
FISH & CHIPS INC, PART I
LEASE ANALYSIS Martha Millon,
If the computer is purchased, a maintenance contract must be obtained at a cost of $25,000, payable at the beginning of each year. After 4 years, the computer will be sold. Millon′s best estimate of its residual value at that time is $125,000. Because technology is changing rapidly however, the residual value is uncertain.
As an alternative. National Leasing is willing to write a 4-year lease on the computer, including maintenance, for payments of $340,000 at the beginning of each year. Fish 4c Chips′s marginal federal-plus-state tax rate is 40%. Help Millon conduct her analysis by answering the following questions.
a. 1. Why is leasing sometimes referred to as "off-balance-sheet" financing?
2. What is the difference between a capital lease and an operating lease?
3. What effect does leasing have on a firm′s capital structure?
b. 1. What is Fish & Chips's
2. Explain the rationale for the discount rate you used to find the PV.
c. 1. What is Fish & Chips′s present value cost of leasing the computer? (Hint: Again, construct a time line.)
2. What is the net advantage to leasing? Does your analysis indicate that the firm should buy or lease the computer? Explain.
d. Now assume that Millon believes that the computer′s residual value could be as low as $0 or as high as $250,000, but she stands by $125,000 as her expected value. She concludes that the residual value is riskier than the other cash flows in the analysis, and she wants to incorporate this differential risk into her analysis. Describe how this can be accomplished. What effect will it have on the lease decision?
e. Millon knows that her firm has been considering moving its headquarters to a new location, and she is concerned that these plans may come to fruition prior to the expiration of the lease. If the move occurs, the company would obtain new computers; hence, Millon would like to include a cancellation clause in the lease contract. What effect would a cancellation clause have on the risk of the lease?
a.1.
To discuss: The reason why leasing is referred as an off-balance-sheet financing.
Introduction:
Off-balance sheet financing is a type of financing where the firm does not include a liability on its balance sheet. This is an accounting term and has impact on firm’s debt level and liabilities.
Explanation of Solution
The reason why leasing is referred as an off-balance-sheet financing is as follows:
At the time when an asset is purchased, this asset will be exhibited on the left-hand side balance sheet’s left hand side and has to offset equity or debt on the balance sheet’s right-hand side. However, when an asset is leased and the lease is not segregated into a capital lease, then it will not be exhibited straightly on the balance sheet. This will only be reported in the footnotes of the financial statement of the company. Therefore, this is the main reason for a leasing, which is being termed as off-balance sheet financing.
a.2
To discuss: The difference between the operating and capital lease.
Introduction:
Capital lease is termed as contract wherein lesser agrees to transfer ownership right to leasee once the completion of lease time. It is a long term lease contracts. There are also termed as finance lease.
Operating lease is a lease on assets, which is not fully amortized in the non-cancelable period. It is considered as a short term lease.
Explanation of Solution
Capital leases are distinguished from operating leases in three factors which are as follows:
- Capital lease does not gives maintenance services.
- Capital lease are not cancelable
- It is fully amortized
a.3.
To discuss: The effect that leasing has on the capital structure of the firm.
Explanation of Solution
The effect that leasing has on the capital structure of the firm is as follows:
Leasing is one substitute for debt financing. The lease payments are considered as a contractual obligation between the corresponding parties. The firm would face bankruptcy when the lease payment is not paid time. As a result the leasing uses up a firm’s debt capacity.
For instance, the F Company’s optimal capital structure comprise of 50 percent of equity and 50 percent debt. At the time when the company leases half of its assets, then the reaming half of asset will be financed by the common equity.
b.1.
To determine: The present value cost of owing the computer.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
F Company has decided to purchase a new computer system on lease. The cost of computer is $1,200,000 and company can provide a term loan for the total amount of 10%. This loan is amortized over the 4-years life of the computer. The MACRS rates are 30 percent, 45 percent, 15 percent, and 7 percent. The maintenance cost of the computer will be $25,000 which is payable in the beginning of every year.
The computer will be sold after 4-years period and its residual value is $125,000. The national leasing is willing to offer 4-years lease on the computer including maintenance for payment of $340,000 and tax rate is 40 percent.
Construct a depreciation schedule in order to determine the cost of owing:
The below table show the Excel formula to compute the depreciation expenses and end-of-year book value:
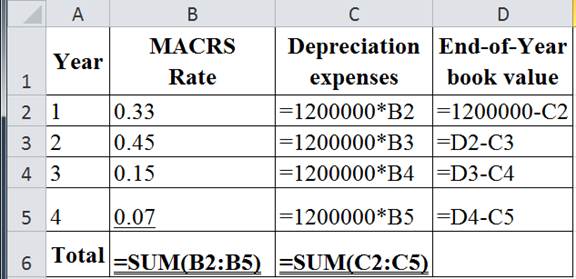
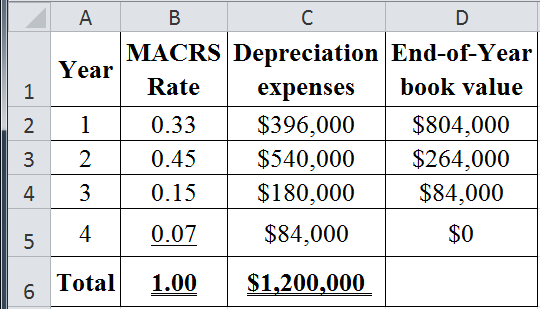
The table below shows the calculated value of depreciation expenses and end-of-year book value:
The table below shows the Excel formula to compute the cash flow:
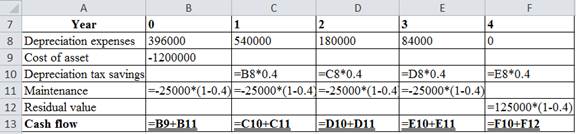
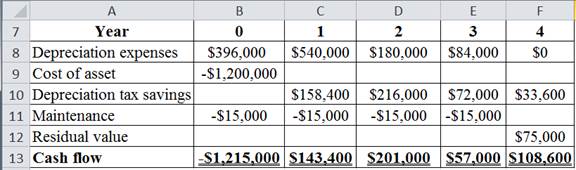
The table below shows the calculated value of cash flows:
Compute the after-tax interest rate:
Hence, the after-tax interest rate is 0.06.
Compute the present value of the cost of owing:
The table below shows the Excel Formula to compute the present value of the cost of owing:
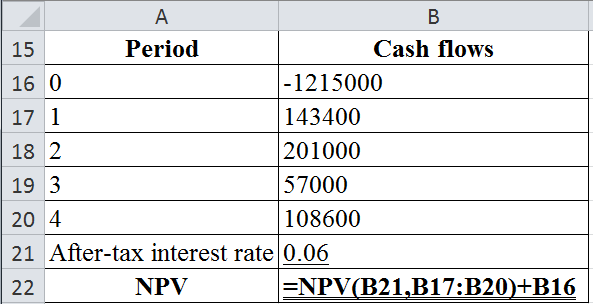
The table below shows the calculated value of present value of the cost of owing:
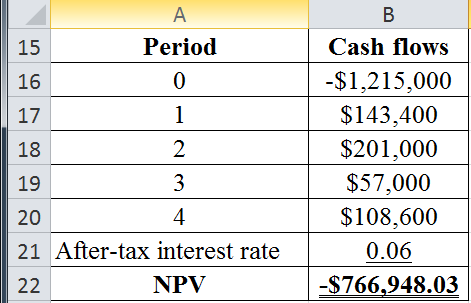
The present value of the cost of owing is −$766,948.03.
b.2.
To discuss: The rationale for the discount rate that is utilised to determine the present value.
Explanation of Solution
The rationale for the discount rate that is used to determine the present value is as follows:
The discount rate used to find the present value depends on the riskless of the cash flows stream and even the level of interest rate. The cost of owing cash flows without including the residual value is fixed by means of the contract. As a result, it is not very risky. However, they have almost the similar risk as the company’s debt flows that are also contractual in nature.
The leasing process use debt capacity, so the similar impact on the financial risk such as debt financing. Therefore, the appropriate interest rate is the cost of debt of the F Company since the flows are after-tax flows. In this case, the F Company’s before-tax debt cost is 10 percent and tax rate is 40 percent. Therefore, the after-tax cost of debt will be 6 percent
c.1.
To determine: The present value cost of leasing the computer.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
F Company has decided to purchase a new computer system on lease. The cost of computer is $1,200,000 and company can give a term loan for the total amount of 10%. This loan is amortized for the 4-years life of the computer. The MACRS rates are 30 percent, 45 percent, 15 percent, and 7 percent. The maintenance cost of the computer will be $25,000 which is payable in the beginning of every year.
The computer will be sold after 4-years period and its residual value is $125,000. The national leasing is wishing to offer 4-years lease on the computer including maintenance for payment of $340,000 and tax rate is 40 percent.
Compute the present value of leasing:
The table below shows the Excel formula to compute the present value of leasing:
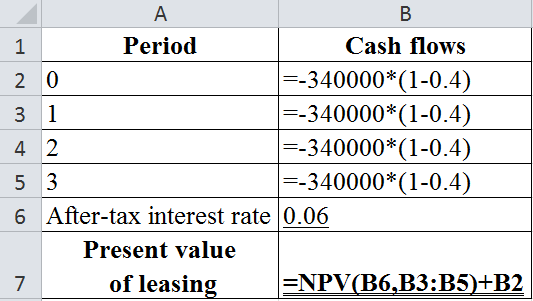
The table below shows the calculated value of present value of leasing:
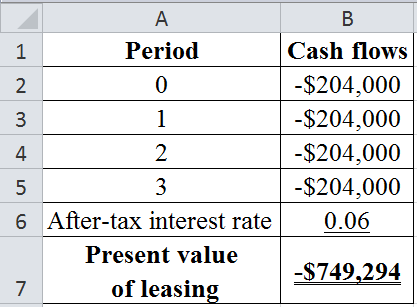
Hence, the present value of leasing is −$749,294.
c.2.
To determine: The net advantage to leasing and whether the analysis indicates that the firm must purchase or lease the computer.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
F Company has decided to purchase a new computer system on lease. The cost of computer is $1,200,000 and company can give a term loan for the total amount of 10 %. This loan is amortized for the 4-years life of the computer. The MACRS rates are 30 percent, 45 percent, 15 percent, and 7 percent. The maintenance cost of the computer will be $25,000 which is payable in the starting of every year.
The computer will be sold after 4-years period and its residual value is $125,000. The national leasing is ready to offer 4-years lease on the computer including maintenance for payment of $340,000 and tax rate is 40 percent.
The formula to calculate the net advantage to leasing is as follows:
Calculate the net advantage to leasing:
Hence the net advantage to leasing is $17,654.03. Here, the net advantage to leasing has a positive value. The cost of owing outweighs the cost of leasing. Therefore, the F Company can lease the computer system than buying it.
d.
To discuss: The way for accomplishing the task and effect that will have on the leasing decision.
Explanation of Solution
The way for accomplishing the task and effect that will have on the leasing decision is as follow:
The rate utilized to discount the residual value cash flow must be raised in order to account for an increased risk. This can result to a lower present value. As a result, the lower present value can leads to a greater cost of owing because the residual value is an inflow. Therefore, the higher risk of the residual value can result in the greater cost of owing and even the leasing becomes much attractive in this stage.
The asset owner bears the residual value risk, so the leasing passes the risk to the lessor. Here, the lessor identifies this risk factor, so the assets with highly uncertain residual value can carry maximum lease payments as compared to the assets with relatively certain residual values.
e.
To discuss: The effect of a cancellation clause has on the risk of the lease.
Explanation of Solution
The effect of a cancellation clause has on the risk of the lease is as follows:
The cancelation clause will lower the risk of the lease for the F Company (lessee). It is because the company is not being obligated to make the payments on lease in all terms. Here, the company can terminate the lease when it does not need a computer or wants to change into a more technological advanced system. On the other hand, a cancellation clause can make the contract more risky for the lessor. As a result, the lessor will not only bear the residual value risk but also the uncertainty of when the contract would be cancelled.
The lessor must increase the annual lease payment to account for extra risks. Moreover, the lessor must include clauses that will prohibit cancellation for some period or impose a penalty charges for cancellation, which might reduce on the cancellation of the lease over time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
FUND.OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT(LL)FDS
- 1. Answer the following and cite references. • what is the whole overview of Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? • what is the green energy equities, green bonds, and green financing and how is this related in Green Markets (Regional or Sectoral Stock Markets)? Give a detailed explanation of each of them.arrow_forwardCould you help explain “How an exploratory case study could be goodness of work that is pleasing to the Lord?”arrow_forwardWhat are the case study types and could you help explain and make an applicable example.What are the 4 primary case study designs/structures (formats)?arrow_forward
- The Fortune Company is considering a new investment. Financial projections for the investment are tabulated below. The corporate tax rate is 24 percent. Assume all sales revenue is received in cash, all operating costs and income taxes are paid in cash, and all cash flows occur at the end of the year. All net working capital is recovered at the end of the project. Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Investment $ 28,000 Sales revenue $ 14,500 $ 15,000 $ 15,500 $ 12,500 Operating costs 3,100 3,200 3,300 2,500 Depreciation 7,000 7,000 7,000 7,000 Net working capital spending 340 390 440 340 ?arrow_forwardWhat are the six types of alternative case study compositional structures (formats)used for research purposes, such as: 1. Linear-Analytical, 2. Comparative, 3. Chronological, 4. Theory Building, 5. Suspense and 6. Unsequenced. Please explainarrow_forwardFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________. QuestFor an operating lease, substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership remain with the _________: A) Tenant b) Lessee lessor none of the above tenant lessee lessor none of the aboveLeasing allows the _________ to acquire the use of a needed asset without having to make the large up-front payment that purchase agreements require Question 4 options: lessor lessee landlord none of the abovearrow_forward
- How has AirBnb negatively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb negatively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb negatively affected homeowners and renters market? What happened to Airbnb in the Tax Dispute in Italy?arrow_forwardHow has AirBnb positively affected the US and global economy? How has Airbnb positively affected the real estate market? How has Airbnb positively affected homeowners and renters market?arrow_forwardD. (1) Consider the following cash inflows of a financial product. Given that the market interest rate is 12%, what price would you pay for these cash flows? Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flow 160 170 180 230arrow_forward
- Explain why financial institutions generally engage in foreign exchange tradingactivities. Provide specific purposes or motivations behind such activities.arrow_forwardA. In 2008, during the global financial crisis, Lehman Brothers, one of the largest investment banks, collapsed and defaulted on its corporate bonds, causing significant losses for bondholders. This event highlighted several risks that investors in corporate bonds might face. What are the key risks an investor would encounter when investing in corporate bonds? Explain these risks with examples or academic references. [15 Marks]arrow_forwardTwo companies, Blue Plc and Yellow Plc, have bonds yielding 4% and 5.3%respectively. Blue Plc has a credit rating of AA, while Yellow Plc holds a BB rating. If youwere a risk-averse investor, which bond would you choose? Explain your reasoning withacademic references.arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781285867977Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





