
The compression ratio of an Otto cycle as shown in Figure 21.12 is VA/VB = 8.00. At the beginning A of the compression process, 500 cm3 of gas is at 100 kPa and 20.0°C. At the beginning of the adiabatic expansion, the temperature is TC = 750°C. Model the working fluid as an ideal gas with γ = 1.40. (a) Fill in this table to follow the states of the gas:
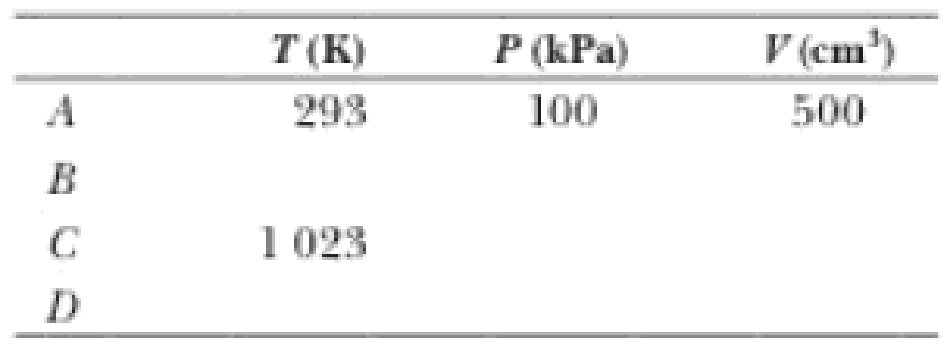
(b) Fill in this table to follow the processes:
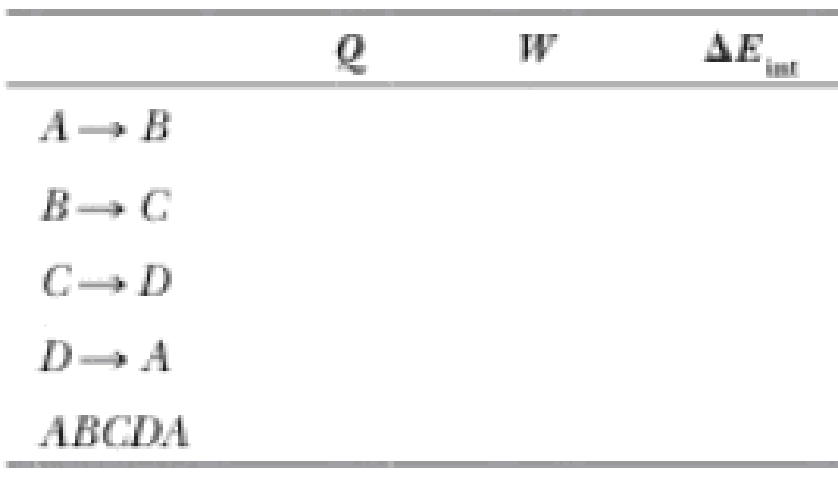
(c) Identify the energy input |Qh|, (d) the energy exhaust |Qc|, and (e) the net output work Weng. (f) Calculate the efficiency. (g) Find the number of crankshaft revolutions per minute required for a one-cylinder engine to have an output power of 1.00 kW = 1.34 hp. Note: The
(a)
The blanks of the table to follow the states of the gas.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The complete table is shown below.
| State |
|
|
|
| A | 293 | 100 | 500 |
| B | 673 |
|
62.5 |
| C | 1023 |
|
62.5 |
| D | 445 | 152 | 500 |
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
Write the expression to calculate the quantity of the gas.
Here,
Substitute
In process
Write the expression to calculate the pressure at point B.
Substitute 8 for
The compression ratio is,
Substitute
Write the expression to calculate the temperature at point B.
Substitute
At state C:
Write the expression to calculate the pressure at point C.
Substitute
State D:
Therefore, the compression ratio is,
Write the expression to calculate the pressure at point D.
Substitute
Write the expression to calculate the temperature at point D.
Substitute
From the above explanation, the complete table is given below.
| State |
|
|
|
| A | 293 | 100 | 500 |
| B | 673 |
|
62.5 |
| C | 1023 |
|
62.5 |
| D | 445 | 152 | 500 |
Conclusion:
Therefore, the complete table is given below.
| State |
|
|
|
| A | 293 | 100 | 500 |
| B | 673 |
|
62.5 |
| C | 1023 |
|
62.5 |
| D | 445 | 152 | 500 |
(b)
The blanks of the table to follow the processes.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The complete table is shown below.
| Process | Q |
|
|
|
|
0 | -162 | 162 |
|
|
149 | 0 | 149 |
|
|
0 | 246 | -246 |
|
|
-65 | 0 | -65 |
|
|
84.3 | 84.3 | 0 |
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
Write the expression to calculate the energy in A to B process.
Substitute
Write the expression of first law of thermodynamics.
Substitute
Write the expression to calculate the energy in B to C process.
Substitute
Write the expression of first law of thermodynamics.
Substitute
Write the expression to calculate the energy in C to D process.
Substitute
Write the expression of first law of thermodynamics.
Substitute
The net work done is,
The net heat energy is,
Substitute
From the above explanation, the complete table is given below.
| Process | Q |
|
|
|
|
0 | -162 | 162 |
|
|
149 | 0 | 149 |
|
|
0 | 246 | -246 |
|
|
-65 | 0 | -65 |
|
|
84.3 | 84.3 | 0 |
Conclusion:
Therefore, the complete table is,
| Process | Q |
|
|
|
|
0 | -162 | 162 |
|
|
149 | 0 | 149 |
|
|
0 | 246 | -246 |
|
|
-65 | 0 | -65 |
|
|
84.3 | 84.3 | 0 |
(c)
The heat input during
Answer to Problem 47CP
The heat input during
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
From part (b), the heat input during
Thus, the heat input during
Conclusion:
Therefore, the heat input during
(d)
The heat exhaust during
Answer to Problem 47CP
The heat exhaust during
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
From part (b)
The heat exhaust during
Thus, the heat exhaust during
Conclusion:
Therefore, the heat exhaust during
(e)
The net work output.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The net work output is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
From part (b)
The net work output is
Thus, the net work output is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net work output is
(f)
The thermal efficiency.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The thermal efficiency is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
Write the expression to calculate the thermal efficiency.
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the thermal efficiency is
(g)
The number of crankshaft revolution per minute.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The number of crankshaft revolution per minute is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The compression ratio of an Otto cycle is
Write the expression to calculate the output power.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the number of crankshaft revolution per minute is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Multi-term
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Silicates Question 18Select one: a. All of these b. Are minerals c. Consist of tetrahedra d. Contain silicon and oxygenarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not one of the major types of metamorphism? Question 20Select one: a. Fold b. Contact c. Regional d. Sheararrow_forwardA bungee jumper plans to bungee jump from a bridge 64.0 m above the ground. He plans to use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 6.00 m above the water. Model his body as a particle and the cord as having negligible mass and obeying Hooke's law. In a preliminary test he finds that when hanging at rest from a 5.00 m length of the cord, his body weight stretches it by 1.55 m. He will drop from rest at the point where the top end of a longer section of the cord is attached to the bridge. (a) What length of cord should he use? m (b) What maximum acceleration will he experience? m/s²arrow_forward
- One end of a light spring with spring constant k is attached to the ceiling. A second light spring is attached to the lower end, with spring constant k. An object of mass m is attached to the lower end of the second spring. (a) By how much does the pair of springs stretch? (Use the following as necessary: k₁, k₂, m, and g, the gravitational acceleration.) Xtotal (b) What is the effective spring constant of the spring system? (Use the following as necessary: k₁, k₂, m, and g, the gravitational acceleration.) Keff (c) What If? Two identical light springs with spring constant k3 are now individually hung vertically from the ceiling and attached at each end of a symmetric object, such as a rectangular block with uniform mass density. In this case, with the springs next to each other, we describe them as being in parallel. Find the effective spring constant of the pair of springs as a system in this situation in terms of k3. (Use the following as necessary: k3, M, the mass of the symmetric…arrow_forwardA object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force FX that varies with position as in the figure below. Fx (N) 4 3 2 1 x(m) 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 i (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m. J (b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 5.00 m to x = 11.0 m. ] (c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 11.0 m to x = 18.0 m. J (d) If the object has a speed of 0.400 m/s at x = 0, find its speed at x = 5.00 m and its speed at x speed at x = 5.00 m speed at x = 18.0 m m/s m/s = 18.0 m.arrow_forwardA crate with a mass of 74.0 kg is pulled up an inclined surface by an attached cable, which is driven by a motor. The crate moves a distance of 70.0 m along the surface at a constant speed of 3.3 m/s. The surface is inclined at an angle of 30.0° with the horizontal. Assume friction is negligible. (a) How much work (in kJ) is required to pull the crate up the incline? kJ (b) What power (expressed in hp) must a motor have to perform this task? hparrow_forward
- A deli uses an elevator to move items from one level to another. The elevator has a mass of 550 kg and moves upward with constant acceleration for 2.00 s until it reaches its cruising speed of 1.75 m/s. (Note: 1 hp (a) What is the average power (in hp) of the elevator motor during this time interval? Pave = hp (b) What is the motor power (in hp) when the elevator moves at its cruising speed? Pcruising hp = 746 W.)arrow_forwardA 1.40-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of v₁ = 3.50 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). d m v=0 -D- www (a) Find the distance of compression d (in m). m (b) Find the speed v (in m/s) at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d). m/s (c) Find the distance D (in m) where the object comes to rest. m (d) What If? If the object becomes attached securely to the end of the spring when it makes contact, what is the new value of the distance D (in m) at which the object will come to…arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a 0.580 kg object is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x. The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the object travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point A, the bottom of a vertical circular track of radius R = 1.00 m, and continues to move up the track. The speed of the object at the bottom of the track is VA = 13.0 m/s, and the object experiences an average frictional force of 7.00 N while sliding up the track. R (a) What is x? m A (b) If the object were to reach the top of the track, what would be its speed (in m/s) at that point? m/s (c) Does the object actually reach the top of the track, or does it fall off before reaching the top? O reaches the top of the track O falls off before reaching the top ○ not enough information to tellarrow_forward
- A block of mass 1.4 kg is attached to a horizontal spring that has a force constant 900 N/m as shown in the figure below. The spring is compressed 2.0 cm and is then released from rest. wwww wwwwww a F x = 0 0 b i (a) A constant friction force of 4.4 N retards the block's motion from the moment it is released. Using an energy approach, find the position x of the block at which its speed is a maximum. ст (b) Explore the effect of an increased friction force of 13.0 N. At what position of the block does its maximum speed occur in this situation? cmarrow_forwardYou have a new internship, where you are helping to design a new freight yard for the train station in your city. There will be a number of dead-end sidings where single cars can be stored until they are needed. To keep the cars from running off the tracks at the end of the siding, you have designed a combination of two coiled springs as illustrated in the figure below. When a car moves to the right in the figure and strikes the springs, they exert a force to the left on the car to slow it down. Total force (N) 2000 1500 1000 500 Distance (cm) 10 20 30 40 50 60 i Both springs are described by Hooke's law and have spring constants k₁ = 1,900 N/m and k₂ = 2,700 N/m. After the first spring compresses by a distance of d = 30.0 cm, the second spring acts with the first to increase the force to the left on the car in the figure. When the spring with spring constant k₂ compresses by 50.0 cm, the coils of both springs are pressed together, so that the springs can no longer compress. A typical…arrow_forwardA spring is attached to an inclined plane as shown in the figure. A block of mass m = 2.71 kg is placed on the incline at a distance d = 0.285 m along the incline from the end of the spring. The block is given a quick shove and moves down the incline with an initial speed v = incline angle is 0 = 20.0°, the spring constant is k = 505 N/m, and we can assume the surface is frictionless. By what distance (in m) is the spring compressed when the block momentarily comes to rest? m k www m 0.750 m/s. Thearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





