
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The reason as to why the
Concept introduction:
A unit cell of the crystal is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms present in the crystal. The unit cell is the smallest and simplest unit of the crystal which on repetition forms an entire crystal. Unit cell can be a cubic unit cell or hexagonal unit cell. The classification of a unit cell depends on the lattice site occupied by the atoms.
Answer to Problem 21.39E
The
Explanation of Solution
Consider a cube having a side of
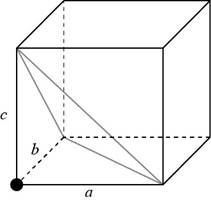
Figure 1
Similarly, consider another
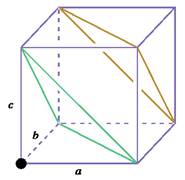
Figure 2
Both the planes are redrawn by using the atoms as shown below.
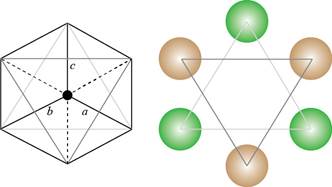
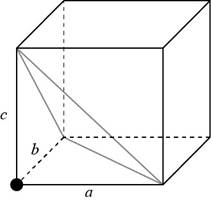
Figure 3
The repeating pattern of Figure 3 is drawn and the path of the diffracted light is shown below.
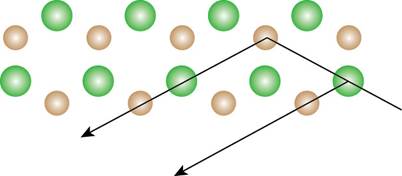
Figure 4
In the body-centered cubic lattice, the atoms are present at the center as well as at the corners. The light is diffracted by the center atoms. The path of diffracted light is shown below.
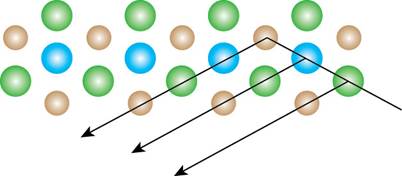
Figure 5
The above diagram is drawn according to the Bragg’s law. The representation of above diagram is shown below.
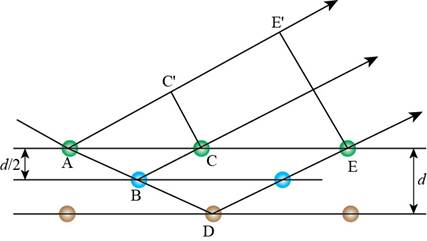
Figure 6
From the Figure 6, the extra distance covered by the light when it is diffracted by the yellow atom (D) is calculated as follows.
Where,
•
• .
•
The distance between two layers is
Substitute
Similarly, the extra distance covered by the light when it is diffracted by the blue atom (B) is calculated as follows.
Where,
•
•
The distance between two layers is
Substitute
Trigonometry is used to calculate the length of
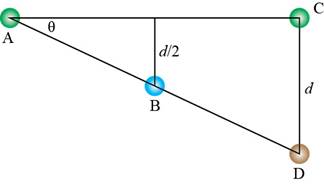
Figure 7
The expression for
The expression for
Substitute equation (5) in above expression.
The trigonometry is used to calculate the length of
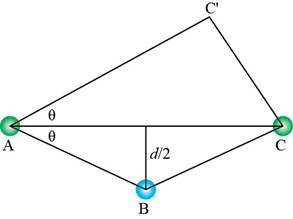
Figure 8
The expression for
The expression for
Substitute equation (8) in equation (7).
Similarly, trigonometry is used to calculate the length of
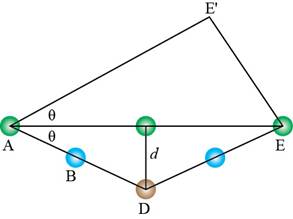
Figure 9
The expression for
The expression for
Substitute equation (11) in equation (10).
Substitute equation (8) in above expression.
Substitute equation (12) and equation (6) in equation (4).
Substitute equation (2) in the above expression.
The above expression shows that the length of thelight passed through the improperly diffracted path is half of the length of the light passed through the properly diffracted path. This indicates that only destructive interference is experienced by the light and it would be cancelled out. Therefore, the
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Ball's Physical Chemistry, 2nd
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forward
- Choose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





