
Concept explainers
a)
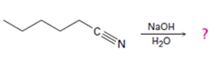
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction are to be given.
Concept introduction:
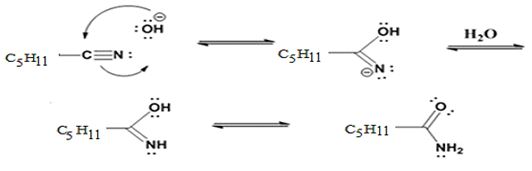
The base catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis into an amide which is then further hydrolyzed to a carboxylate anion and ammonia takes place through the following steps. i) Nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion to the cyanide triple bond to yield an imideanion. ii)Protonation of the imine anion by water to yield a hydroxylamine.iii) Tautomerization of the hydroxylimine to an amide iv) Hydrolysis of the amide to carboxylate anion and ammonia.
To give:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and hexanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:
Hydrolysis of the amide:
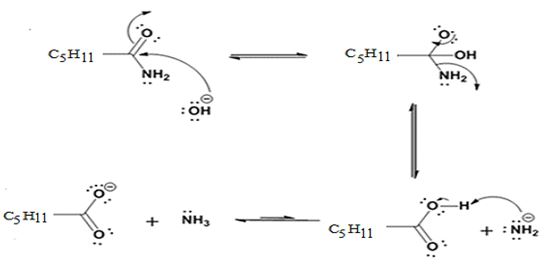
Where C5H11 = -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
Explanation of Solution
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion the nitrile carbon in hexanenitrile yields an imine anion as the product which in the next step gets protonated to produce a hydroxylimine. The hydroxylamine then tautomerizes to give hexanamide.
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of the amide and subsequent loss an amide ion yields hexanoic acid. The deprotonation of the acid by the amide anion leads to the formation of carboxylate anion with the liberation of ammonia.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and hexanoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:

Hydrolysis of the amide:

Where C5H11 = -CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
b)
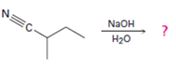
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction are to be given.
Concept introduction:
The base catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis into an amide which is then further hydrolyzed to a carboxylate anion and ammonia takes place through the following steps. i) Nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion to the cyanide triple bond to yield an imideanion. ii)Protonation of the imine anion by water to yield a hydroxylamine.iii) Tautomerization of the hydroxylimine to an amide iv) Hydrolysis of the amide to carboxylate anion and ammonia.
To give:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclobutanecarboxylate anion.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:
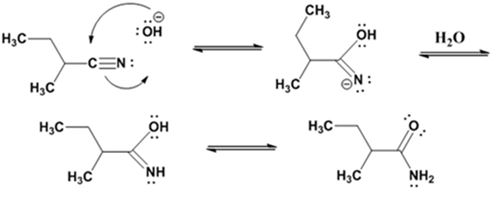
Hydrolysis of the amide:
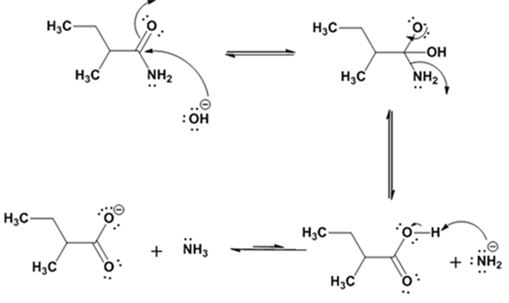
Explanation of Solution
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion the nitrile carbon in 2-methylbutanenitrile yields an imine anion as the product which in the next step gets protonated to produce a hydroxylimine. The hydroxylamine then tautomerizes to give 2-methylbutanamide.
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of the amide and subsequent loss an amide ion yields butanoic acid. The deprotonation of the acid by the amide anion leads to the formation of carboxylate anion with the liberation of ammonia.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclobutanecarboxylate anion.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:

Hydrolysis of the amide:

c)
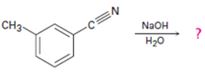
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction is to be given along with the mechanism of the reaction.
Concept introduction:
The base catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis into an amide which is then further hydrolyzed to a carboxylate anion and ammonia takes place through the following steps. i) Nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion to the cyanide triple bond to yield an imideanion. ii)Protonation of the imine anion by water to yield a hydroxylamine. iii) Tautomerization of the hydroxylimine to an amide iv) Hydrolysis of the amide to carboxylate anion and ammonia.
To give:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and m-methylbenzamide.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:
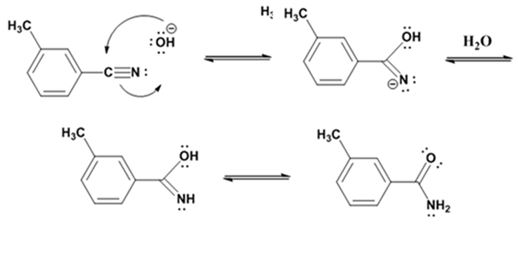
Hydrolysis of the amide:
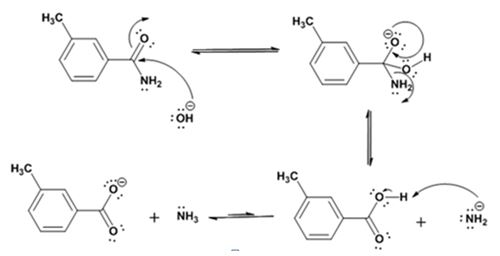
Explanation of Solution
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion the nitrile carbon in m-methylbenzonitrile yields an imine anion as the product which in the next step gets protonated to produce a hydroxylimine. The hydroxylamine then tautomerizes to give 3-methylbenzamide.
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of the amide and subsequent loss an amide ion yields m-methylbenzoic acid. The deprotonation of the acid by the amide anion leads to the formation of the carboxylate anion with the liberation of ammonia.
The products of the reaction are ammonia and m-methylbenzamide.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:

Hydrolysis of the amide:

d)
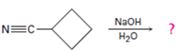
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The base catalyzed nitrile hydrolysis into an amide which is then further hydrolyzed to a carboxylate anion and ammonia takes place through the following steps. i) Nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion to the cyanide triple bond to yield an imideanion. ii)Protonation of the imine anion by water to yield a hydroxylamine.iii) Tautomerization of the hydroxylimine to an amide iv) Hydrolysis of the amide to carboxylate anion and ammonia.
To give:
The products of the reaction along with the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclobutanecarboxylate ion.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:
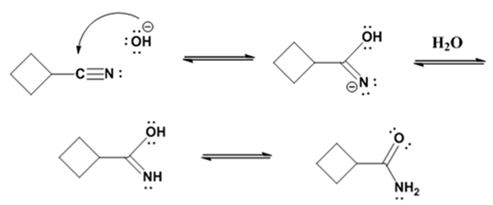
Hydrolysis of the amide:
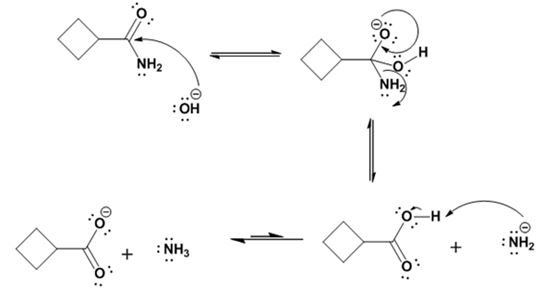
Explanation of Solution
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion the nitrile carbon in cyclobutanenitrile yields an imine anion as the product which in the next step gets protonated to produce a hydroxylimine. The hydroxylamine then tautomerizes to give cyclobutanecarboxylamide.
The nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of the amide and subsequent loss an amide ion yields cyclobutane
The products of the reaction are ammonia and cyclobutanecarboxylate ion.
The mechanism of the reaction is given below.
Formation of the amide:

Hydrolysis of the amide:

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward

 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


