
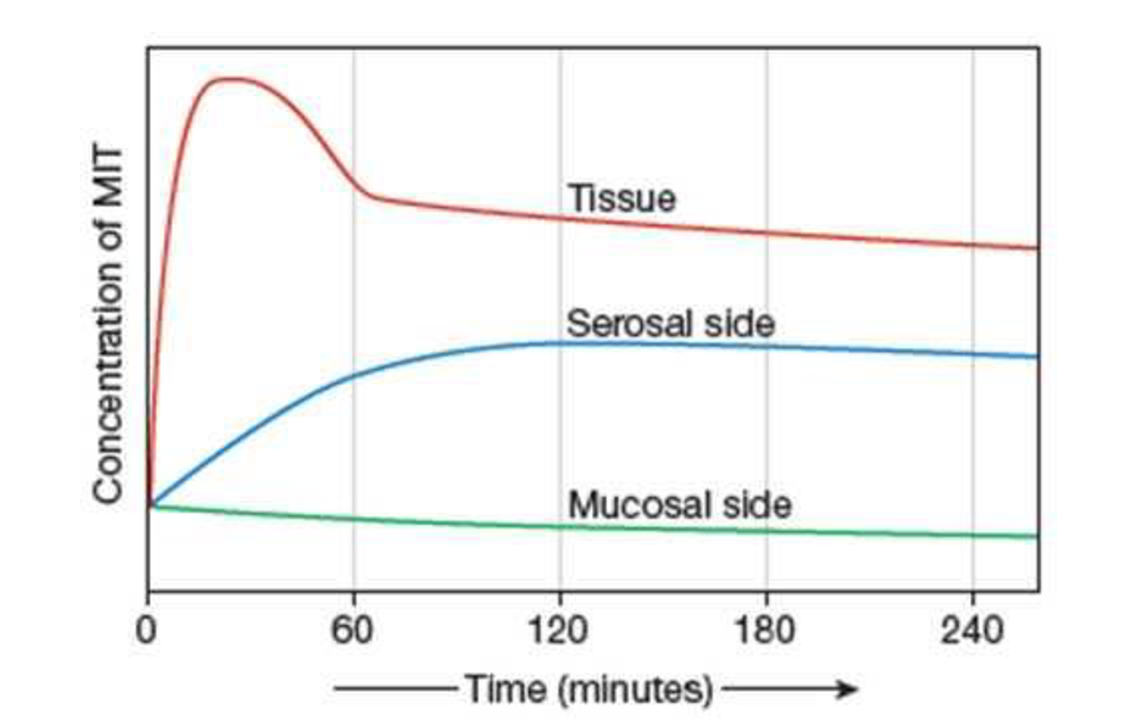
Intestinal transport of the amino acid analog MIT (monoiodotyrosine) can be studied using the “everted sac” preparation. A length of intestine is turned inside out, filled with a solution containing MIT, tied at both ends, and then placed in a bath containing nutrients, salts, and an equal concentration of MIT. Changes in the concentration of MIT are monitored in the bath (mucosal or apical side of the inverted intestine), in the intestinal cells (tissue), and within the sac (serosal or basolateral side of the intestine) over a 240-minute period. The results are displayed in the graph shown here. (Data from Nathans et al., Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 41: 271–282, 1960.)
- a. Based on the data shown, is the transepithelial transport of MIT a passive process or an active process?
- b. Which way does MIT move: (1) apical to tissue to basolateral, or (2) basolateral to tissue to apical? Is this movement absorption or secretion?
- c. Is transport across the apical membrane active or passive? Explain your reasoning.
- d. Is transport across the basolateral membrane active or passive? Explain your reasoning.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Pearson eText Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Identify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forwardWhere did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forward
- What specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated? (Aristolochia stem x.s.) vessel element sieve element ○ companion cell O O O O O tracheid O guard cell none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the tissue. parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem O phloem O none of thesearrow_forward
- Please answer q3arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: How might CRISPR-Cas 9 be used in research or, eventually, therapeutically in patients? What are some potential ethical issues associated with using this technology? Do the advantages of using this technology outweigh the disadvantages (or vice versa)? Explain your position.arrow_forwardYou are studying the effect of directional selection on body height in three populations (graphs a, b, and c below). (a) What is the selection differential? Show your calculation. (2 pts) (b) Which population has the highest narrow sense heritability for height? Explain your answer. (2 pts) (c) If you examined the offspring in the next generation in each population, which population would have the highest mean height? Why? (2 pts) (a) Midoffspring height (average height of offspring) Short Short Short Short (c) Short (b) Short Tall Short Tall Short Short Tall Midparent height (average height of Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inchesarrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





