
Education levels: The following frequency distribution categorizes US. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.

- Construct a frequency bar graph.
- Construct a relative frequency distribution.
- Construct a relative frequency bar graph.
- Construct a frequency distribution with the following categories: 8 years or less, 9—11 years, High school graduate, Some college but no degree: College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s): Graduate degree Master’s, Professional, or Doctoral).
- Construct a pie chart for the frequency distribution in part (d).
- What proportion of people did not graduate from high school?
a.
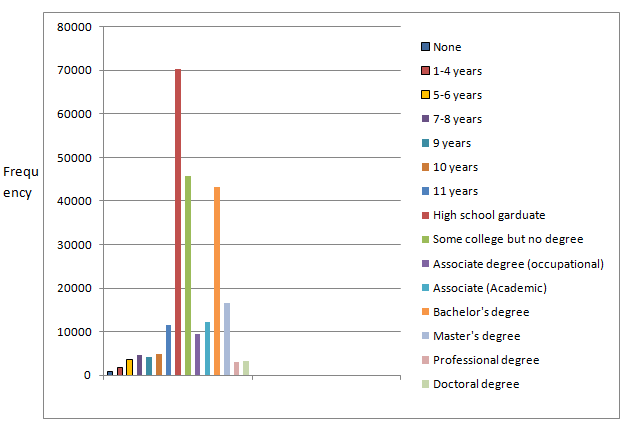
To construct: A frequency bar graph.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| None | 834 |
| 1-4 years | 1764 |
| 5-6 years | 3618 |
| 7-8 years | 4575 |
| 9 years | 4068 |
| 10 years | 4814 |
| 11 years | 11429 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 9380 |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 12100 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43277 |
| Master’s degree | 16625 |
| Professional degree | 3099 |
| Doctoral degree | 3191 |
Solution:
From the given table, the frequency bar graph is given by
b.
To construct: The relative frequency distribution.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| None | 834 |
| 1-4 years | 1764 |
| 5-6 years | 3618 |
| 7-8 years | 4575 |
| 9 years | 4068 |
| 10 years | 4814 |
| 11 years | 11429 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 9380 |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 12100 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43277 |
| Master’s degree | 16625 |
| Professional degree | 3099 |
| Doctoral degree | 3191 |
Formula used:
Calculation:
From the given table,
The sum of all frequency is
The table of relative frequency is given by
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) | Relative frequency |
| None | 834 | |
| 1-4 years | 1764 | |
| 5-6 years | 3618 | |
| 7-8 years | 4575 | |
| 9 years | 4068 | |
| 10 years | 4814 | |
| 11 years | 11429 | |
| High school graduate | 70441 | |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 | |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 9380 | |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 12100 | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43277 | |
| Master’s degree | 16625 | |
| Professional degree | 3099 | |
| Doctoral degree | 3191 |
c.
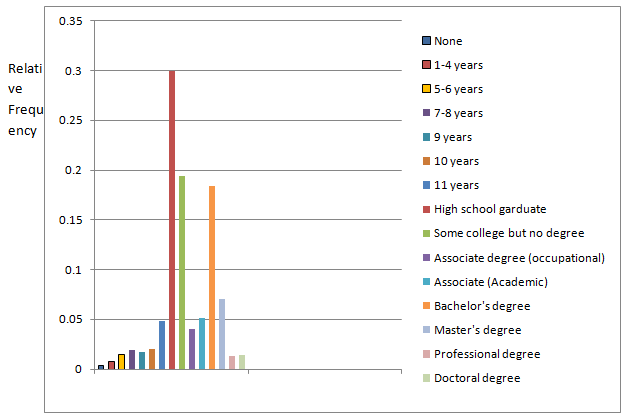
To construct: A relative frequency bar graph.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| None | 834 |
| 1-4 years | 1764 |
| 5-6 years | 3618 |
| 7-8 years | 4575 |
| 9 years | 4068 |
| 10 years | 4814 |
| 11 years | 11429 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 9380 |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 12100 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43277 |
| Master’s degree | 16625 |
| Professional degree | 3099 |
| Doctoral degree | 3191 |
Definition used:
Histogram based on relative frequency is called relative frequency histogram.
Solution:
The following table gives the relative frequency.
| Educational attainment | Relative frequency |
| None | 0.0036 |
| 1-4 years | 0.0075 |
| 5-6 years | 0.0154 |
| 7-8 years | 0.0195 |
| 9 years | 0.0173 |
| 10 years | 0.0205 |
| 11 years | 0.0487 |
| High school graduate | 0.2999 |
| Some college but no degree | 0.1945 |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 0.0399 |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 0.0515 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 0.184 |
| Master’s degree | 0.0708 |
| Professional degree | 0.0132 |
| Doctoral degree | 0.0136 |
From the above table, the relative frequency bar graph is given by
d.
To construct: A frequency distribution with the following categories: 8 years or less, 9-11 years, High school graduate, Some college but no degree, College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s), Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral)
Answer to Problem 28E
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| 8 years or less | 10791 |
| 9-11 years | 20311 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | 64757 |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) | 22915 |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| None | 834 |
| 1-4 years | 1764 |
| 5-6 years | 3618 |
| 7-8 years | 4575 |
| 9 years | 4068 |
| 10 years | 4814 |
| 11 years | 11429 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| Associates degree (Occupational) | 9380 |
| Associates degree (Academic) | 12100 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 43277 |
| Master’s degree | 16625 |
| Professional degree | 3099 |
| Doctoral degree | 3191 |
Solution:
The required frequency distribution with the given categories is given by
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| 8 years or less | |
| 9-11 years | |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) |
e.
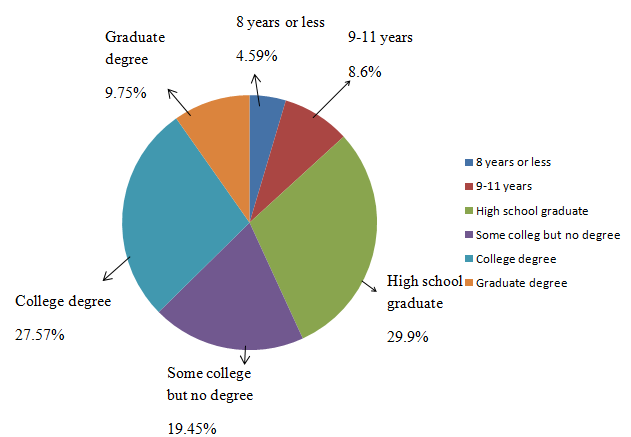
To construct: A pie chart
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| 8 years or less | 10791 |
| 9-11 years | 20311 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | 64757 |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) | 22915 |
Solution:
From the given table, the percentage of each gender and age group is given by
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) | Relative frequency | Percentage |
| 8 years or less | 10791 | 0.0459 | 4.59 % |
| 9-11 years | 10311 | 0.086 | 8.6% |
| High school graduate | 70441 | 0.299 | 29.9% |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 | 0.1945 | 19.45% |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | 64757 | 0.2757 | 27.57% |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) | 22915 | 0.0975 | 9.75% |
From the above table, the pie chart is given by
f.
To find: The proportion of people did not graduate from high school.
Answer to Problem 28E
The proportion of people did not graduate from high school is 0.132.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The following frequency distribution categorises U.S. adults aged 18 and over by educational attainment in a recent year.
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) |
| 8 years or less | 10791 |
| 9-11 years | 20311 |
| High school graduate | 70441 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | 64757 |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) | 22915 |
Solution:
From the given table, the percentage of each gender and age group is given by
| Educational attainment | Frequency(in thousands) | Relative frequency |
| 8 years or less | 10791 | 0.0459 |
| 9-11 years | 20311 | 0.086 |
| High school graduate | 70441 | 0.299 |
| Some college but no degree | 45685 | 0.1945 |
| College degree (Associate’s or Bachelor’s) | 64757 | 0.2757 |
| Graduate degree (Master’s, professional, or Doctoral) | 22915 | 0.0975 |
The people did not graduate from high school are people whose educations are 8 years or less and 9-11 years.
The proportion of people did not graduate from high school is
Hence, the proportion of people did not graduate from high school is 0.132.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Elementary Statistics
- (c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward
- (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward29. State the Borel-Cantelli Lemmas without proof. What is the primary distinction between Lemma 1 and Lemma 2?arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


