
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
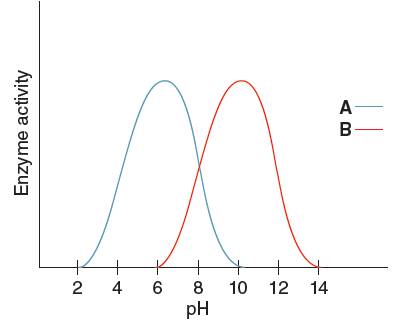
The optimum pH for enzyme 'A' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'A' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
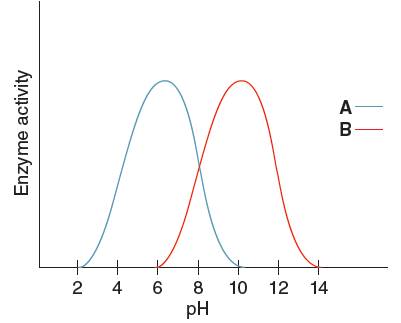
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme A is maximum at pH 6. Hence the optimum pH of enzyme A is 6.
(b)
Interpretation:
The optimum pH for enzyme 'B' needs to be determined, using the given pH versus enzyme activity graph for enzyme A and B.
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Optimum pH for enzyme 'B' is
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. By increasing temperature, rate of reaction also increases until its maximum activity occurs that is at
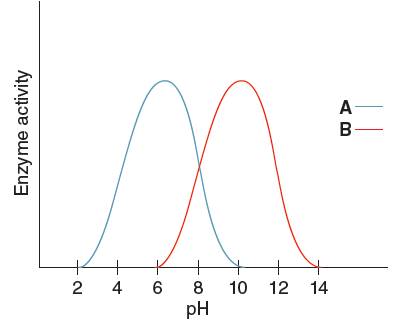
Optimum pH is the pH at which the activity of an enzyme is maximum. So, from the given graph, the activity of enzyme B is maximum at pH 10.
Hence, the optimum pH of enzyme B is 10.
(c)
Interpretation:
The enzyme having the higher activity when pH is
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Enzyme 'A' will have higher pH at
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
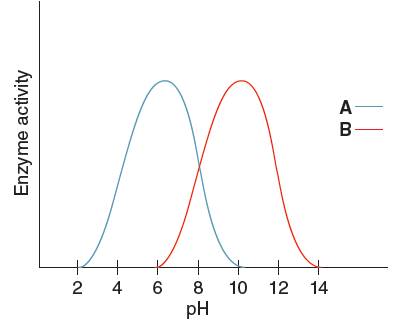
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards. So, before pH 2 enzyme A is inactive and before pH 6 enzyme B is inactive. Therefore, at pH 4 the activity of enzyme A is higher than that of enzyme B.
(d)
Interpretation:
The enzyme having the higher activity at pH
Concept Introduction:
Enzymes are defined as a biological catalyst for various reactions in the living organisms. Enzymes are like all catalyst as it also increases the rate reaction but they themselves do not changed permanently during the process. Enzyme does not alter the position of equilibrium and the relative energy of both the reactant and the products. Reaction when catalyzed by an enzyme increases the rate of reaction by
Answer to Problem 21.83P
Enzyme 'B' will have the higher activity at pH
Explanation of Solution
The activity of enzyme is affected by both the temperature and pH. Optimum pH is the pH value at which the enzyme is most active. The rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction is maximum at optimum pH
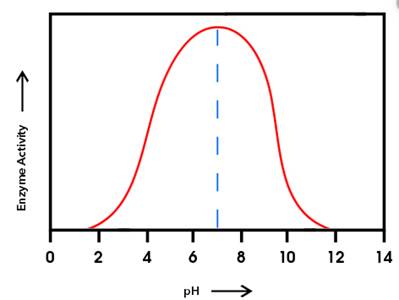
The graph shown below clearly explains the activity of an enzyme with change in pH values:
From the given graph, it can be seen that the activity of enzyme B starts from pH 6 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 10and then activity of enzyme starts decreasing. And activity of enzyme A starts from pH 2 onwards and becomes maximum at pH 6 and then starts decreasing.
At pH 9, activity of enzyme A is decreasing and that of enzyme B is increasing. Hence, at pH 9 activity of enzyme B is higher than that of enzyme A.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- no AI walkthrough current image is wrong answerarrow_forwarda. Determine whether each of the Followery Molecules is in the R- On the y- Configuration 1-01"/ 1-6-4 Br 4 I el Br b. Draw The Fisher projection For all the Meso compounds that can exist FOR The Following molenlearrow_forward1- Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer each of the following question(s): CH₂OH CHO CH₂OH CH₂OH 0 H- OH 0 0 HO- H H- -OH HO H HO H H OH HO- H CH₂OH H. OH HO H HO- H CH₂OH CH₂OH CH3 a. Sorbose b. Rhamnose c. Erythrulose d. Xylulose Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose. a. Xylulose is .. b. Erythrulose is . c. Sorbose is .. d. Rhamnose is .. 2- Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). CHO H OH CH₂OH CH₂OH HO- H HO HO + H. -OH HO OH HO. H OH OH H -OH H OH CH₂OH Q Z a. Refer to Exhibit 25-11. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q. Compound Z is: b. 1. the D-anomer. 2. the a-anomer. 3. the ẞ-anomer. 4. the L-anomer. c. Which anomer is the LEAST stable? d. Q and Z are cyclic examples of: a. acetals b. hemiacetals c. alditols d. hemialditolsarrow_forward
- i need help identifying the four carbon oxygen bonds in the following:arrow_forwardImagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule HO H3N + The solution is... X O acidic OH O basic H3N-CH-C-O O neutral ○ (unknown) O acidic ○ basic CH2 CH 3-S-CH2 O neutral ○ (unknown) H3N O OH O acidic O basic Oneutral O (unknown) 0 H3N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 O acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? olo Ar BHarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughs need other product (product in picture is wrong dont submit the same thing)arrow_forward
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





