
a.
To find: The
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The plot is:
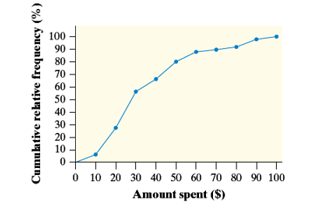
From the provided plot, the third
Thus, the interquartile
Thus, the required value is 28.
b.
To find: The percentile for the shopper.
b.
Answer to Problem 12E
The percentile is 25.
Explanation of Solution
It has been provided that the amount spent by the shopper is $19.50. To find the percentile, construct a vertical line that cuts the x -axis at 19.50. Now, construct a horizontal line for the intersection of the vertical line.
It could be seen that both the line intersecting at 25th percentile.
Thus, the required percentile is 25.
c.
To explain: The reason of curve being flat between $10 and $30.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Here, the cumulative relative frequency is increasing between the values
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- (c) Because logistic regression predicts probabilities of outcomes, observations used to build a logistic regression model need not be independent. A. false: all observations must be independent B. true C. false: only observations with the same outcome need to be independent I ANSWERED: A. false: all observations must be independent. (This was marked wrong but I have no idea why. Isn't this a basic assumption of logistic regression)arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forwardSpam filters are built on principles similar to those used in logistic regression. We fit a probability that each message is spam or not spam. We have several variables for each email. Here are a few: to_multiple=1 if there are multiple recipients, winner=1 if the word 'winner' appears in the subject line, format=1 if the email is poorly formatted, re_subj=1 if "re" appears in the subject line. A logistic model was fit to a dataset with the following output: Estimate SE Z Pr(>|Z|) (Intercept) -0.8161 0.086 -9.4895 0 to_multiple -2.5651 0.3052 -8.4047 0 winner 1.5801 0.3156 5.0067 0 format -0.1528 0.1136 -1.3451 0.1786 re_subj -2.8401 0.363 -7.824 0 (a) Write down the model using the coefficients from the model fit.log_odds(spam) = -0.8161 + -2.5651 + to_multiple + 1.5801 winner + -0.1528 format + -2.8401 re_subj(b) Suppose we have an observation where to_multiple=0, winner=1, format=0, and re_subj=0. What is the predicted probability that this message is spam?…arrow_forward
- Consider an event X comprised of three outcomes whose probabilities are 9/18, 1/18,and 6/18. Compute the probability of the complement of the event. Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.2/18 C.16/18 D.16/3arrow_forwardJohn and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. What is the simple moving average root mean square error? Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 207.13 B. 20.12 C. 14.39 D. 0.21arrow_forward
- The details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. If the smoothing constant is assumed to be 0.7, and setting F1 and F2=A1, what is the exponential smoothing sales forecast for week 7? Round to the nearest whole number. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 80 clocks B. 60 clocks C. 70 clocks D. 50 clocksarrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. Calculate the value of the simple moving average mean absolute percentage error. Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Part 1 A. 14.39 B. 25.56 C. 23.45 D. 20.90arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
- The accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Develop line charts for each variable and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). What is the line chart for the variable Fossil Fuels Production?arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





