
Concept explainers
Bar AB has a cross-sectional area of 1200 mm2 and is made of a steel that is assumed to be elastoplastic with E = 200 GPa and σY = 250 MPa. Knowing that the force F increases from 0 to 520 kN and then decreases to zero, determine (a) the permanent deflection of point C, (b) the residual stress in the bar.
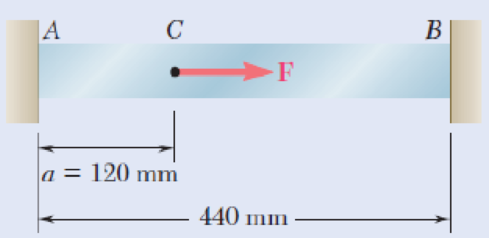
Fig. P2.122
*2.123 Solve Prob. 2.122, assuming that a = 180 mm.
(a)
The permanent deflection of point C.
Answer to Problem 123P
The permanent deflection of point C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The distance between member AC (a) is
The cross sectional area A of section AB is
The modulus of elasticity E is
The yield stress
The force F is
Calculation:
Determine the force to yield portion AC using the relation:
Substitute
Sketch the bar ACB as shown in Figure 1.
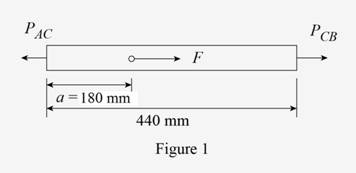
Find the load
Substitute
Find the length
Refer to Figure 1.
Find the deflection at point C using the relation:
Here,
Substitute
Find the stress in rod along CB using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the load
Here,
Substitute
Find the force
Substitute
Determine the deflection at point C
Substitute
Calculate the stress at along AC using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the stress along BC using the relation:
Substitute
Determine the permanent deflection at point C using the relation:
Substitute
Thus, the permanent deflection of point C is
(b)
Find the residual stress in bar AC and CB.
The residual stress in bar AC is
The residual stress in bar CB is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the residual stress in bar AC using the relation:
Substitute
Thus, the residual stress in bar AC is
Find the residual stress in bar BC using the relation:
Substitute
Thus, the residual stress in bar CB is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- Problem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forwardProblem 20: Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG. After the truss is sectioned use a single equation of equilibrium for the calculation of each force. State if the members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B D E F 3 m -5 m- -5 m- 5 m 5 m-arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (19): Given the value of Qp [m³/s], and assuming Reynolds number similitude between the water main and experimental tube, calculate the flow rate in the model tube (Qm) in [lit/s]. = 30.015 m^3/sarrow_forward
- Problem 11: The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by the six cords connected together as shown. Determine the tension in each cord and the angle 0 for equilibrium. Cord BC is horizontal. E 30° B 60° Aarrow_forwardProblem 10: If the bucket weighs 50 lb, determine the tension developed in each of the wires. B $30° 5 E D 130°arrow_forwardProblem 3: Four-Force Equilibrium Knowing the forces in members A and C, determine the force of B and D, assuming the system is in equilibrium. A structural joint is held in equilibrium by four forces acting along different members. • Member A applies a force of 4 kN at an angle of 60° above the positive x-axis. • Member C applies a force of 2 kN horizontally to the left along the x-axis. • Member B applies an unknown force along the horizontal direction. • Member D applies an unknown force at an angle of 45° above the negative x-axis. Determine the forces in members B and D, assuming the system is in static equilibrium. 4 kN 2 kN C 45° A D 60° FB Barrow_forward
- Problem 18: Determine the force in each member of the truss. State if the members are in tension or compression. 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft B D 4 ft 4 ft. 130 lb Earrow_forwardProblem 16: Determine the force in each of the member of the truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. Set P₁ = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. 2 m G F E A A 1 m B 2 m 1 m P1 Darrow_forwardProblem 7: Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium of the 60-kg bucket. D E 4 m 4 m B 3 m- 3 m- 3 m.arrow_forward
- Problem 15: Determine the reactions at the pin A and the tension in cord BC. Set F = 40 kN. Neglect the thickness of the beam. 26 kN F 13 12 -2 m 4 m B 4arrow_forwardProblem 21: Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC and state if the members are in tension or compression. 1.5 m 4 kN E D 8 kN B 2 m 2 marrow_forwardProblem 8: If the cords suspend the two buckets in the equilibrium position, determine the weight of bucket B. Bucket A has a weight of 60 lb. E 65° C 20° 40° F B 20° Aarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
