
Concept explainers
An entrepreneur wants to determine whether it would be pro�table to establish a gardening service in a local suburb. The entrepreneur believes that there are four possible levels of demand for this gardening service:
Very low demand-
Low demand-
Moderate demand-
High demand-
Based on past experiences in other suburbs. the entrepreneur as- signs the following probabilities to the various demand levels:
P(Very low demand)
P(Low demand) = 0.50
P(Moderate demand)
P(High demand)
The entrepreneur has calculated the following pro�ts or losses ($) of this garden service for each demand level (over a period of one year):
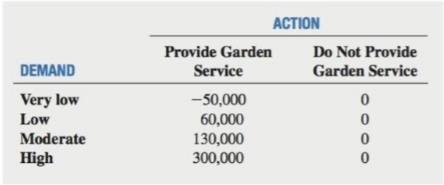
a. Construct a decision tree.
b. Construct an opportunity loss table.
c. Compute the expected monetary value (EMV) for offering this garden service.
d. Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for offering this garden service.
e. Explain the meaning of the
f. Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for offering this garden service.
g. Based on the results of (c), (d), and (f), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why?
Before making a �nal decision, the entrepreneur conducts a survey to determine demand for the gardening service. A random sample of 20 households is selected, and 3 indicate that they would use this gardening service.
h. Revise the prior probabilities in light of this sample information.
i. Use the revised probabilities in (h) to repeat (c) through (g).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition (13th Edition)
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardDATA TABLE VALUES Meal Price ($) 22.78 31.90 33.89 22.77 18.04 23.29 35.28 42.38 36.88 38.55 41.68 25.73 34.19 31.75 25.24 26.32 19.57 36.57 32.97 36.83 30.17 37.29 25.37 24.71 28.79 32.83 43.00 35.23 34.76 33.06 27.73 31.89 38.47 39.42 40.72 43.92 36.51 45.25 33.51 29.17 30.54 26.74 37.93arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardSales personnel for Skillings Distributors submit weekly reports listing the customer contacts made during the week. A sample of 65 weekly reports showed a sample mean of 19.5 customer contacts per week. The sample standard deviation was 5.2. Provide 90% and 95% confidence intervals for the population mean number of weekly customer contacts for the sales personnel. 90% Confidence interval, to 2 decimals: ( , ) 95% Confidence interval, to 2 decimals:arrow_forwardA simple random sample of 40 items resulted in a sample mean of 25. The population standard deviation is 5. a. What is the standard error of the mean (to 2 decimals)? b. At 95% confidence, what is the margin of error (to 2 decimals)?arrow_forward
- mean trough level of the population to be 3.7 micrograms/mL. The researcher conducts a study among 93 newly diagnosed arthritis patients and finds the mean trough to be 4.1 micrograms/mL with a standard deviation of 2.4 micrograms/mL. The researcher wants to test at the 5% level of significance if the trough is different than previously reported or not. Z statistics will be used. Complete Step 5 of hypothesis testing: Conclusion. State whether or not you would reject the null hypothesis and why. Also interpret what this means (i.e. is the mean trough different from 3.7 or noarrow_forward30% of all college students major in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math). If 48 college students are randomly selected, find the probability thata. Exactly 12 of them major in STEM. b. At most 17 of them major in STEM. c. At least 12 of them major in STEM. d. Between 9 and 13 (including 9 and 13) of them major in STEM.arrow_forward7% of all Americans live in poverty. If 40 Americans are randomly selected, find the probability thata. Exactly 4 of them live in poverty. b. At most 1 of them live in poverty. c. At least 1 of them live in poverty. d. Between 2 and 9 (including 2 and 9) of them live in poverty.arrow_forward
- 48% of all violent felons in the prison system are repeat offenders. If 40 violent felons are randomly selected, find the probability that a. Exactly 18 of them are repeat offenders. b. At most 18 of them are repeat offenders. c. At least 18 of them are repeat offenders. d. Between 17 and 21 (including 17 and 21) of them are repeat offenders.arrow_forwardConsider an MA(6) model with θ1 = 0.5, θ2 = −25, θ3 = 0.125, θ4 = −0.0625, θ5 = 0.03125, and θ6 = −0.015625. Find a much simpler model that has nearly the same ψ-weights.arrow_forwardLet {Yt} be an AR(2) process of the special form Yt = φ2Yt − 2 + et. Use first principles to find the range of values of φ2 for which the process is stationary.arrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning


