
A second identical bulb is flow added to the circuit as shown. The capacitor is discharged.
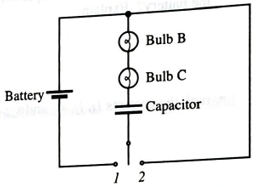
i. The switch is now moved to position 1.
Describe the behavior of bulbs B and C from just after the switch is closed until a long time later. Explain.
How does the initial brightness of bulb C compare to the initial brightness of bulb A in question i of part a? Explain your reasoning.
A long time after the switch is closed, is the potential difference across the capacitor greater than, less than, or equal to the potential difference across the battery? Explain.
ii. The switch is now moved to position 2
Describe the behavior of bulbs B and C from just after the switch is closed until a long time later. Explain your reasoning.
How does the initial brightness of bulb C compare to the initial brightness of bulb A in question ii of part a? Explain your reasoning.
A long time after the switch is closed, is the potential difference across the capacitor greater than, less than, or equal to the potential difference across the battery? Explain.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 20 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
College Physics
Introduction to Electrodynamics
University Physics Volume 3
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Physics (5th Edition)
- Please help me explain e and g. I’m really confused about it.arrow_forwardConsider the diagram at the right of a parallel circuit. Each light bulb has an identical resistance of R and the battery voltage is V. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. a. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location B is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) b. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location D is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) c. If the current at location A is I amperes, then the current at location L is ____ amperes. (Answer in terms of I.) d. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location A would be ____ (two times, four times, one-half, one-fourth, etc.) the original value. e. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location B would be ____ (two times, four times, one-half, one-fourth, etc.) the original value. f. If the voltage of the battery is doubled, then the current at location D would be ____ (two times, four times,…arrow_forwardConsider the diagram at the right of a parallel circuit. Each light bulb in the circuit has an identical resistance. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. Each question may have one, less than one, or more than one answer. a. The electric potential at point A is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. b. The electric potential at point D is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. c. The electric potential at point J is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. d. The electric potential difference between points A and J is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. e. The electric potential difference between points D and G is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any…arrow_forward
- 1. For all practical purposes, a capacitor is considered fully discharged (or fully charged) after 5 time constants. What is the voltage across a discharging capacitor in a RC circuit that has V₁ = 10V, and t = 5 t seconds? Show your work 2. What is the purpose of finding t in a RC circuit? 3. In the virtual simulation, the light bulb is a nice visual indicator of the behavior of a discharging series RC circuit. However, explain why is it easier to find C using a resistor instead of a Light Bulb.arrow_forwardHow to find g? Please explain so I can understand.arrow_forwardPlease help me find the Current I, Voltage drops for V1, V2, V3, and Currents for I2 and I3. R2 =20ohms R3 =100 ohms and are in parallel. R1= 10 ohmsarrow_forward
- Please solve sub-parts c,d,earrow_forwardPart B. Finding the PD Directions: Solve the following problems. Write your answer on a clean sheet of paper. Show your solutions. 1. To carry how much charge between two points having potential difference equal to 220 V, 1760 J of work is done? Ans. 8 C 2. The EMF of a cell falls from 3 volts to 2.8 volts when its terminals are joined to an electrical load of 4 Ohms. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.arrow_forwardP-3 Please help me with this problem very clearly with step by step explanation.arrow_forward
- Answer the following questions. 1. Why does the voltage across the resistor for charging and discharging processes change the sign from positive to negative? Hint: think about the direction of current. 2. Does the voltage V across the resistor for charging and discharging obey by the same equation: V = Vo eRC 3. What is the sum of the voltages across the capacitor Vc and across the resistor VR at any point in time during the charging and discharging processes? Use a snipping tool to copy and paste the waveform chart and graph for the charging and discharging curves into the lab report.arrow_forwardThe direction to answer the problem is on the first picture.arrow_forwardI need help with parts B & C please.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





