
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cholesterol reacts with hydrogen in presence of palladium-carbon has to be drawn.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol with hydrogen:
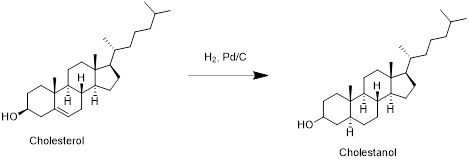
Cholesterol reacts with hydrogen in presence of palladium-carbon to reduce double bond to single bond and forms cholestanol. Therefore, the product obtained is cholestanol which is shown in the above scheme.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cholesterol reacts with acetyl chloride has to be drawn
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol with acetyl chloride:
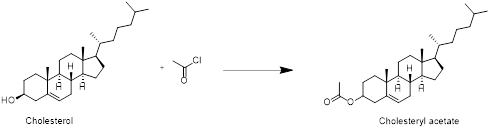
Cholesterol reacts with acetyl chloride in which acetylation reaction take place at hydroxyl group and forms cholesteryl acetate. Therefore, the product obtained is cholesteryl acetate which is shown in the above scheme.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cholesterol reacts with sulfuric acid followed by heating has to be drawn.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol with sulfuric acid:
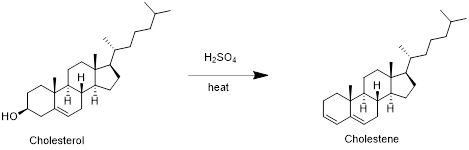
Cholesterol reacts with sulfuric acid in which removal of water molecule take place and forms cholestene. Therefore, the product obtained is cholestene which is shown in the above scheme.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cholesterol reacts with water in presence of acid has to be drawn.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol with water:
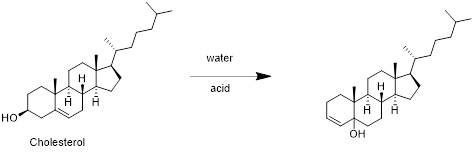
Cholesterol reacts with water in presence of water in which removal of water molecule take place and forms desired product. Therefore, the product obtained is is shown in the above scheme.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cholesterol reacts with peroxy acid has to be drawn
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Cholesterol with peroxy acid:
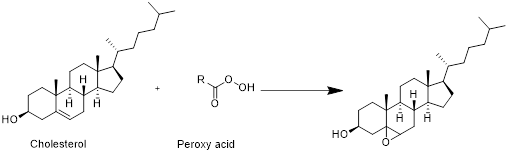
Cholesterol reacts with peroxy acid in presence of water in which reaction take place at double bond and forms
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- 136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- Identifying the stereochemistry of natural Write the complete common (not IUPAC) name of each molecule below. Note: if a molecule is one of a pair of enantiomers, be sure you start its name with D- or L- so we know which enantiomer it is. molecule H O-C-CH2 H3N. HN N H C=O common name (not the IUPAC name) NH3 ☐ H3N H ☐ CH2 Xarrow_forward> Draw the structure of alanine at pH 1.2. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardUnderstanding the general acid-base properties of amino acids O Proteins Imagine each of the molecules shown below was found in an aqueous solution. Can you tell whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral? molecule The solution is... 010 H3N-CH-C-OH CH HO CH3 O acidic O basic neutral O (unknown) H3N HO 0 O acidic O basic neutral ○ (unknown) H3N-CH-C-O CH2 CH3-CH-CH3 O acidic O basic Oneutral ○ (unknown) O= X H2N-CH-C-O CH3 CH CH3 acidic O basic O neutral ○ (unknown) ? 000arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

