
Concept explainers
Draw enol tautomer(s) for each compound. Ignore stereoisomers.
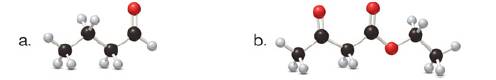
(a)
Interpretation: Enol tautomer(s) of the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Tautomers are the isomers which differ only in the position of the hydrogens and electrons of electronegative element, generally oxygen. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
The very common example of tautomerism is Keto-enol tautomerism. It can be acid or base catalysed.
Answer to Problem 30P
. The enol tautomer of this compound is shown below:
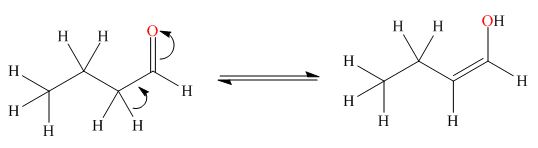
Explanation of Solution
Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. The ball and stick model as shown in Figure 1.
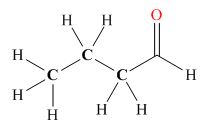
Figure 1
The enol tautomer of this compound is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The tautomer of the given compound is showed in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation: Enol tautomer(s) of the given compound is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Tautomers are the isomers which differ only in the position of the hydrogens and electrons of electronegative element, generally oxygen. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. This phenomenon which involves simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is known as tautomerism.
The very common example of tautomerism is Keto-enol tautomerism. It can be acid or base catalysed.
Answer to Problem 30P
. The enol tautomer of this compound is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Tautomers are isomers which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons of the compound. There is no change in the carbon skeleton of the compound. The ball and stick model as shown in Figure 3.
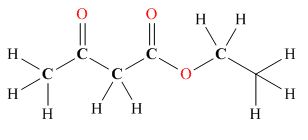
Figure 3
The enol tautomer of this compound is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4
The tautomer of the given compound is showed in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Connect Online Access 1-Semester for Organic Chemistry
- Identify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forwardH- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forwardWhy doesn't this carry on to form a ring by deprotonating the alpha carbon and the negatively-charged carbon attacking the C=O?arrow_forward
- 6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward
- 7. Describe the expected 31P and 19F (where applicable) NMR spectral patterns for the following compounds (indicate number of signals and their splitting patterns). a) tetraphenyldiphosphine Ph Ph P-P Ph Ph Ph Ph ' b) tetraphenyldiphosphine monoxide P-P-Ph Ph (2 points) (2 points c) tetrafluorophosphonium hexafluorophosphate [PF4]*[PF6]¯ (4 points)arrow_forward3. For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ Which (if any) of these complexes would be expected to display Jahn-Teller distortion? (2 points)arrow_forwardWhat is Instrumental Neutron Activation and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications? (I'm doing an in class assignment and need better understanding of what the instrument can be used for) Please include references so that I can better understand the application of how the instrument works!arrow_forward
- What is Isotope Analysis and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications and instrumentalization? Please include references so that I can better understand how the instrument works!arrow_forward5. Count the electrons on the following complexes and state whether they follow the 18- electron rule: (3 points) Fe(CO)5 Ni(PMe3)4 PMe3 is trimethylphosphine Mn(CO)5Brarrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]+, [CoCl4]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 2. Draw the corresponding d-orbital splitting for each of the complexes; predict the spin- state (low-spin/high spin) for each of the complexes (if applicable); explain your arguments. Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy for each complex (in Ao or At). (6 points)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
