
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 80GP
DATA A current-carrying wife of length 0.15 m is in a perpendicular magnetic field. The magnetic force on the wire is measured as a function of the current through the wire. The resulting data are given in the table.
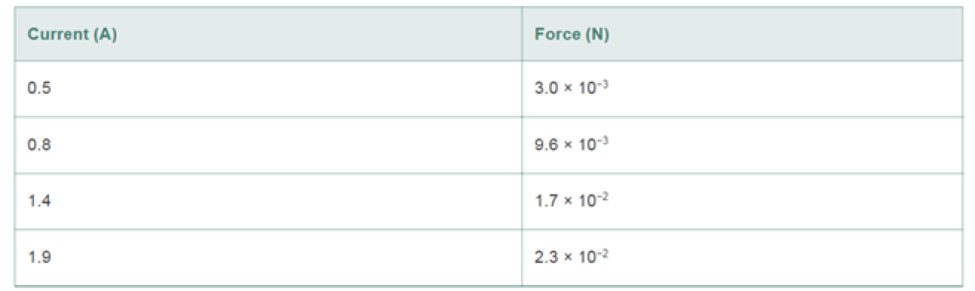
Make a plot of the force as a function of the current. Using a “best fit” to the data, determine the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank you
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
Chapter 20 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 20 - If an electron beam in a cathode-ray tube travels...Ch. 20 - Why is it not a good idea to call magnetic field...Ch. 20 - If the magnetic force does no work on a charged...Ch. 20 - A permanent magnet can be used to pick up a string...Ch. 20 - Streams of charged particles emitted from the sun...Ch. 20 - A student once proposed to obtain an isolated...Ch. 20 - The magnetic force on a moving charged particle is...Ch. 20 - The text discusses the magnetic field of an...Ch. 20 - Two parallel conductors carrying current in the...Ch. 20 - Household wires (such as lamp cords) often carry...
Ch. 20 - Can a charged particle move through a magnetic...Ch. 20 - Prob. 12CQCh. 20 - An electron traveling with a speed v enters a...Ch. 20 - A beam of protons is directed horizontally into...Ch. 20 - A wire carrying a current in the direction shown...Ch. 20 - A solenoid is connected to a battery as shown in...Ch. 20 - Two very long, straight, parallel wires carry...Ch. 20 - A light circular wire suspended by a thin silk...Ch. 20 - An electron is moving di'ectly toward you in a...Ch. 20 - Three particles having the same mass and the same...Ch. 20 - A metal bar connected by metal leads to the...Ch. 20 - A certain current produces a magnetic field 8 near...Ch. 20 - A coil is connected to a battery as shown in...Ch. 20 - A particle enters a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 20 - In a 1.25 T magnetic field directed vertically...Ch. 20 - An ion having charge +6e is traveling horizontally...Ch. 20 - A proton traveling at 3 60 km/s suddenly enters a...Ch. 20 - A particle having a mass of 0.195 g carries a...Ch. 20 - At a given instant, a particle with a mass of 5.00...Ch. 20 - If the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton...Ch. 20 - A particle with mass 3 102 kg and charge +5 C...Ch. 20 - A particle with a charge of 2.50 108 C is moving...Ch. 20 - A particle with mass 1.81 103 kg and a charge of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 10PCh. 20 - Prob. 11PCh. 20 - An electron moves at 2.50 106 m/s through a...Ch. 20 - In a cloud chamber- experiment, 3 proton enters a...Ch. 20 - An alpha particle (a He nucleus, containing two...Ch. 20 - A deuteron particle (the nucleus of an isotope of...Ch. 20 - A beam of protons traveling at 1.20 km/s enters a...Ch. 20 - A uniform magnetic field bends an electron in a...Ch. 20 - 18. An electron at point A in Figure 20.59 has a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 19PCh. 20 - A 3.25 g bullet picks up an electric charge of...Ch. 20 - An electron travels into a 0.3 magnetic field...Ch. 20 - Prob. 22PCh. 20 - Singly ionized (one electron removed) atoms are...Ch. 20 - Ancient meat eating. The amount of meat in...Ch. 20 - A straight vertical wire carries a current of 1.20...Ch. 20 - Magnetic force on a lightning bolt. Currents...Ch. 20 - A horizontal rod 0.200 m long carries a current...Ch. 20 - A straight 2.5 m wire carries a typical household...Ch. 20 - A magnetic field is used to suspend a wire of mass...Ch. 20 - A rectangular 10.0 cm by 20.0 cm circuit carrying...Ch. 20 - A long wire carrying a 6.00 A current reverses...Ch. 20 - As long wire carrying 4.50 A or current makes two...Ch. 20 - The 20.0 cm by 35.0 cm rectangular circuit shown...Ch. 20 - Prob. 34PCh. 20 - A circular coil of wire 8.6 cm in diameter has 15...Ch. 20 - A coil having 165 turns and a radius of 1.2 cm...Ch. 20 - A circular coil of 50 loops and diameter 20.0 cm...Ch. 20 - You want to produce a magnetic field of magnitude...Ch. 20 - Household magnetic fields. Home circuit breakers...Ch. 20 - (a) How large a current would a very long,...Ch. 20 - Currents in the heart. The body contains many...Ch. 20 - Magnetic sensitivity of electric fish. Electric...Ch. 20 - A jumper cable is used to start a car that has a...Ch. 20 - If the magnetic field due to a long, straight,...Ch. 20 - A long, straight wire carries a current l0 and...Ch. 20 - EMF. Currents in dc transmission lines can be 100...Ch. 20 - A long, straight telephone cable contains six...Ch. 20 - Two insulated wires perpendicular to each other in...Ch. 20 - Two long straight parallel wires are 10.0 cm apart...Ch. 20 - Set Up: B=0l2r The direction of BB is given by the...Ch. 20 - Two high-current transmission lines carry currents...Ch. 20 - Prob. 52PCh. 20 - Prob. 53PCh. 20 - An electric bus operates by drawing current from...Ch. 20 - A circular metal loop is 22 cm in diameter, (a)...Ch. 20 - A closely wound circular coil with a diameter of...Ch. 20 - A closely wound circular coil has a radius of 6.00...Ch. 20 - BIO Currents in the brain. The magnetic field...Ch. 20 - A closely wound, circular coil with radius 2.40 cm...Ch. 20 - Two circular concentric loops of wire lie on a...Ch. 20 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 20 - A solenoid contains 750 coils of very thin wire...Ch. 20 - As a new electrical technician, you are designing...Ch. 20 - A solenoid is designed to produce a 0.0279 T...Ch. 20 - As shown in Figure 20.67, a single circular...Ch. 20 - A solenoid that is 35 cm long and contains 450...Ch. 20 - You have 25 m of wire, which you want to use to...Ch. 20 - A toroidal solenoid (see Figure 20.42) has inner...Ch. 20 - Three long, straight electrical cables, running...Ch. 20 - A long, straight, cylindrical wire of radius R...Ch. 20 - Platinum is a paramagnetic metal having a relative...Ch. 20 - When a certain paramagnetic material is placed in...Ch. 20 - A 150 g ball containing 4.00 108 excess electrons...Ch. 20 - Magnetic balance. The circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 20 - A thin 50.0-cm-long metal bar with mass 750 g...Ch. 20 - 76. A long, straight wire containing a...Ch. 20 - A singly charged an of Li (on isotope of lithium...Ch. 20 - An insulated circular ring of diameter 6.50 cm...Ch. 20 - The effect of transmission lines. Two hikers are...Ch. 20 - DATA A current-carrying wife of length 0.15 m is...Ch. 20 - Two very long, straight wires carry currents as...Ch. 20 - Prob. 82GPCh. 20 - Prob. 83GPCh. 20 - Prob. 84GPCh. 20 - A long wire carrying 6.50 A of current makes two...Ch. 20 - BIO Magnetic fields and MRI. Magnetic resonance...Ch. 20 - Prob. 87PPCh. 20 - The large magnetic fields used in MRI can produce...Ch. 20 - BIO Studying magnetic bacteria. Some types of...Ch. 20 - To use a larger sample of bacteria, the...Ch. 20 - BIO Studying magnetic bacteria. Some types of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
30. A 3000-rn-high mountain is located on the equator. How much faster does a climber on top of the mountain mo...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Identify each of the following reproductive barriers as prezygotic or postzygotic. a. One lilac species lives o...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
18. SCIENTIFIC THINKING By measuring the fossil remains of Homo floresiensis, scientists have estimated its wei...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Draw the following orbitals: a. 3s orbital b. 4s orbital c. 3p orbital
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- A long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forward
- Explain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forward
- For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY