
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 21, Problem 21MCQ
A 1.0 nC positive point charge is located at point A in Figure Q21.21. The electric potential at point B is
Figure Q21.21
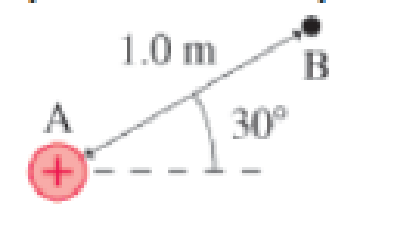
A. 9.0 v
B. 9.0sin30° V
C. 9.0cos30° V
D. 9.0tan30° V
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
pls help
No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer
PART III - RESISTORS IN PARALLEL
Consider (but do not yet build) the circuit shown in the circuit diagram
to the left, which we will call Circuit 3. Make sure you are using Bert
bulbs. You may want to wire two batteries in series rather than use a
single battery.
7. Predict:
a) How will the brightness of bulb B3A compare to the brightness
to bulb B3B?
c)
X
E
B3A
b) How will the brightness of bulb BзA compare to the brightness of bulb B₁ from Circuit 1?
How will the currents at points X, Y, and Z be related?
www
d) How will the current at point X in this circuit compare to the current at point X from Circuit 1?
Y
Z
B3B
www
Chapter 21 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 21 - By moving a 10 nC charge from point A to point B,...Ch. 21 - Charge q is fired through a small hole in the...Ch. 21 - Why is the potential energy of two opposite...Ch. 21 - An electron (q = e) completes half of a circular...Ch. 21 - An electron moves along the trajectory from i to f...Ch. 21 - The graph in Figure Q21.61Q shows the electric...Ch. 21 - As shown in Figure Q21.7, two protons are launched...Ch. 21 - Each part of Figure Q21.8 shows one or more point...Ch. 21 - Figure Q21.9 shows two points inside a capacitor....Ch. 21 - A capacitor with plates separated by distanced is...
Ch. 21 - Rank in order, from most positive to most...Ch. 21 - Figure Q21.12 shows two points near a positive...Ch. 21 - A. Suppose that E = 0, throughout some region of...Ch. 21 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 21 - Figure Q21.16 shows an electric field diagram....Ch. 21 - Figure Q21.17 shows a negatively charged...Ch. 21 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 21 - A parallel-plate capacitor with plate separation d...Ch. 21 - A proton is launched from point 1 in Figure Q21...Ch. 21 - A 1.0 nC positive point charge is located at point...Ch. 21 - A 100 V battery is connected across the plates of...Ch. 21 - The electric potential is 300 V at x = 0 cm, is...Ch. 21 - What is the potential at point c? A. 400 v B. 350...Ch. 21 - At which point, a, b, or c, is the magnitude of...Ch. 21 - What is the approximate magnitude of the electric...Ch. 21 - The direction of the electric field at point b is...Ch. 21 - A +10 nC charge is moved from point c to point a....Ch. 21 - A bug zapper consists of two metal plates...Ch. 21 - An atom of helium and one of argon are singly...Ch. 21 - The dipole moment of the heart is shown at a...Ch. 21 - Moving a charge from point A, where the potential...Ch. 21 - The graph in Figure P21.2 shows the electric...Ch. 21 - It takes 3.0 J of work to move a 15 nC charge from...Ch. 21 - A 20 nC charge is moved from a point where V = 150...Ch. 21 - At one point in space, the electric potential...Ch. 21 - An electron has been accelerated from rest through...Ch. 21 - A proton has been accelerated from rest through a...Ch. 21 - What potential difference is needed to accelerate...Ch. 21 - An electron with an initial speed of 500,000 m/s...Ch. 21 - A proton with an initial speed of 800,000 m/s is...Ch. 21 - The electric potential at a point that is halfway...Ch. 21 - A 2.0 cm 2.0 cm parallel-plate capacitor has a...Ch. 21 - Two 2.00 cm 2.00 cm plates that form a...Ch. 21 - A. In Figure P21.14, which capacitor plate, left...Ch. 21 - A +25 nC charge is at the origin. How much farther...Ch. 21 - A. What is the electric potential at points A, B,...Ch. 21 - A 1.0-cm-diameter sphere is charged to a potential...Ch. 21 - What is the electric potential at the point...Ch. 21 - a. What is the potential difference between the...Ch. 21 - A. In Figure P21.20, which point, A or B, has a...Ch. 21 - In Figure P21.21, the electric potential at point...Ch. 21 - What is the potential difference between xi = 10...Ch. 21 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 21 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 21 - Two 2.0 cm 2.0 cm square aluminum electrodes,...Ch. 21 - An uncharged capacitor is connected to the...Ch. 21 - You need to construct a 100 pF capacitor for a...Ch. 21 - A switch that connects a battery to a 10 F...Ch. 21 - What is the voltage of a battery that will charge...Ch. 21 - Two electrodes connected to a 9.0 V battery are...Ch. 21 - Initially, the switch in Figure P21 .33 is open...Ch. 21 - A 1.2 nF parallel-plate capacitor has an air gap...Ch. 21 - A science-fair radio uses a homemade capacitor...Ch. 21 - A 25 pF parallel-plate capacitor with an air gap...Ch. 21 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter electrodes with a 0.1...Ch. 21 - A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a...Ch. 21 - A parallel-plate capacitor is charged by a 12.0 V...Ch. 21 - To what potential should you charge a 1.0 F...Ch. 21 - A pair of 10 F capacitors in a high-power laser...Ch. 21 - Capacitor 2 has half the capacitance and twice the...Ch. 21 - Two uncharged metal spheres, spaced 15.0 cm apart,...Ch. 21 - 50 pJ of energy is stored in a 2.0 cm 2.0 cm 2.0...Ch. 21 - A 2.0-cm-diameter parallel-plate capacitor with a...Ch. 21 - What is the change in electric potential energy of...Ch. 21 - What is the potential difference V34 in Figure...Ch. 21 - A 50 nC charged particle is in a uniform electric...Ch. 21 - At a distance r from a point charge, the electric...Ch. 21 - The 4000 V equipotential surface is 10.0 cm...Ch. 21 - What is the electric potential energy of the...Ch. 21 - Two point charges 2.0 cm apart have an electric...Ch. 21 - Two positive point charges are 5.0 cm apart. If...Ch. 21 - A +3.0 nC charge is at x = 0 cm and a 1.0 nC...Ch. 21 - A 3.0 nC charge is on the x-axis at x = 9 cm and a...Ch. 21 - A 10.0 nC point charge and a +20.0 nC point charge...Ch. 21 - A 2.0-mm-diameter glass bead is positively...Ch. 21 - In a semiclassical model of the hydrogen atom, the...Ch. 21 - What is the electric potential at the point...Ch. 21 - a. What is the electric potential at point A in...Ch. 21 - A protons speed as it passes point A is 50,000...Ch. 21 - A proton follows the path shown in Figure P21.63....Ch. 21 - Electric outlets have a voltage of approximately...Ch. 21 - Estimate the magnitude of the electric field in a...Ch. 21 - A Na+ion moves from inside a cell, where the...Ch. 21 - Suppose that a molecular ion with charge 10e is...Ch. 21 - The electric field strength is 50,000 V/m inside a...Ch. 21 - A parallel-plate capacitor is charged to 5000 V. A...Ch. 21 - A proton is released from rest at the positive...Ch. 21 - The electric field strength is 20,000 V/m inside a...Ch. 21 - In the early 1900s, Robert Millikan used small...Ch. 21 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter disks spaced 2.0 mm apart form...Ch. 21 - In proton-beam therapy, a high-energy beam of...Ch. 21 - A 2.5-mm-diameter sphere is charged to 4.5 nC. An...Ch. 21 - A proton is fired from far away toward the nucleus...Ch. 21 - Two 10.0-cm-diameter electrodes 0.50 cm apart form...Ch. 21 - Two 10.0-cm-diameter electrodes 0.50 cm apart form...Ch. 21 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 21 - Figure P21.81 shows the electric potential on a...Ch. 21 - A capacitor consists of two 6.0-cm-diameter...Ch. 21 - The dielectric in a capacitor serves two purposes....Ch. 21 - The highest magnetic fields in the world are...Ch. 21 - The flash unit in a camera uses a special circuit...Ch. 21 - A Lightning Strike Storm clouds build up large...Ch. 21 - A Lightning Strike Storm clouds build up large...Ch. 21 - A Lightning Strike Storm clouds build up large...Ch. 21 - A Lightning Strike Storm clouds build up large...Ch. 21 - A Lightning Strike Storm clouds build up large...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What type of cut would separate the brain into anterior and posterior parts?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Examine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n = 6, and identify what stage of...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Carefully examine the common sedimentary rocks shown In Figure 2.13. Use these photos and the preceding discuss...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on extranuclear inheritance and how traits can be determined by gen...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
41. A 0.300 kg oscillator has a speed of 95.4cm/s when its displacement is 3.00cm and 71.4 cm/s when its displ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PART II - RESISTORS IN SERIES Consider (but do not yet build) the circuit shown in the circuit diagram to the left, which we will call Circuit 2. Make sure you are using Bert bulbs. You may want to wire two batteries in series rather than use a single battery. 4. Predict: a) How will the brightness of bulb B₂ compare to the brighness to bulb B2B? X B2A E Y B2B Ꮓ b) How will the brightness of bulb B2A compare to the brightness of bulb B₁ from Circuit 1? c) How will the currents at points X, Y, and Z be related? d) How will the current at point X in this circuit compare to the current at point X from Circuit 1?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardWhat is the practical benefit (in terms of time savings and efficiency) of defining the potential energy? Be clear about what is required in terms of calculation if we do not use the concept of potential energy.arrow_forward
- What is the critical angle fir the light travelling from the crown glass(n=1.52) into the air(n=1.00)?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardYou are working with a team that is designing a new roller coaster-type amusement park ride for a major theme park. You are present for the testing of the ride, in which an empty 150 kg car is sent along the entire ride. Near the end of the ride, the car is at near rest at the top of a 100 m tall track. It then enters a final section, rolling down an undulating hill to ground level. The total length of track for this final section from the top to the ground is 250 m. For the first 230 m, a constant friction force of 370 N acts from computer-controlled brakes. For the last 20 m, which is horizontal at ground level, the computer increases the friction force to a value required for the speed to be reduced to zero just as the car arrives at the point on the track at which the passengers exit. (a) Determine the required constant friction force (in N) for the last 20 m for the empty test car. Write AK + AU + AE int = W+Q + TMW + TMT + TET + TER for the car-track-Earth system and solve for…arrow_forward
- = 12 kg, and m3 Three objects with masses m₁ = 3.8 kg, m₂ find the speed of m3 after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s 19 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m2. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to m m2 m3 iarrow_forwardThree objects with masses m₁ = 3.8 kg, m₂ = 12 kg, and m 19 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m2. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to find the speed of m¸ after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s m m2 mgarrow_forwardIn order for Jane to return to base camp, she needs to swing across a river of width D that is filled with alligators. She must swing into a wind exerting constant horizontal force F, F = 110 N, L = 40.0 m, 0 = 50.0°, and her mass to be 50.0 kg. Wind →F Tarzan! Jane (a) with what minimum speed (in m/s) must Jane begin her swing to just make it to the other side? (If Jane can make it across with zero initial velocity, enter 0.) m/s on a vine having length L and initially making an angle with the vertical (see below figure). Take D = 48.0 m, (b) Shortly after Jane's arrival, Tarzan and Jane decide to swing back across the river (simultaneously). With what minimum speed (in m/s) must they begin their swing? Assume that Tarzan has a mass of 80.0 kg. m/sarrow_forward
- R=2.00 12V 2.00 4.00 4.002 What is the current in one of the 4.0 Q resistors? An isolated point charge q is located at point X. Two other points Y and Z are such that YZ2 XY. Y X What is (electric field at Y)/(electric field at Z)?arrow_forwardTwo objects (m₁ = 4.75 kg and m₂ 2.80 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.75-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table mg m (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s (b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.75-kg object hits the table. m/s (c) How much higher does the 2.80-kg object travel after the 4.75-kg object hits the table? marrow_forwardA cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to three identical resistors. The current in the cell is 3.0 A. The resistors are now arranged in series. What is the new current in the cell?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY