
Concept explainers
The Islander Fishing Company purchases clams for
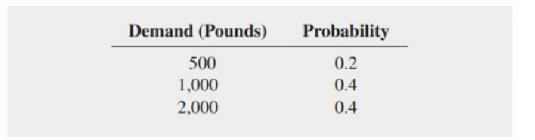
a. For each possible purchase level (500, 1,000, or 2,000 pounds). compute the profit (or loss) for each level of demand.
b. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax criterion.
c. Determine the optimal action based on the maximax criterion.
d. Using the expected monetary value (EMV) criterion, determine the optimal number of pounds of clams the company should purchase from the fishermen. Discuss.
e. Compute the standard deviation for each possible purchase level.
f. Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams.
g. Explain the meaning of the
h. Compute the coefficient of variation for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams. Discuss.
i. Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for purchasing 500, 1,000, and 2,000 pounds of clams. Discuss.
j. Based on (d) and (1). would you choose to purchase 500, 1,000, or 2,000 pounds of claims? Why?
k. Compare the results of (d), (f), (h), and (i) and explain any differences.
l. Suppose that clams can be sold to restaurants for
m. What would he the effect on the results in (a) through (k) if the probability of the demand for 500, 1,000, and 2,000 clams were 0.4, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition (13th Edition)
- Scrie trei multiplii comuni pentru numerele 12 și 1..arrow_forwardIntroduce yourself and describe a time when you used data in a personal or professional decision. This could be anything from analyzing sales data on the job to making an informed purchasing decision about a home or car. Describe to Susan how to take a sample of the student population that would not represent the population well. Describe to Susan how to take a sample of the student population that would represent the population well. Finally, describe the relationship of a sample to a population and classify your two samples as random, systematic, cluster, stratified, or convenience.arrow_forward1.2.17. (!) Let G,, be the graph whose vertices are the permutations of (1,..., n}, with two permutations a₁, ..., a,, and b₁, ..., b, adjacent if they differ by interchanging a pair of adjacent entries (G3 shown below). Prove that G,, is connected. 132 123 213 312 321 231arrow_forward
- You are planning an experiment to determine the effect of the brand of gasoline and the weight of a car on gas mileage measured in miles per gallon. You will use a single test car, adding weights so that its total weight is 3000, 3500, or 4000 pounds. The car will drive on a test track at each weight using each of Amoco, Marathon, and Speedway gasoline. Which is the best way to organize the study? Start with 3000 pounds and Amoco and run the car on the test track. Then do 3500 and 4000 pounds. Change to Marathon and go through the three weights in order. Then change to Speedway and do the three weights in order once more. Start with 3000 pounds and Amoco and run the car on the test track. Then change to Marathon and then to Speedway without changing the weight. Then add weights to get 3500 pounds and go through the three gasolines in the same order.Then change to 4000 pounds and do the three gasolines in order again. Choose a gasoline at random, and run the car with this gasoline at…arrow_forwardAP1.2 A child is 40 inches tall, which places her at the 90th percentile of all children of similar age. The heights for children of this age form an approximately Normal distribution with a mean of 38 inches. Based on this information, what is the standard deviation of the heights of all children of this age? 0.20 inches (c) 0.65 inches (e) 1.56 inches 0.31 inches (d) 1.21 inchesarrow_forwardAP1.1 You look at real estate ads for houses in Sarasota, Florida. Many houses range from $200,000 to $400,000 in price. The few houses on the water, however, have prices up to $15 million. Which of the following statements best describes the distribution of home prices in Sarasota? The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is less than the median. The distribution is roughly symmetric with a few high outliers, and the mean is approximately equal to the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is less than the median.arrow_forward
- During busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?arrow_forwardPlease could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanksarrow_forward28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are independent? (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) = E(X)E(Y); (e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





