
Concept explainers
Estimate ΔH for the following reactions using bond energies given in Table 8.5.
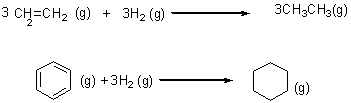
3CH2=CH2(g) + 3H2(g) → 3CH2–CH3(g)
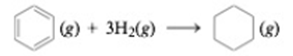
The enthalpies of formation for C6H6(g) and C6H12 (g) are 82.9 and −90.3 kJ/mol. respectively. Calculate ΔH° for the two reactions using standard enthalpies of formation from Appendix 4. Account for any differences between the results obtained from the two methods.
Interpretation:
The estimation has to be done using bond energy values and standard enthalpy of formation values.
Concept Introduction:
Enthalpy is heat content of the system. The value of enthalpy does not depend on the path of a reaction but depend on state of the system. It has a unique value for each state of the system. Thus, enthalpy is a state function. Enthalpy is represented as,
Enthalpy change, denoted by
Where
Energy required to break the existing bonds carries positive sign as energy is supplied to the system and the energy released in formation of new bonds carries negative as energy is removed from the system.
Answer to Problem 158CP
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
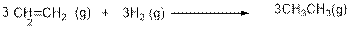
In the above reaction, Hydrogen atoms are added to the
Energy required to break the existing bonds carries positive sign as energy is supplied to the system and the energy released in formation of new bonds carries negative as energy is removed from the system.
Accordingly, the enthalpy change for the above reaction is calculated as –
Enthalpy of formation of ethylene, hydrogen and ethane are
The term “bond energy” and “enthalpy of formation” are not similar. Bond energy refers to energy released or absorbed when isolated elements combine to form a bond. Enthalpy of formation refers to the energy released or absorbed during formation of a compound from other compounds.
Thus, enthalpy of formation of each of the compound on the reactant and product side is widely different from bond energy of the same compounds. Hence enthalpy of reaction calculated using these two different parameters is not same.
The another reaction is,
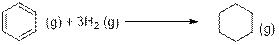
In the above reaction, Hydrogen atoms are added to the
Accordingly, the enthalpy change for the above reaction is calculated as –
Enthalpy of formation of benzene, hydrogen and cyclohexane are
As we discussed earlier, enthalpy of formation of each of the compound on the reactant and product side is widely different from bond energy of the same compounds. Hence enthalpy of reaction calculated using these two different parameters is not same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





