
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
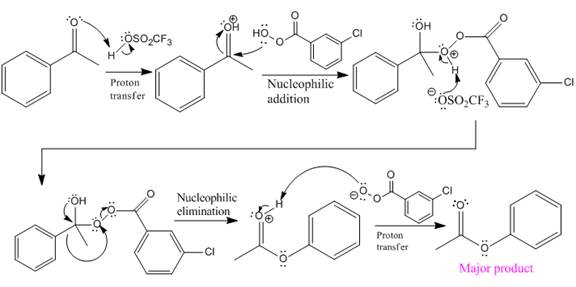
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
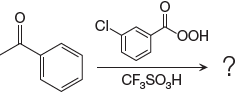
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and an aryl group. According to migratory aptitude, the aryl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and phenyl group, initially bonded to the carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of the given reaction conditions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
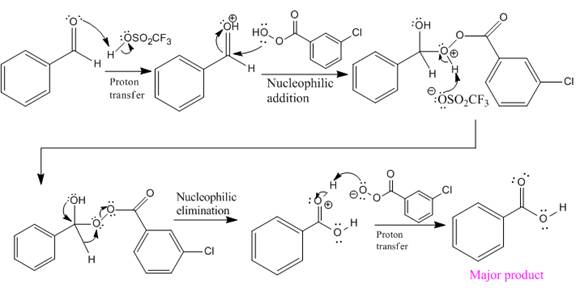
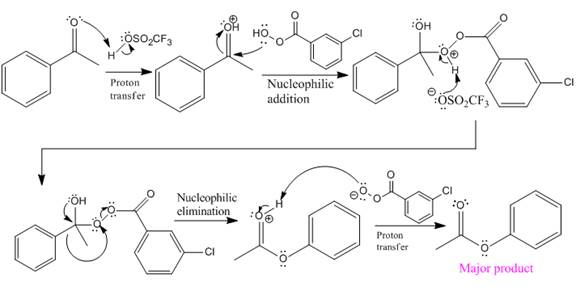
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
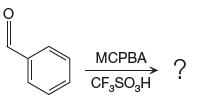
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a H atom and an aryl group. According to the migratory aptitude, the H atom has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the H atom, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
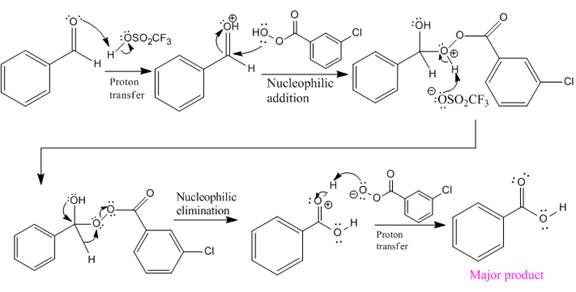
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
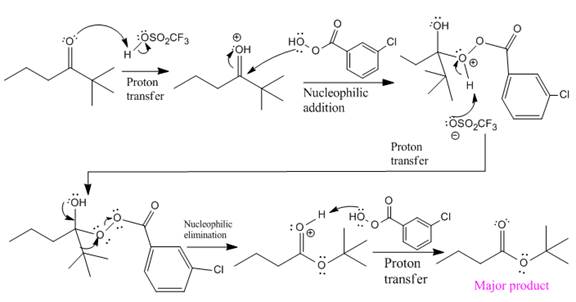
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
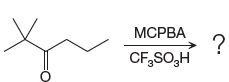
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and tertiary alkyl group. According to migratory aptitude, the tertiary alkyl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the tertiary alkyl group, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:

The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Draw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forwardExplanation Check F1 H₂O H₂ Pd 1) MCPBA 2) H3O+ 1) Hg(OAc)2, H₂O 2) NaBH4 OH CI OH OH OH hydration halohydrin formation addition halogenation hydrogenation inhalation hydrogenation hydration ☐ halohydrin formation addition halogenation formation chelation hydrogenation halohydrin formation substitution hydration halogenation addition Ohalohydrin formation subtraction halogenation addition hydrogenation hydration F2 80 F3 σ F4 F5 F6 1 ! 2 # 3 $ 4 % 05 Q W & Å © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. F7 F8 ( 6 7 8 9 LU E R T Y U A F9arrow_forwardShow the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forward
- Soap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the mechanism for this transformation: *see imagearrow_forwardAssign all the signals individually (please assign the red, green and blue)arrow_forwardThe two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





