
Student Workbook for College Physics: A Strategic Approach Volume 1 (Chs. 1-16)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321908865
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 37P
Molecules of carbon mon-oxide are permanent electric dipoles due to unequal sharing of electrons between the carbon and oxygen atoms. Figure P20.37 shows the distance and charges. Suppose a carbon monoxide molecule with a horizontal axis is in a vertical electric field of strength 15,000 N/C.
Figure P20.37
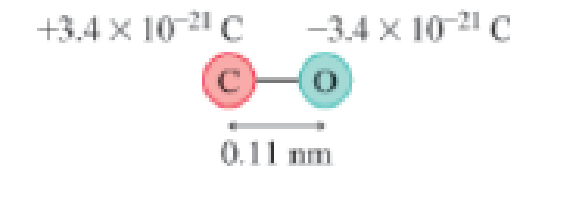
a. What is the magnitude of the net force on the molecule?
b. What is the magnitude of the torque on the molecule?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 16
2.9 Three Pulleys
2.9a A thin, light rope is draped over three frictionless pulleys arranged around the origin as shown. Each pulley is a solid disk of radius r=2cm and is equidistant from the origin. 5kg mass is attached to one side and a 7kg mass to the other.
Before the masses are released and in motion, what is the total angular momentum in kgm2/s around the origin?
Question 17
2.9b What fraction of the angular momentum is in the pulleys?
At what temperature would water boil if the outside pressure was only 19,900 Pa in degrees Celsius?
Which of these properties of a sound wave is associated with the pitch of the sound that we hear?
amplitudefrequency intensity levelintensity
Chapter 20 Solutions
Student Workbook for College Physics: A Strategic Approach Volume 1 (Chs. 1-16)
Ch. 20 - Four lightweight balls A, B, C, and D are...Ch. 20 - Plastic and glass rods that have been charged by...Ch. 20 - a. Can an insulator be charged? If so, how would...Ch. 20 - When you take clothes out of the drier right after...Ch. 20 - The positive charge in Figure Q20.5 is +Q. What is...Ch. 20 - As shown in Figure Q20.6, metal sphere A has 4...Ch. 20 - Figure Q20.7 shows a positively charged rod held...Ch. 20 - A plastic balloon that has been rubbed with wool...Ch. 20 - You are given two metal spheres on portable...Ch. 20 - A honeybee acquires a positive electric charge as...
Ch. 20 - A metal rod A and a metal sphere B, on insulating...Ch. 20 - Iontophoresis is a noninvasive process that...Ch. 20 - A 10 nC charge sits at a point in space where the...Ch. 20 - A hollow soda straw is uniformly charged, as shown...Ch. 20 - A positively charged particle is in the center of...Ch. 20 - Two charged particles are separated by 10 cm....Ch. 20 - A small positive charge q experiences a force of...Ch. 20 - A typical commercial airplane is struck by...Ch. 20 - Microbes such as bacteria have small positive...Ch. 20 - a. Is there a point between a 10 nC charge and a...Ch. 20 - Two lightweight, electrically neutral conducting...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.23 have the same...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.241Q have the same...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.25 have the same...Ch. 20 - A glass bead charged to +3.5 nC exerts an 8.0 104...Ch. 20 - A +7.5 nC point charge and a 2.0 nC point charge...Ch. 20 - Three point charges are arranged as shown in...Ch. 20 - A positive charge is brought near to a dipole, as...Ch. 20 - A glass rod is charged to +5.0 nC by rubbing. a....Ch. 20 - A plastic rod is charged to 20 nC by rubbing. a....Ch. 20 - Prob. 3PCh. 20 - A plastic rod that has been charged to 15.0 nC...Ch. 20 - A glass rod that has been charged to +12.0 nC...Ch. 20 - Two identical metal spheres A and Bare in contact....Ch. 20 - Two identical metal spheres A and Bare connected...Ch. 20 - If two identical conducting spheres are in...Ch. 20 - Two 1.0 kg masses are 1.0 m apart on a...Ch. 20 - A small metal sphere has a mass of 0.15 g and a...Ch. 20 - A small plastic sphere with a charge of 5.0 nC is...Ch. 20 - A small metal bead, labeled A, has a charge of 25...Ch. 20 - A small glass bead has been charged to +20 nC. A...Ch. 20 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 20 - In Figure P20.15, charge q2 experiences no net...Ch. 20 - Object A, which has been charged to +10 nC, is at...Ch. 20 - A small glass bead has been charged to +20 nC....Ch. 20 - What magnitude charge creates a 1.0 N/C electric...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - A 30 nC charge experiences a 0.035 N electric...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - A +1 0 nC charge is located at the origin. a. What...Ch. 20 - A 10 nC charge is located at the origin. a. What...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of an electric...Ch. 20 - A 0.10 g plastic bead is charged by the addition...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is constructed of two...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is formed from two 4.0...Ch. 20 - Two identical closely spaced circular disks form a...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is constructed of two...Ch. 20 - Storm clouds may build up large negative charges...Ch. 20 - A neutral conducting sphere is between two...Ch. 20 - One kind of e-book display consists of millions of...Ch. 20 - A protein molecule in an electrophoresis gel has a...Ch. 20 - Large electric fields in cell membranes cause ions...Ch. 20 - Molecules of carbon mon-oxide are permanent...Ch. 20 - A 2.0-mmdiameter copper ball is charged to +50 nC....Ch. 20 - Pennies today are copper-covered zinc, but older...Ch. 20 - Two protons are 2.0 fm apart. (1 fm= 1 femtometer...Ch. 20 - The nucleus of a 12Xe atom (an isotope of the...Ch. 20 - Two equally charged, 1.00 g spheres are placed...Ch. 20 - Objects A and Bare both positively charged. Both...Ch. 20 - An electric dipole is formed from 1.0 nC point...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What is the force on the 1.0 nC charge in Figure...Ch. 20 - What is the force on the 1.0 nC charge in Figure...Ch. 20 - What is the magnitude of the force on the 1.0 nC...Ch. 20 - What are the magnitude and direction of the force...Ch. 20 - As shown in Figure P20.52, a 5.0 nC charge sits at...Ch. 20 - Two particles have positive charges q and Q. A...Ch. 20 - Model a pollen grain as a sphere of carbon 0.10 mm...Ch. 20 - In a simple model of the hydrogen atom, the...Ch. 20 - A 0.10 g honeybee acquires a charge of +23 pC...Ch. 20 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter disks face each other, 1.0 mm...Ch. 20 - The electron gun in a television tube uses a...Ch. 20 - A 0.020 g plastic bead hangs from a lightweight...Ch. 20 - A 4.0 mg bead with a charge of 2.5 nC rests on a...Ch. 20 - Two 3.0 g spheres on 1.0-m-long threads repel each...Ch. 20 - An electric field E = (100,000 N/C, right) causes...Ch. 20 - An electric field E = (200,000 N/C, right) causes...Ch. 20 - A small charged bead has a mass of 1.0 g. It is...Ch. 20 - A bead with a mass of 0.050 g and a charge of 15...Ch. 20 - A small bead with a positive charge q is free to...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor consists of two plates,...Ch. 20 - If the charging collar has a positive charge, the...Ch. 20 - Which of the following describes the charges on...Ch. 20 - Because the droplets are conductors, a droplet's...Ch. 20 - Another way to sort the droplets would be to give...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Calculate the mass of NaCl in a 35-mL sample of a 1.3 M NaCl solution.
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
2. List the subdivisions of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
According to the logistic growth equation dNdt=rN(KN)K (A) the number of individuals added per unit time is gre...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
What is the reducing agent in the following reaction?
2 Br –– (aq) + H2 O2 (aq) + 2 H+ (aq) → Br2 (aq) + 2 H2 ...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wave travels upward in a medium (vertical wave velocity). What is the direction of particle oscillation for the following? (a) a longitudinal wave parallel to the direction of propagationperpendicular to the direction of propagationarrow_forwardThe faster a molecule is moving in the upper atmosphere, the more likely it is to escape Earth's gravity. Given this fact, and your knowledge of rms speed, which of the following molecules can escape most easily from Earth's atmosphere if they are all at the same temperature?arrow_forwardThe temperature in one part of a flame is 2,100 K. What is the rms velocity of the carbon dioxide molecules at this temperature? Give your answer as the number of meters per second. mass of 1 mole of CO2 = 44.0 grams 1 mole contains 6.02 x 1023 molecules the Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/Karrow_forward
- The specific heat of a certain substance is 375 J/(kg°C). How much heat energy would you have to add to increase the temperature of 22 kg of this substance from 33°C up to 44°C in a number of Joules?arrow_forward3.9 moles of an ideal gas are sealed in a container with volume 0.22 m3, at a pressure of 146,000 N/m2. What is the temperature of the gas in degrees Celsius?arrow_forwardwhen a cannon is launched at a 65 degree angle, will it have the same horizontal velocity as when it is launched from a 25 degree angle as long as the initial speed is the same?arrow_forward
- Please solve the problem step by step with explanations along each step explaining what's been done.Thank you!!arrow_forwardFigure 8.14 shows a cube at rest and a small object heading toward it. (a) Describe the directions (angle 1) at which the small object can emerge after colliding elastically with the cube. How does 1 depend on b, the so-called impact parameter? Ignore any effects that might be due to rotation after the collision, and assume that the cube is much more massive than the small object. (b) Answer the same questions if the small object instead collides with a massive sphere.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, 0, y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0.,y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY