
(a)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension A to dimension B is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
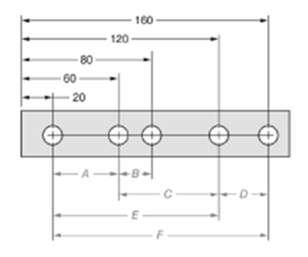
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension A is given by,
The measure of dimension B is given by,
The ratio of dimension A to dimension B is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension A to Dimension B is
(b)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension A to dimension C is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
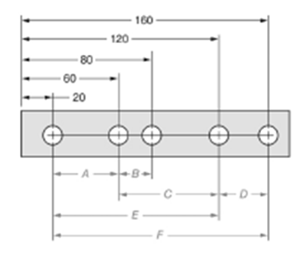
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension A is given by,
The measure of dimension C is given by,
The ratio of dimension A to dimension C is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension A to Dimension C is
(c)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension C to dimension D is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
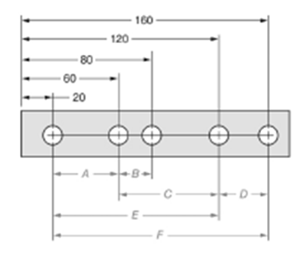
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension C is given by,
The measure of dimension D is given by,
The ratio of dimension C to dimension D is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension C to Dimension D is
(d)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension C to dimension E is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
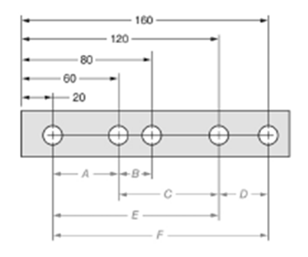
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension C is given by,
The measure of dimension E is given by,
The ratio of dimension C to dimension E is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension C to Dimension E is
(e)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension D to dimension F is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
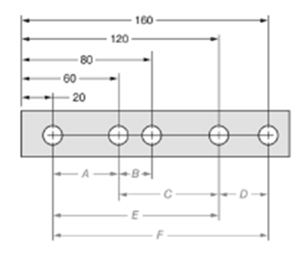
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension D is given by,
The measure of dimension F is given by,
The ratio of dimension D to dimension F is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension D to Dimension F is
(f)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension F to dimension B is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
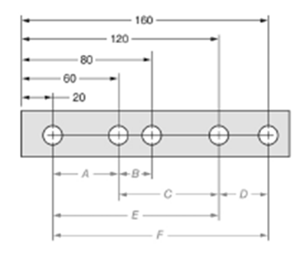
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension F is given by,
The measure of dimension B is given by,
The ratio of dimension F to dimension B is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension F to Dimension B is
(g)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension F to dimension C is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
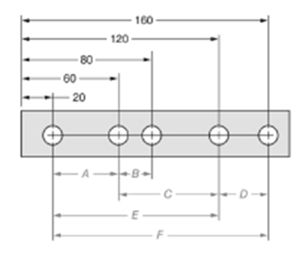
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension F is given by,
The measure of dimension C is given by,
The ratio of dimension F to dimension C is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension F to Dimension C is
(h)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension E to dimension A is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
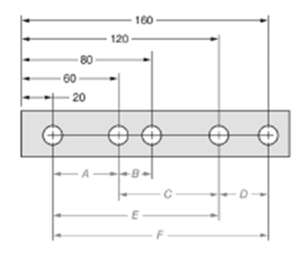
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of nearer hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension E is given by,
The measure of dimension A is given by,
The ratio of dimension E to dimension A is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension E to Dimension A is
(i)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension D to dimension B is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
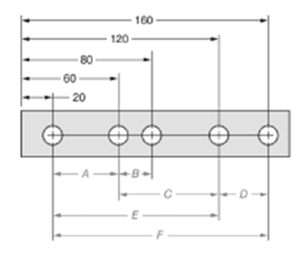
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance the near hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension D is given by,
The measure of dimension B is given by,
The ratio of dimension D to dimension B is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension D to Dimension B is
(j)
The indicated ratios in lowest fractional form.
Answer to Problem 19A
The ratio of dimension C to dimension F is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is as follows:
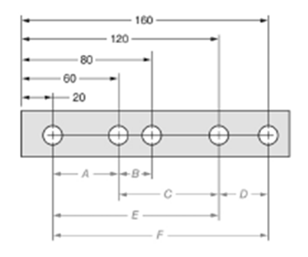
Concept used:
The dimension can be calculated by subtracting the distance of nearer hole from the one which is farther.
Calculation:
From the given figure, it is clear that the measure of dimension C is given by,
The measure of dimension F is given by,
The ratio of dimension C to dimension F is given by,
Thus, the ratio is
Conclusion:
The ratio of Dimension C to Dimension F is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
- To manage the production of an animated movie, Pixar Animation Studios has listed the major activities involved, the predecessor relationships, and activity times (in months). The project is completed when activities F and G are both complete. Activity Immediate Predecessor G A B CD E A A C, B C, B D, E Time 4 6 2 6 3 3 5 (a) Find the critical path. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list.) (b) The project must be completed in 1.5 years. Do you anticipate difficulty in meeting the deadline? Explain. The critical path activities require months to complete. Thus the project ---Select--- be completed in 1.5 years.arrow_forwardTo help with preparations, a couple has devised a project network to describe the activities that must be completed by their wedding date. In addition, they have estimated the time of each activity (in weeks). Start D F B E G Activity A B C DEFGH Time 5 3 6 6 6 3 11 10 (a) Identify the critical path. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list.) H Finish (b) How much time (in weeks) will be needed to complete this project? week(s) (c) Can activity D be delayed without delaying the entire project? If so, by how many weeks? (If the activity can not be delayed, enter 0.) week(s) (d) Can activity C be delayed without delaying the entire project? If so, by how many weeks? (If the activity can not be delayed, enter 0.) week(s) (e) What is the schedule for activity E (in weeks)? Earliest Start Latest Start Earliest Finish Latest Finish week(s) week(s) week(s) week(s)arrow_forward30.6. Classify the zeros and singularities of the functions tanz (a). f(z)=sin(1-2-1), (b). f(2) = (c). f(z)= tanh .arrow_forward
- 1. Locate the singularities of three of the following functions, and determine their type. (a) f(z)=2(z-sinz). (b) f(z) = (-) (c) f(z) = (z+2-22²)-1 (d) f(z) = sinzarrow_forwardQ 2/classify the zeros and poles of the function f(z) = tanz Zarrow_forward30.1. Show that z = 0 is a removable singularity of the following functions. Furthermore, define f(0) such that these functions are analytic at z = 0. (a). f(z) = 2 sin z- z 1-12² - cos z (b). f(z) = (c). f(z) = sin 22arrow_forward
- 3. Consider the polynomial equation 6-iz+7z² -iz³ +z = 0 for which the roots are 3i, -2i, -i, and i. (a) Verify the relations between this roots and the coefficients of the polynomial. (b) Find the annulus region in which the roots lie.arrow_forward30.3. Find and classify the isolated singularities of the following func- tions: (a). 23+1 22(2-1) (b). ²e¹/, (c). sin 3z (d). COS 2arrow_forward3. Consider the polynomial equation 6-iz+7z2-iz³ +z = 0 for which the roots are 3i, -2i, -i, and i. (a) Verify the relations between this roots and the coefficients of the polynomial. (b) Find the annulus region in which the roots lie.arrow_forward
- Determine the set of odd primes p for which 23 is a quadratic residue.arrow_forwardQ/ Find and classify the singularities of the functions- = 52+3 (1-2) sin² Z a fcz) b f(z) = tanz Z © f(2)= [z (e²-1)]arrow_forwardA linear programming computer package is needed. As part of the settlement for a class action lawsuit, Hoxworth Corporation must provide sufficient cash to make the following annual payments (in thousands of dollars). Year 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 Payment 210 235 260 305 335 480 The annual payments must be made at the beginning of each year. The judge will approve an amount that, along with earnings on its investment, will cover the annual payments. Investment of the funds will be limited to savings (at 4% annually) and government securities, at prices and rates currently quoted in The Wall Street Journal. Hoxworth wants to develop a plan for making the annual payments by investing in the following securities (par value = $1,000). Funds not invested in these securities will be placed in savings. Security Current Price Rate (%) Years to Maturity 1 2 $1,055 $1,000 6.750 5.125 3 4 Assume that interest is paid annually. The plan will be submitted to the judge and, if approved, Hoxworth will be…arrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,



