
(a)
Interpretation: In the given synthetic scheme, the structures of compounds B and C have to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The given synthetic transformation scheme is shown here:
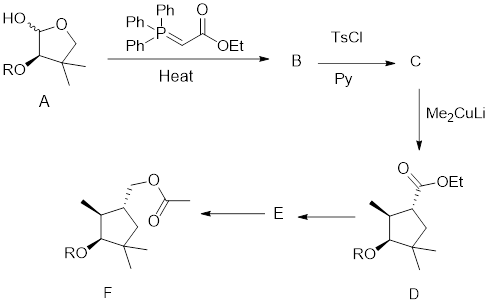
For any given transformation, the following mandatory observations have to be made clear to predict the synthetic scheme:
- Observe whether there is any change in the carbon skeleton.
- Observe whether there is any change in the location of the
functional group . - Predict the synthetic scheme in such a way that these two observations have to be achieved within the minimum chemo selective steps.
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) which yields tosylated product this reaction is called as alkyl tosylate and which is shown below,
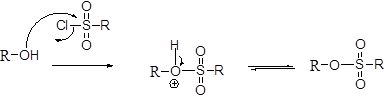
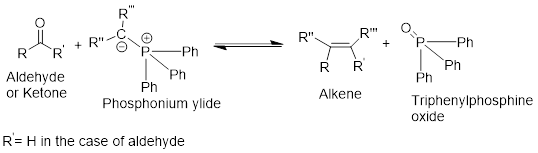
Wittig reaction:
It is the conversion of a
General Scheme
(b)
Interpretation: The conversion C to D has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
The given synthetic transformation scheme is shown here:

For any given transformation, the following mandatory observations have to be made clear to predict the synthetic scheme:
- Observe whether there is any change in the carbon skeleton.
- Observe whether there is any change in the location of the functional group.
- Predict the synthetic scheme in such a way that these two observations have to be achieved within the minimum chemo selective steps.
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) which yields tosylated product this reaction is called as alkyl tosylate and which is shown below,
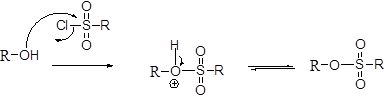
Wittig reaction:
It is the conversion of a ketone or an aldehyde into alkene using the ylide of phosphorus.
General Scheme

Gillman’s reagent:
It is the organometallic reagent that will be widely used to alkylate
It is represented as
(c)
Interpretation:
- The reagents used to convert D into F have to be identified.
- The structure of E has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
The given synthetic transformation scheme is shown here:

For any given transformation, the following mandatory observations have to be made clear to predict the synthetic scheme:
- Observe whether there is any change in the carbon skeleton.
- Observe whether there is any change in the location of the functional group.
- Predict the synthetic scheme in such a way that these two observations have to be achieved within the minimum chemo selective steps.
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) which yields tosylated product this reaction is called as alkyl tosylate and which is shown below,
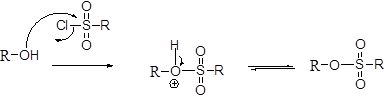
Wittig reaction:
It is the conversion of a ketone or an aldehyde into alkene using the ylide of phosphorus.
General Scheme

Gillman’s reagent:
It is the organometallic reagent that will be widely used to alkylate
It is represented as
Reduction with Lithium Aluminum hydride
Lithium Aluminum hydride reduces aldehydes, ketones and esters into alcohol.
Conversion of ketone into alcohol:

Conversion of aldehyde into alcohol:

Conversion of ester into alcohol:

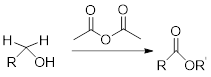
Reaction of alcohol with acetic anhydride:
Alcohols react with acetic anhydride to give ester.
General scheme:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Consider the solubility products (Ksp values) for the following compounds:SrSO4 (Ksp = 7.6 x 10−7), BaSO4 (Ksp = 1.5 x 10−9), SrCO3 (Ksp = 7.0 x 10−10), BaCO3 (Ksp = 1.6 x 10−9)Which anion is the harder base, CO32− or SO42−? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardQ1: a) Arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pKa, highest first. ОН ΟΗ ῸΗ дон ОН ОН CI Brarrow_forward(4 pts - 2 pts each part) A route that can be taken to prepare a hydrophobic (water-repellent) aerogel is to start with trichloromethylsilane, CH3SiCl3 as the silicon source. a. What is the chemical reaction that this undergoes to form a product with Si-OH groups? Write as complete of a chemical equation as you can. CI CI-SI-CH3 CI b. The formation of a byproduct is what drives this reaction - what is the byproduct (if you didn't already answer it in part (a)) and how/why does it form?arrow_forward
- b) Circle the substrate that would not efficiently generate a Grignard reagent upon reaction with Mg in ether. CI Br ד c) Circle the Grignard reagents that contain incompatible functional groups. MgBr HO MgBr MgBr MgBr MgBr HO MgBrarrow_forwardQ2: Predict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable. PCC OH a) CH2Cl2 Page 2 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 HW Problem Sets b) .OH Na2Cr2O7, H+ OH PCC CH2Cl2 c) OHarrow_forwardd) Circle the substrates that will give an achiral product after a Grignard reaction with CH3MgBr. Harrow_forward
- Explain why the S-F bond strength is 367 kJ/mol in SF2 and 329 kJ/mol in SF6.arrow_forwardWould Si(CH3)3F react with AgCl? If so, write out the balanced chemical equation. If not,explain why no reaction would take place.arrow_forwardNH3 reacts with boron halides (BX3 where X = F, Cl, Br, or I) to form H3N-BX3 complexes.Which of these complexes will have the strongest N-B bond? Justify your answerarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





