
Prepare the
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below.
Record the effect of the event in the accounting equation.
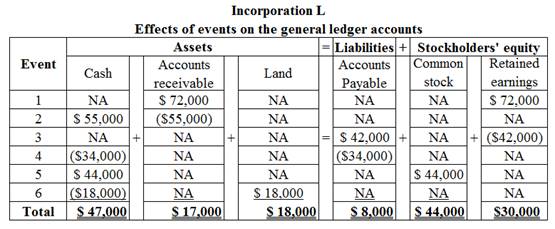
Table (1)
a.
Identify the amount of revenue that is reported on the Year 1 income statement.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is a financial statement that shows the net income earned or net loss suffered by Incorporation through reporting all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a specific period of time. An income statement is also known as an operations statement, an earnings statement, a revenue statement, or a
- The amount of revenue recognized is $72,000 (Amount earned by providing services to the customers) is reported on the Year 1 income statement.
b.
Identify the amount of cash flow from revenue will be reported on the statement of
b.
Explanation of Solution
Cash Flow Statement:
Cash Flow Statement is a fundamental financial statement that renders valuable information regarding the cash inflows or the cash receipts of a business and the cash outflows or cash payments for a specific period of time.
- The amount of cash flows from revenue that is reported on the statement of cash flows is $55,000 (Amount collected from
accounts receivable ).
c.
Calculate the amount of net income for the period.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Net income:
Net income is the excess amount of revenue which arises after deducting all the expenses of a company. In simple terms, it is the difference between total revenue and total expenses of the company.
Prepare the income statement to calculate the amount of net income.
| Incorporation L | ||
| Income statement | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | $72,000 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Operating expenses | $42,000 | |
| Net income | $30,000 | |
Table (2)
The amount of net income for the period is $30,000.
d.
Identify the amount of cash flow from operating activities for the period.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Cash Flow Statement:
Cash Flow Statement is a fundamental financial statement that renders valuable information regarding the cash inflows or the cash receipts of a business and the cash outflows or cash payments for a specific period of time.
Cash flows from operating activities refer to the cash received or cash paid in day-to-day operating activities of a company.
Prepare the statement of cash flow to calculate the cash flow from operating activities.
| Incorporation L | ||
| Cash flow statement | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flow from operating activities | ||
| Cash from revenue | $55,000 | |
| Cash paid for expenses | $34,000 | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $21,000 | |
Table (3)
The net cash flow from operating activities for the period is $21,000.
e.
Explain the reason for difference in the net income from cash flow from operating activities.
e.
Explanation of Solution
There is a difference of $17,000 between the net income and the actual amount collected from revenue, as the income earned is $72,000 but the actual revenue that is collected during the period is $55,000. There is a difference of $8,000 between the net income and the actual amount cash paid for expense, because the expenses incurred during the period is $42,000 but only $34,000 is the payment made for the expenses. So, there is a difference in the net income and it is higher than the cash flow from operating activities.
f.
Identify the amount of net cash flow from investing activities.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Investing activities:
Investing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company for acquisition of long term assets. The examples for investing activities are purchase of equipment, long term investment, sale of land, and others. Investing cash flows causes changes in non-current assets.
- The amount of
cash outflow from investing activities is $18,000 (Purchase of land).
g.
Identify the amount of net cash flow from financing activities.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Financing activities:
Financing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company to mobilize funds to carry out the business activities. The examples for financing activities are purchase of bonds, issuance of common shares, and others. Financing cash flows have an impact on non-current liabilities and
- The amount of
cash inflow from financing activities is $44,000 (Issue of common stock).
h.
Identify the amount of total assets, total liabilities, and total stockholders’ equity will be reported on the year-end balance sheet.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet:
This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors.
Prepare the balance sheet to identify the amount of total assets, total liabilities, and total stockholders’ equity.
| Incorporation L | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $47,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | $17,000 | |
| Land | $18,000 | |
| Total assets | $82,000 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | $8,000 | |
| Total liabilities | $8,000 | |
| Stockholders' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | $30,000 | |
| Common stock | $44,000 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $74,000 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $82,000 | |
Table (4)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





