them.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the population from question #1 (data is in table below) is experiencing inbreeding depression (F=.25) (and no longer experiencing natural selection). Calculate the new expected genotype frequencies (f) in this population after one round of inbreeding. Please round to 3 decimal places. Genotype Adh Adh Number of Flies 595 Adh Adh 310 Adhs Adhs 95 Total 1000 fladh Adh- flAdn Adh fAdhs Adharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forwardThis question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forward
- They got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forwardThis question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forward

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





