
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between actic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The product of the given reaction is
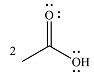
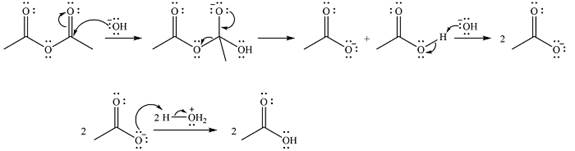
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is NaOH followed by
Thus, the product of the reaction will be

The reaction will start with the nucleophilic addition of hydroxide ion from NaOH, producing a tetrahedral intermediate.
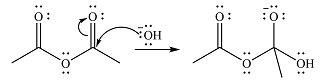
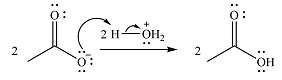
In the second step, one lone pair from negatively charged oxygen will move back to the carbon to reform the carbonyl group and eliminate an acetate ion. This step will produce one acetate ion and one acetic acid molecule, but under the strongly basic conditions, the acid will be irreversibly deprotonated to produce two carboxylate anions.
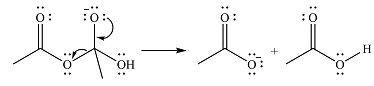
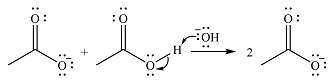
The addition of the acid (
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as
The product of the reaction and its mechanism were determined based on the relative stability of the produc, and the nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The products of the given reaction are
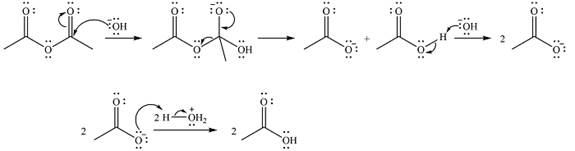
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
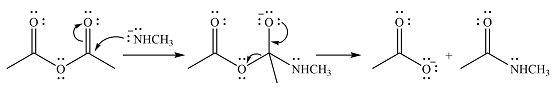
Explanation of Solution
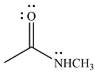
The given reactant is
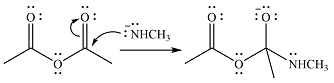
One lone pair on negatively charged oxygen will move back toward the carbon to reform the carbnyl group and eliminate an acetate ion to form the final product.
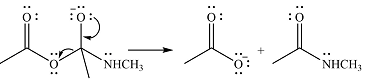
Thus, the product of the reaction will be

And the complete mechanism can be drawn as

The product of the reaction and its mechanism were dsetermined based on the relative stability of the product and the nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The product of the given reaction is
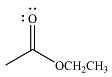
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
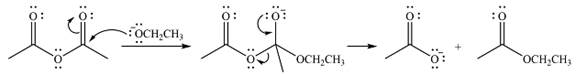
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is
Therefore, the product of the reaction will be

In the first step, the incoming nucleophile will add to the carbonyl carbon, producing a tetrahedral intermediate.
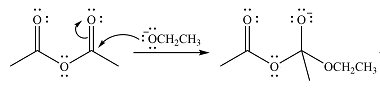
The lone pair on negativey charged ocygen will move back toward the carbon to reform the carbonyl group and eliminate acetate anion to form the final product, an ester.
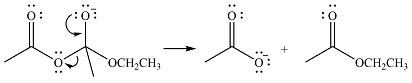
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

The product of the reaction and its mechanism were dsetermined based on the relative stability of the product and the nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between aceetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The product of the given reaction is
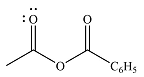
The complete mechanism of the reaction is
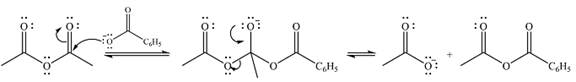
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is
Therefore, the product of the reaction will be

In the first step, the nucleophile will add to the carbonyl carbon to produce a tetrahedral intermediate.
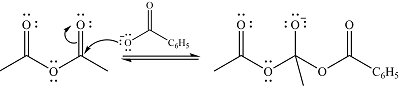
In the second step, one lone pair of negatively charged oxygen will move back to the carbon to reform the carbonyl group and eliminate acetate anion to form the final product.
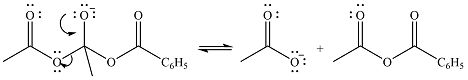
Thus, the complete mechanism can be drawn as

The product of the reaction and its mechanism were dsetermined based on the relative stability of the product and the nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
There will be no reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is NaBr, a source of the nucelophile
Therefore, the reaction will not occur.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination cannot occur since the possible product is of lower stability than the reactant.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The reaction will not occur.
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is
Therefore, there will be no reaction.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination is not possible in this case as the nucleophile is weak and does not add to a carbonyl carbon.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The reaction will not occur.
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is
Therefore, there will be no reaction.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination is not possible in this case as the given reactant is an electrophile.
(h)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction between acetic anhydride and the given reactant is to be predicted. A complete, detailed mechanism is to be drawn if the reaction occurs.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo acyl group substitution reactions when treated with appropriate nucleophiles. The reaction occurs via nucleophilic addition-elimination involving a tetrahedral intermediate. It may also involve proton transfer step(s). The reaction occurs if the possible product is more stable than the reactant. If the two are of comparable stability, the reaction will occur reversibly. The order of increasing stability of acid derivatives is
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The reaction will not occur.
Explanation of Solution
The given reactant is hexanal with an electrophilic carbon.
Therefore, there will be no reaction.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination is not possible in this case as the reactant is an electrophile.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- Identify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: X + Y H+ two steps Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х :arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism of friedel-crafts acylation using acetyl chloride of m-Xylenearrow_forwardI need help naming these in IUPACarrow_forward
- H R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardDraw the friedel-crafts acylation mechanism of m-Xylenearrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 1. Base on this experimental results, how do you know that the product which you are turning in is methyl 3-nitrobenzoate(meta substituted product ) rather than either of the other two products? 2. What observation suggests that at least a small amount of one or both of the other two isomers are in the mother liquor?arrow_forwardExplain Huckel's rule.arrow_forwardhere is my question can u help me please!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





