
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound using a Claisen condensation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In Claisen condensation, ethyl ethanoate (ethyl acetate) is treated with sodium ethoxide, followed by acid work up, a
Answer to Problem 21.67P
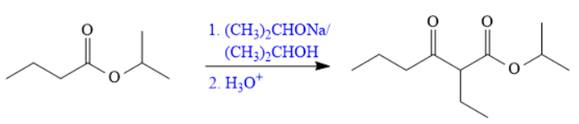
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
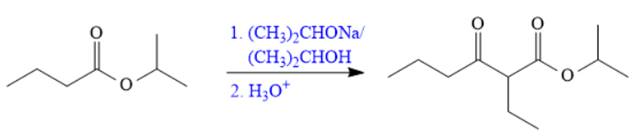
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
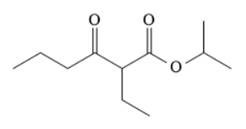
The disconnection of
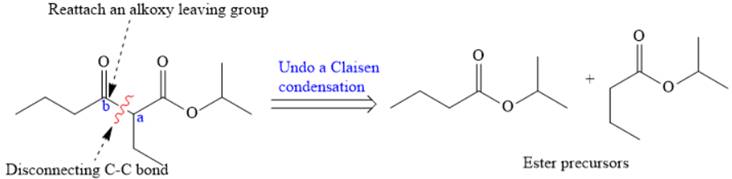
The Claisen reaction in the forward direction would proceed as follows:
The Claisen and Dieckmann condensations are new
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound using a Claisen condensation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In Claisen condensation, ethyl ethanoate (ethyl acetate) is treated with sodium ethoxide, followed by acid work up, a
Answer to Problem 21.67P
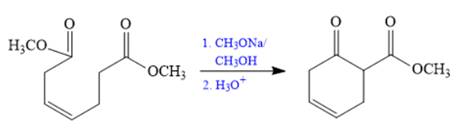
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
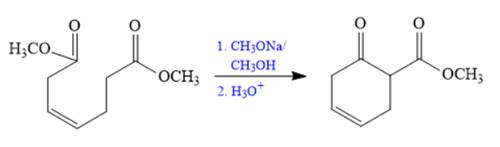
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
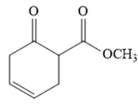
The disconnection of
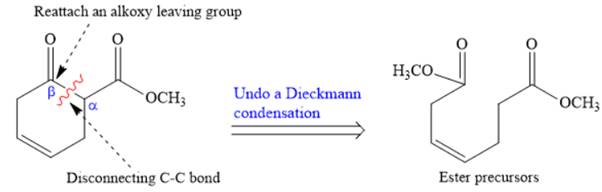
The Dieckmann reaction in the forward direction would proceed as follows:
The Claisen and Dieckmann condensations are new
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound using a Claisen condensation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In Claisen condensation, ethyl ethanoate (ethyl acetate) is treated with sodium ethoxide, followed by acid work up, a
Answer to Problem 21.67P
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
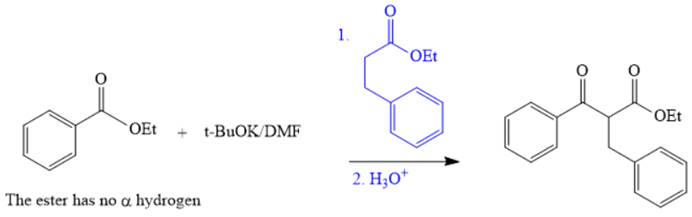
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
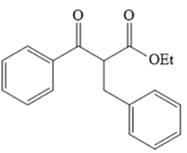
The disconnection of
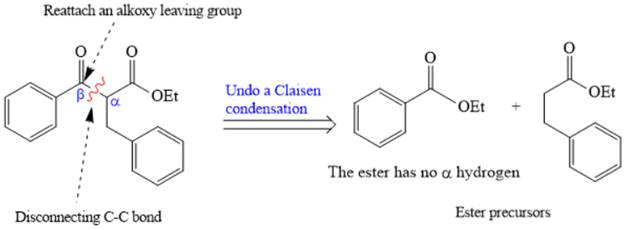
The crossed Claisen reaction in the forward direction would proceed as follows:
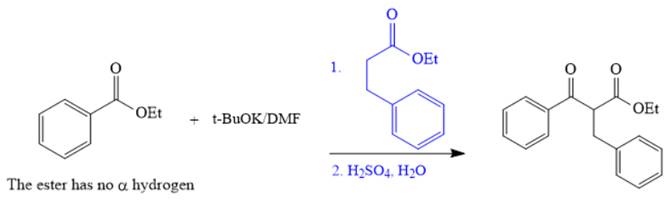
The Claisen and Dieckmann condensations are new
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of given compound using a Claisen condensation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
In Claisen condensation, ethyl ethanoate (ethyl acetate) is treated with sodium ethoxide, followed by acid work up, a
Answer to Problem 21.67P
The synthesis of given compound is shown below.
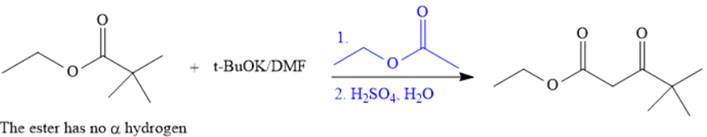
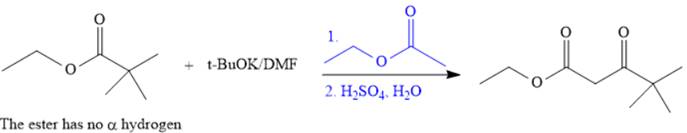
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
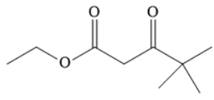
The disconnection of
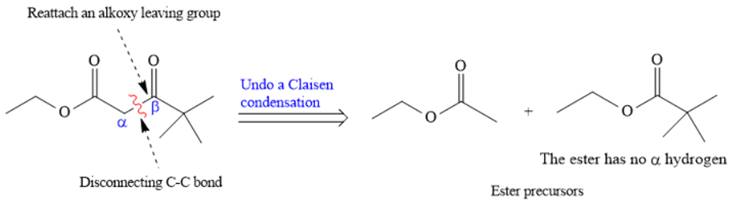
The crossed Claisen reaction in the forward direction would proceed as follows:
The Claisen and Dieckmann condensations are new
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- What would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





