DRAW IT Show where the following antibiotics work: ciprofloxacin, tetracvcline, streptomycin, vancomycin, polymyxin B, sulfanilamide, rifampin, erythromycin.
To review:
Themode of action of given antibiotics in a bacterial cell.
Concept introduction:
The antibiotics can either act as a bacteriostatic (prevent growth of bacteria) or bactericidal (kill bacteria) agents. These drugs with a specific mode of action inhibits the essential biological processes of the target pathogen, including disruption of plasma membrane permeability, inhibition of cell wall, protein and nucleic acid synthesis, and inhibition of essential metabolites synthesis.
Answer to Problem 1R
Correct answer:
| ANTIBIOTICS | MODE OF ACTION |
| Ciprofloxacin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid replication |
| Tetracycline | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Streptomycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Vancomycin | Inhibition of the cell wall synthesis |
| Polymyxin B | Injury to the plasma membrane |
| Sulfanilamide | Inhibition of the essential metabolite synthesis |
| Rifampin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid transcription |
| Erythromycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
Explanation of Solution
Diagram:
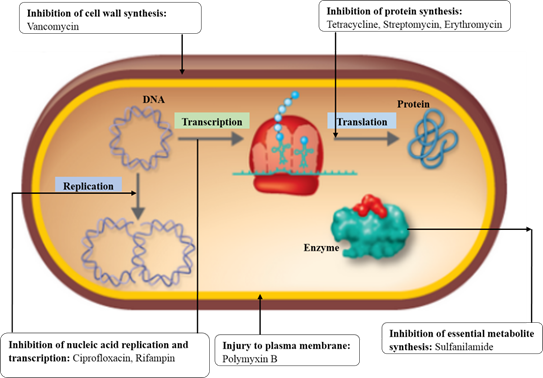
Explanation:
The mechanism of action of the given antibacterial drugs:
Ciprofloxacin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent inhibits the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase and blocks DNA synthesis. The DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme which is specifically involved in the introduction of negative supercoiling.
Tetracycline – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA from binding to bacterial 30S ribosome. By binding to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome, the tetracycline blocks the association of aminoacyl tRNA with the acceptor site.
Streptomycin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent by acting on 70S ribosome inhibits the protein synthesis. It binds to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome and disrupts the protein synthesis (initiation and elongation step).
Vancomycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the assembly of cell wall of bacteria. The N-acetylmuramic acid (NAG) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAM) monomers are the the building blocks of peptidoglycan cell wall. By binding to NAG and NAM, the vancomycin prevents the action of transpeptidase enzyme which is involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan.
Polymyxin B – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent with a cationic detergent action disrupts the permeability of the plasma membrane.
Sulfanilamide – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent acts as a competitive inhibitor of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). The sulfanilamide with a similar chemical structure competitively prevents the action of PABA and inhibits the folic acid biosynthesis. This arrests the bacterial growth and ultimately results in the elimination of the bacteria.
Rifampin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent specifically inhibits the function of RNA polymerase in the bacteria. Rifampin forms a stable complex with the enzyme, thereby inhibits its activity in the nucleic acid transcription.
Erythromycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial 50S ribosome. It inhibits the activity of peptidyl transferase and intervenes with the amino acid translocation and protein assembly.
The specific site of action of the given antibacterial agents, namely cell wall synthesis (vancomycin), protein synthesis (tetracycline, streptomycin, erythromycin), essential metabolite synthesis (sulfanilamide), nucleic acid synthesis (ciprofloxacin), nucleic acid transcription (rifampin), and plasma membrane integrity (polymyxin B) is shown.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- With reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forward
- During a routine medical check up of a healthy man it was found that his haematocrit value was highly unusual – value of 60%. What one of the options below is the most likely reason? He will have a diet high in iron. He is likely to be suffering from anaemia. He lives at high altitude. He has recently recovered from an accident where he lost a lot of blood. He has a very large body size.arrow_forwardExplain what age of culture is most likely to produce an endospore?arrow_forwardExplain why hot temperatures greater than 45 degrees celsius would not initiate the sporulation process in endospores?arrow_forward
- Endospore stain: Consider tube 2 of the 7-day bacillus culture. After is was heated, it was incubated for 24 hours then refrigerated. Do you think the cloudiness in this tube is due mostly to vegetative cells or to endospores? Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardReactunts C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 2NAD+ + 2ADP 2 Pyruvic acid + 2NADH + 2ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? GHz 06 (glucose) d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? NAD e. Which of the products have been reduced? NADH f. Which of the products have been oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 3arrow_forwardThere is ________ the concept of global warming. Very strong evidence to support Some strong evidence to support Evidence both supporting and against Evidence againstarrow_forward
- How many types of reactions can an enzyme perform?arrow_forwardYour goal is to produce black seeds resistant to mold. So you make the same cross again (between a homozygous black seeded, mold susceptible parent and a homozygous white seeded and mold resistant parent), and, again, advance progeny by SSD to create 100 F10 generation plants. Based on the information you obtained from your first crossing experiment (Question #4), how many F10 plants would you expect to have black seeds and be resistant to mold? Assume that a toxin produced by the mold fungus has been isolated. Only mold resistant seeds will germinate in the presence of the toxin. Could you use this toxin screening procedure to have segregation distortion work in your favor in the F2 generation? Explain your answer. Info from Question 4 a. P Locus (Seed Color): Hypothesis: The null hypothesis (H₀) is that seed color is controlled by alleles at a single locus. Observed Data: Total white seeds: 45 (resistant plants) + 6 (susceptible plants) = 51 Total black seeds: 7 (resistant…arrow_forward10. Consider the following enzyme and its substrate where the "+" and "-" indicate cations and anions, respectively. Explain which of the following inhibitors could inhibit this enzyme? Which type of inhibitor would it be and why? (Video 5-2) Substrate Enzyme Potential inhibitorsarrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage





