
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants store energy of sunlight as chemical energy. Process happens in the chloroplast of a plant cell. Photosynthesis happens in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 23P
- a) Calvin cycle − the dark reactions
Explanation of Solution
Photosynthesis happens via two main stages as light reaction and dark reaction. Light reaction happens in the presence of sunlight. Two photosystems called PS I and PS II absorbs energy of sun light. At the end of light reaction ATP, NADPH and O2 produce. Next, the dark reaction (which is also known as Calvin cycle) starts which uses ATP and NADPH.
For the dark reaction there is no need of sunlight which happens within the stroma. This is a series of
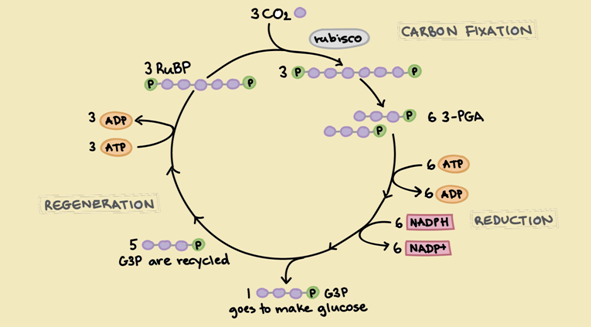
Figure 1: Calvin cycle
(b)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants store energy of sunlight as chemical energy. Process happens in the chloroplast of a plant cell. Photosynthesis happens in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 23P
- b) Rubisco − catalyzes CO2 fixation
Explanation of Solution
Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), is an enzyme used in the dark reaction of photosynthesis. It catalyzes the carbon fixation process where atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted to glucose by photosynthetic organisms..
The enzyme is capable of fixing both CO2 and O2. This enzyme is comparatively less efficient at low CO2 concentrations and tends to bind O2. This series of reactions start with O2 to finally produce CO2. The process is known as photorespiration.
(c)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Rubisco activase enzyme is important in activating Rubisco. Rubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), is an enzyme used in the dark reaction of photosynthesis. It catalyzes the carbon fixation process where atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted to glucose.
Answer to Problem 23P
- c) Carbamate − required for the rubisco activity
Explanation of Solution
In plants and some types of green algae, an enzyme called RuBisCO activase is present. This is required to allow the rapid formation of carbamate in the active site of rubisco. RuBisCO activase is required because the ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RUBP) substrate binds more strongly to the active sites lacking carbamate and hence slows down the activation process.
(d)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Starch is a
Answer to Problem 23P
- d) Starch − storage form of carbohydrates
Explanation of Solution
Starch is a polymeric carbohydrate produced by joining a large number of glucose units via glycosidic bonds.
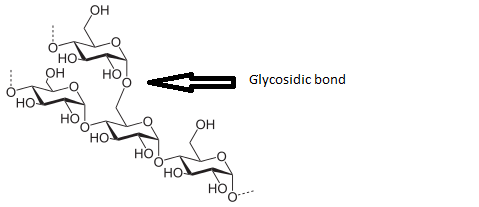
Figure 2: Structure of starch
After plants produce glucose by photosynthesis, it is stored in the cells as starch. Starch is insoluble in plant cell. So, unlike starch glucose increases the concentration of the plant cell.
(e)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Sucrose is a disaccharide of Glucose and fructose, having twelve carbon atoms. Disaccharide consists of two monosaccharides, having six carbon atoms each.
Answer to Problem 23P
- a) Sucrose − transport form of carbohydrates
Explanation of Solution
Sucrose consists of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule joined through a glycosidic bond.
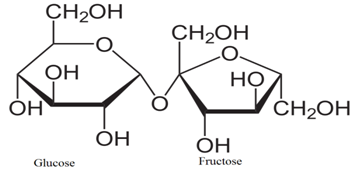
Figure 3: Structure of Sucrose
Plants store glucose (produced in photosynthesis) as starch in different places such as in fruits, seeds, and roots. Starch is insoluble in water and cannot be transported. When the plant needs energy, starch is converted to sucrose and transported. Even though glucose is soluble in water, plant does not convert starch to glucose. Since glucose is highly reactive compared to sucrose, it can transform into other intermediate compounds during transportation. Once it reaches the destination, sucrose is converted to glucose.
(f)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Amylose is a polysaccharide made up of glucose units. These glucose molecules are bonded to each other through a (1→4) glycosidic bonds. Due to its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is resistant to digestive enzymes and therefore known as a resistant starch.
Answer to Problem 23P
- b) Amylose -
Explanation of Solution
As indicated in the figure, the first and fourth carbon of the glucose monomers react to form a bond between them. This bond is known as 1, 4 glycosidic bond.
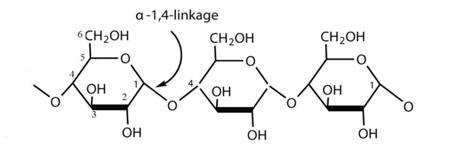
Figure 4: Structure of amylose
(g)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Amylopectin is a highly branched
Answer to Problem 23P
- c) Amylopectin − includes
Explanation of Solution
Amylopectin is a highly branched polymer. This is also known as polysaccharide. The primary unit is glucose. Like amylose, the glucose units are linked in a linear way with a (11→4) glycosidic bonds. This
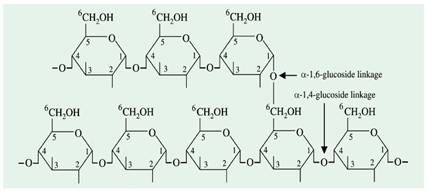
Figure 5: Structure of amylopectin
(h)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants store energy of sunlight as chemical energy. Process happens in the chloroplast of a plant cell. Photosynthesis happens in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction. The dark reaction consists either of the two
Answer to Problem 23P
- d) C3 plants − 3 − Phosphoglycerate is formed after carbon fixation
Explanation of Solution
The dark reaction of photosynthesis consists of two metabolic pathways, that is, C3 and C4 cycle. All the green plant uses one of these two pathways. The nomenclature is based on the number of carbon atoms present in the first metabolite produced after CO2 fixation.
The first metabolite produced in C3 cycle composed of three carbons while a four carbon metabolite is produced in C4 cycle.
The light reaction is common to both C3 and C4 cycle. But the type of enzymes and intermediate produced during the dark reaction are different.
RUBP (Ribulose Bisphosphate) carboxylase is the enzyme of C3 cycle which fixes CO2, present in the atmosphere. After Co2 fixation, a five-carbon molecule, RUBP (Ribulose bisphosphate) reacts with CO2 to form a six-carbon complex. The six-carbon molecule break immediately and form two 3- phosphoglycerate. 3- phosphoglycerate consists of three carbon atoms.
So, this is the first stable product of CO2 fixation. This is the reason why the mechanism is known as C3 cycle.
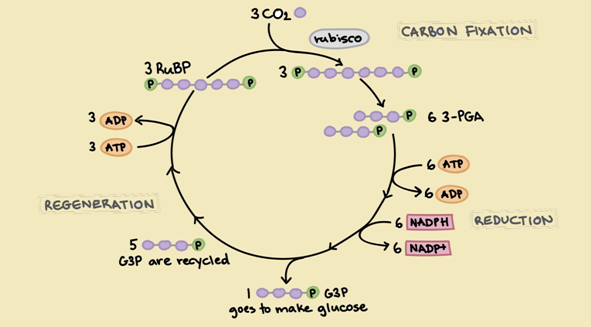
Figure 6: Calvin cycle of C3photosynthesis representing the carbon fixation.
(i)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants store energy of sunlight as chemical energy. Process happens in the chloroplast of a plant cell. Photosynthesis happens in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction. The dark reaction consists either of the two metabolic pathways, that is, C3 and C4 cycle.
Answer to Problem 23P
- e) C4 plants − carbon fixation results in oxaloacetate formation
Explanation of Solution
The dark reaction of photosynthesis consists of two metabolic pathways, that is, C3 and C4 cycle. All the green plant uses one of these two pathways. The nomenclature is based on the number of carbon atoms present in the first metabolite produced after CO2 fixation.
As explained earlier, the first metabolite produced in C3 cycle composed of three carbons while a four-carbon metabolite is produced in C4 cycle.
Out of the two steps of photosynthesis (light and dark reaction), light reaction is common. But the type of enzymes and intermediate produced during the dark reaction are different.
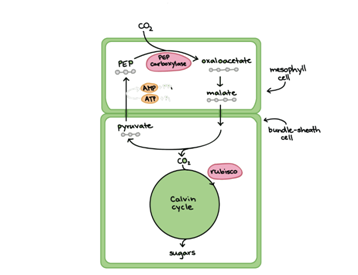
PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate) carboxylase is the primary enzyme of C4 mechanism which catalyzes the fixation of CO2 in chloroplast. For this, a three-carbon molecule (PEP) reacts with CO2 to form a four-carbon molecule which is known as oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is the first stable product of C4 cycle.
This is the reason why the mechanism is called C4 mechanism. The reactions take place in mesophyll cells.
(j)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Stomata are pores, found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs that facilitate gaseous exchange.
Answer to Problem 23P
- f) Stomata − allow exchange of gases
Explanation of Solution
Stomata are the pores which are mostly found in the epidermis of leaves and stems. It facilitates gaseous exchange. This stomatal pore is bordered by the guard cells which regulates the stomatal opening and closing.
Atmospheric air consists of carbon dioxide and oxygen enters the plant through these openings. These gases are crucial for photosynthesis and respiration, respectively. Also, water vapor releases to the atmosphere through the stomata. The process is known as transpiration.
So, stomata are the structures, present in the plant leaves crucial for all types of gaseous exchanges.
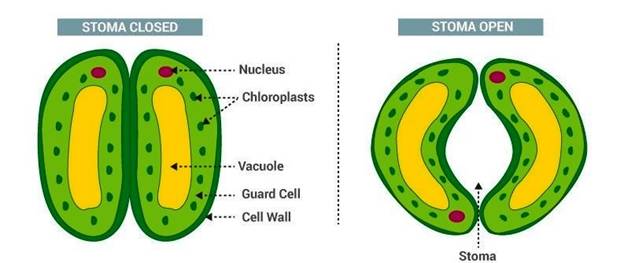
Figure 8: Microscopy view of stomata
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
SAPLINGPLUS F/BIOCHEM+ICLICKER REEF-CODE
- Please help determine the standard curve for my Kinase Activity in Excel Spreadsheet. Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B958f5aee-aabd-45d7-9f7e-380002892ee0%7D&action=default&slrid=9b178ea1-b025-8000-6e3f-1cbfb0aaef90&originalPath=aHR0cHM6Ly9tbnNjdS1teS5zaGFyZXBvaW50LmNvbS86eDovZy9wZXJzb25hbC92aTIxNjNzc19nb19taW5uc3RhdGVfZWR1L0VlNWFqNVc5cXRkRm4zNDRBQUtKTHVBQldtcEtWSUdNVmtJMkoxQzl3dmtPVlE_cnRpbWU9eEE2X291ZHIzVWc&CID=e2126631-9922-4cc5-b5d3-54c7007a756f&_SRM=0:G:93 Determine the amount of VRK1 is present 1. Average the data and calculate the mean absorbance for each concentration/dilution (Please over look for Corrections) 2. Blank Correction à Subtract 0 ug/mL blank absorbance from all readings (Please over look for Corrections) 3. Plot the Standard Curve (Please over look for Corrections) 4. Convert VRK1 concentration from ug/mL to g/L 5. Use the molar mass of VRK1 to convert to M and uM…arrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Cholesterol synthesis begins with the formation of mevalonate from acetyl CoA. This process activates mevalonate and converts it to isopentenyl pyrophosphate. Identify the atoms in mevalonate and isopentenyl pyrophosphate that will be labeled from acetyl CoA labeled with 14C in the carbonyl carbon. Place 14C atoms and C atoms to denote which carbon atoms are labeled and which are not labeled. H₂C COA 14C-labeled acetyl-CoA HHH [c] H H OH 014C - OH H HH H Mevalonate CH3 H H 14C H Η H H Incorrect Answer of o -P-O-P-0- Isopentenyl pyrophosphate с Answer Bank 14Carrow_forwardDraw the reaction between sphingosine and arachidonic acid. Draw out the full structures.arrow_forward
- Draw both cis and trans oleic acid. Explain why cis-oleic acid has a melting point of 13.4°C and trans-oleic acid has a melting point of 44.5°C.arrow_forwardDraw the full structure of the mixed triacylglycerol formed by the reaction of glycerol and the fatty acids arachidic, lauric and trans-palmitoleic. Draw the line structure.arrow_forwardDraw out the structure for lycopene and label each isoprene unit. "Where is lycopene found in nature and what health benefits does it provide?arrow_forward
- What does it mean to be an essential fatty acid? What are the essential fatty acids?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast primary and secondary active transport mechanisms in terms of energy utilisation and efficiency. Provide examples of each and discuss their physiological significance in maintaining ionic balance and nutrient uptake. Rubric Understanding the key concepts (clearly and accurately explains primary and secondary active transport mechanisms, showing a deep understanding of their roles) Energy utilisation analysis ( thoroughly compares energy utilisation in primary and secondary transport with specific and relevant examples Efficiency discussion Use of examples (provides relevant and accurate examples (e.g sodium potassium pump, SGLT1) with clear links to physiological significance. Clarity and structure (presents ideas logically and cohesively with clear organisation and smooth transition between sections)arrow_forward9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate? 요요. 1. NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH 1. NaOH, H₂O 2. H3O+ 3. A OCH2CH3 2. ethyl acetoacetate ii A 3. H3O+ OH B C D Earrow_forward
- 7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. Which one is it? Ph کہ A B C D Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forwardwhat is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





