
Concept explainers
Find the dead loads acting on the girder AE and beam CD.
Answer to Problem 6P
The dead load acting on the beam CD is
Dead load in Girder AE:
The dead load at C, A, and E are
The uniformly distributed load in the girder AE is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of the reinforced concrete slab is
The area of cross-section of the steel floor beam is
The area of cross-section of the steel girder is
The length, height, and thickness of the brick wall are
Calculation:
Show the floor systemof the building as shown in Figure 1.
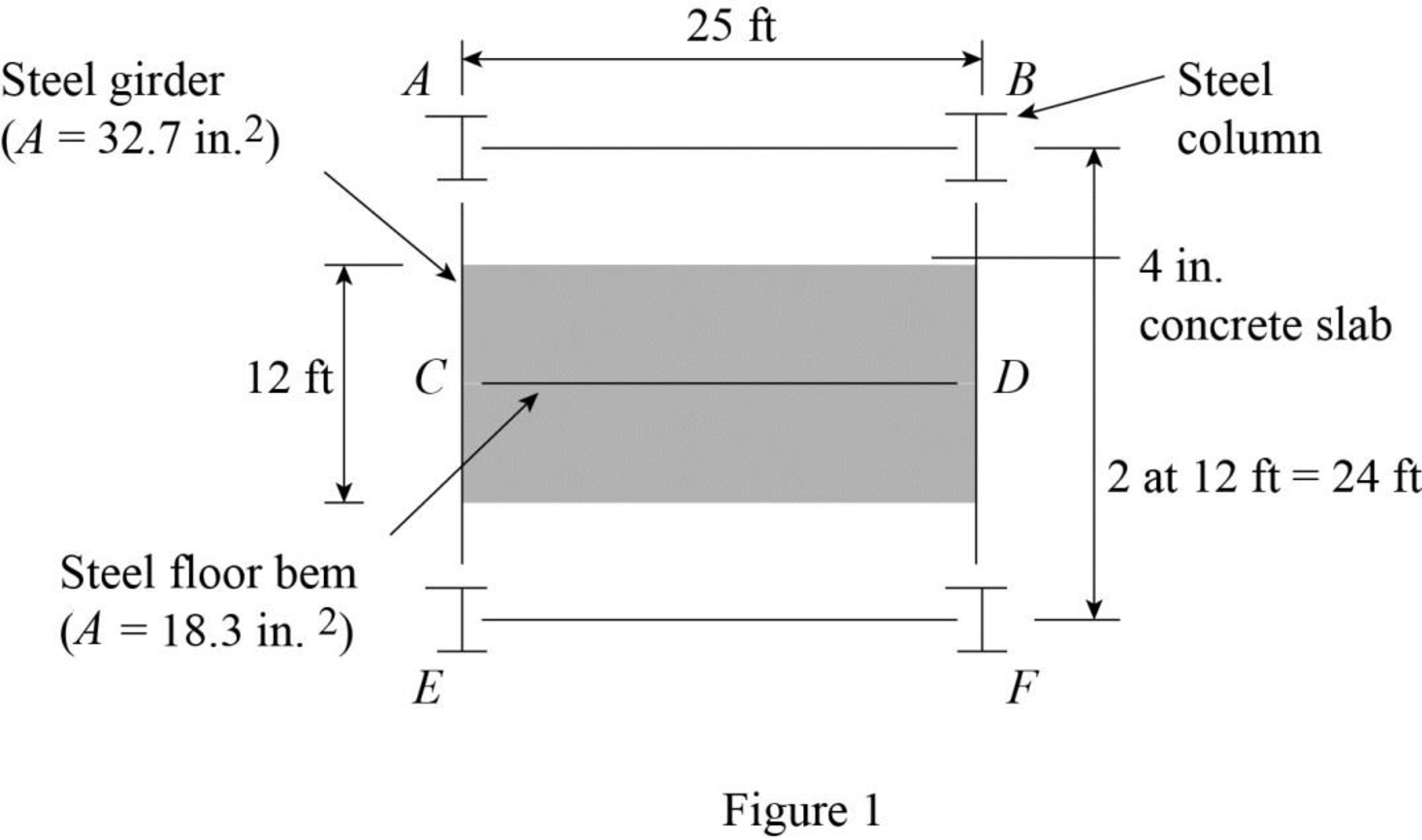
Refer Figure 1.
The tributary area of the beam CD is represented by the shaded region.
Tributary area of the beam CD:
The width of the tributary area of the beam CD is
The width of the tributary area of the beam CD is same as the length of the beam CD. Then,
The length of the tributary area of the beam CD is
The thickness of the concrete slab is
Refer Table 2.1 “Unit Weights of Construction Materials” in the text book.
The unit weight of the reinforced concrete is
The unit weight of the structural steel is
The unit weight of the brick wall is
Calculate the dead load per unit length of the beam CD as follows:
Concrete Slab:
Calculate the dead load of the concrete slab using the relation:
Substitute
Steel beam:
Calculate the dead load of the steel beam using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the dead load of the brick wall using the relation:
Calculate the dead load of the beam CD as follows:
The dead load of
Show the dead load acting on the beam as shown in Figure 2.
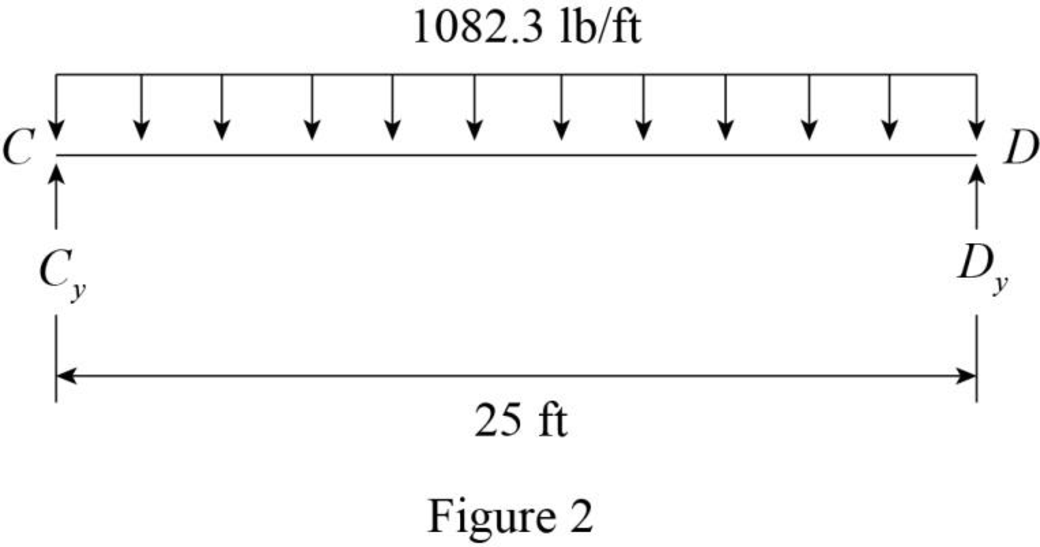
Refer Figure 2.
The reaction at C and D are denoted by
The dead load on the beam is symmetrical. Then,
Show the dead load acting on the beam as shown in Figure 3.
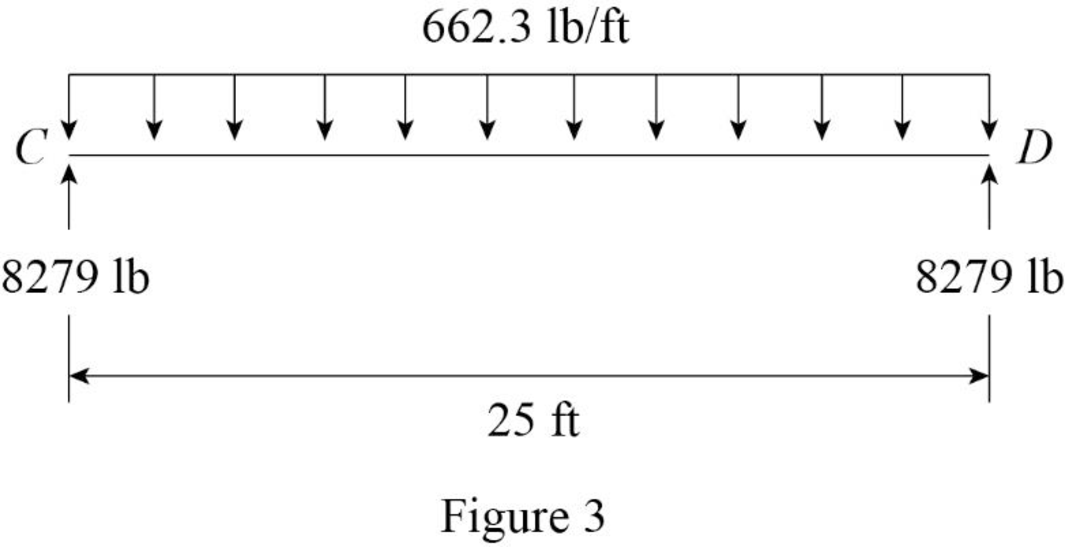
Refer Figure 3.
Thus, the dead load acting on the beam CD is
Show the floor system of the building as shown in Figure 4.
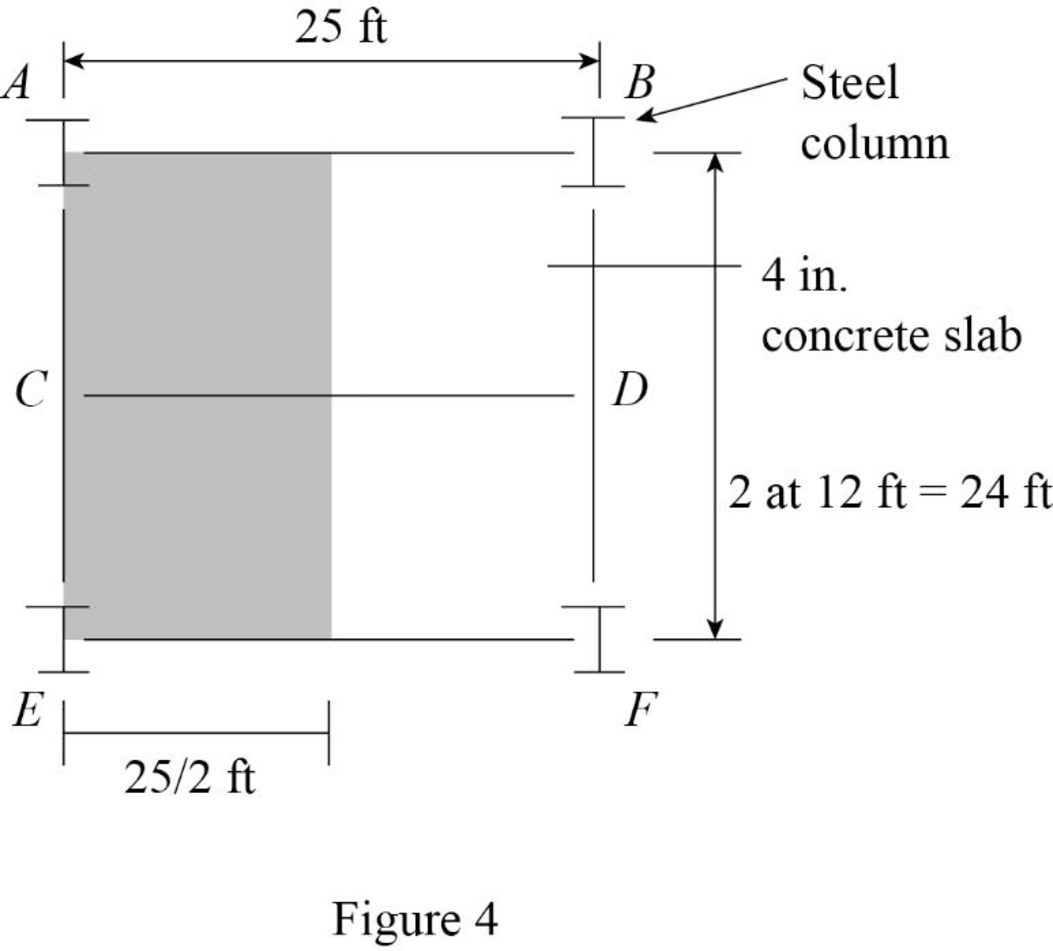
Refer Figure 4.
Tributary area of the girder AE:
The width of the tributary area of the girder AE is
The width of the tributary area of the girder AE is same as the length of the girder AE. Then,
The length of the tributary area of the girder AE is
The thickness of the reinforced concrete slab is
Calculate the dead load per unit length of the girder AE as follows:
Steel beam:
Calculate the dead load of the girder AE using the relation:
Substitute
Concentrated load at A and E.
Show the tributary area of column at A and E as shown in Figure 5.
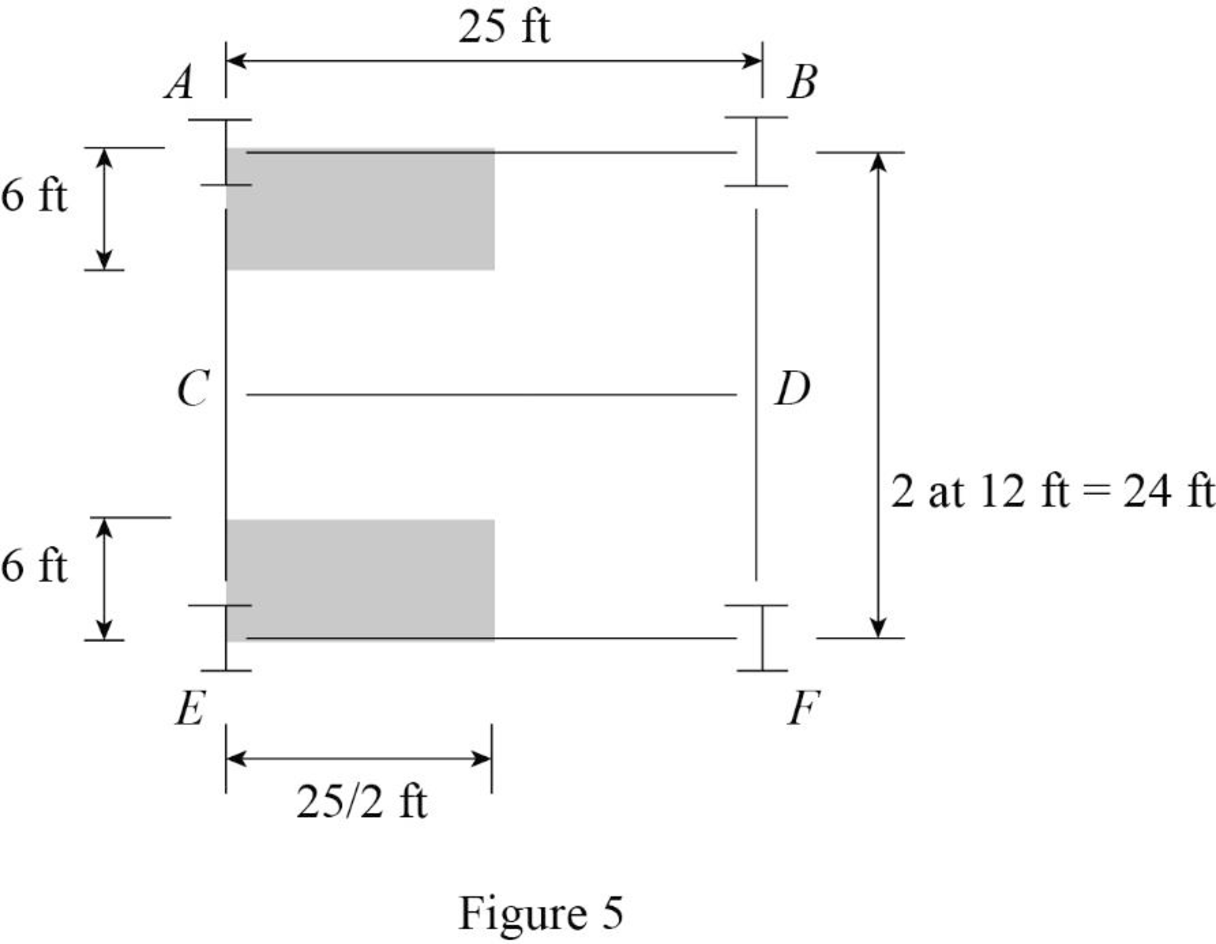
Refer Figure 5.
The tributary area of column at A and E are Equal.
The tributary area of column at A and E are
Calculate the concentrated load (P) at the column A and E the using the relation:
Substitute
Refer Figure 3.
The concentrated load at the column C is
Show the loading on the girder AE as shown in Figure 6.
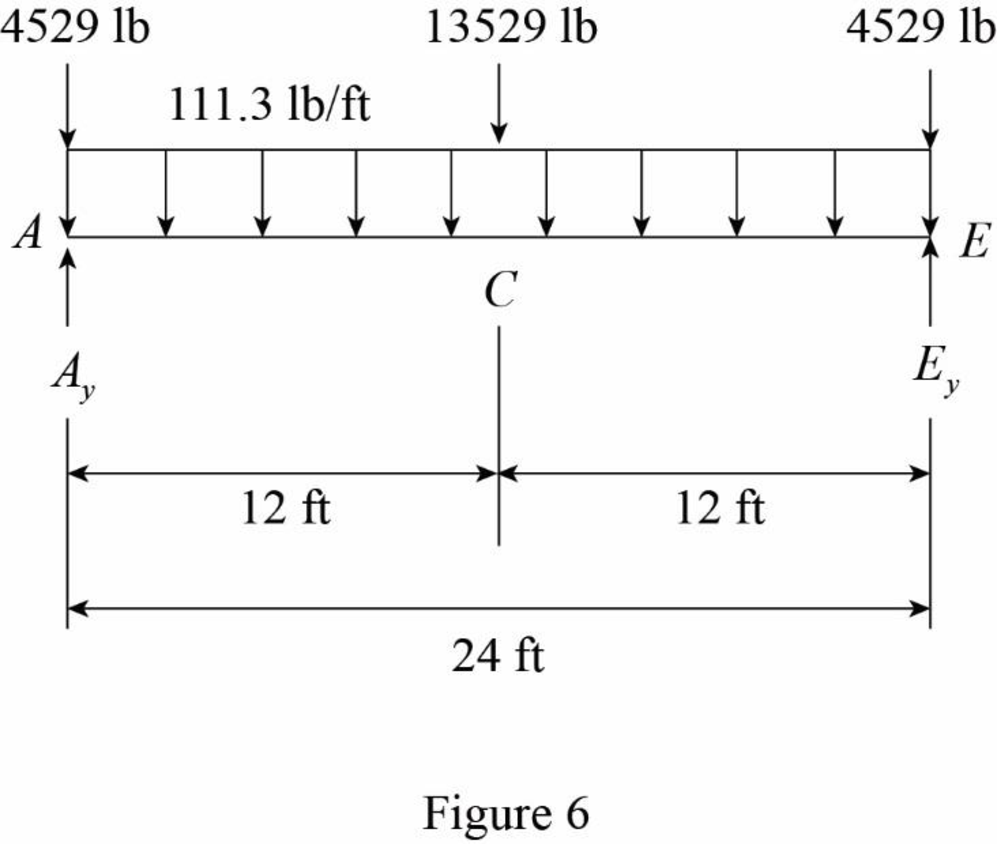
Refer Figure 6.
The reaction at A and E are denoted by
The dead load on the beam is symmetrical. Then,
Show the loading on the girder AE as shown in Figure 7.
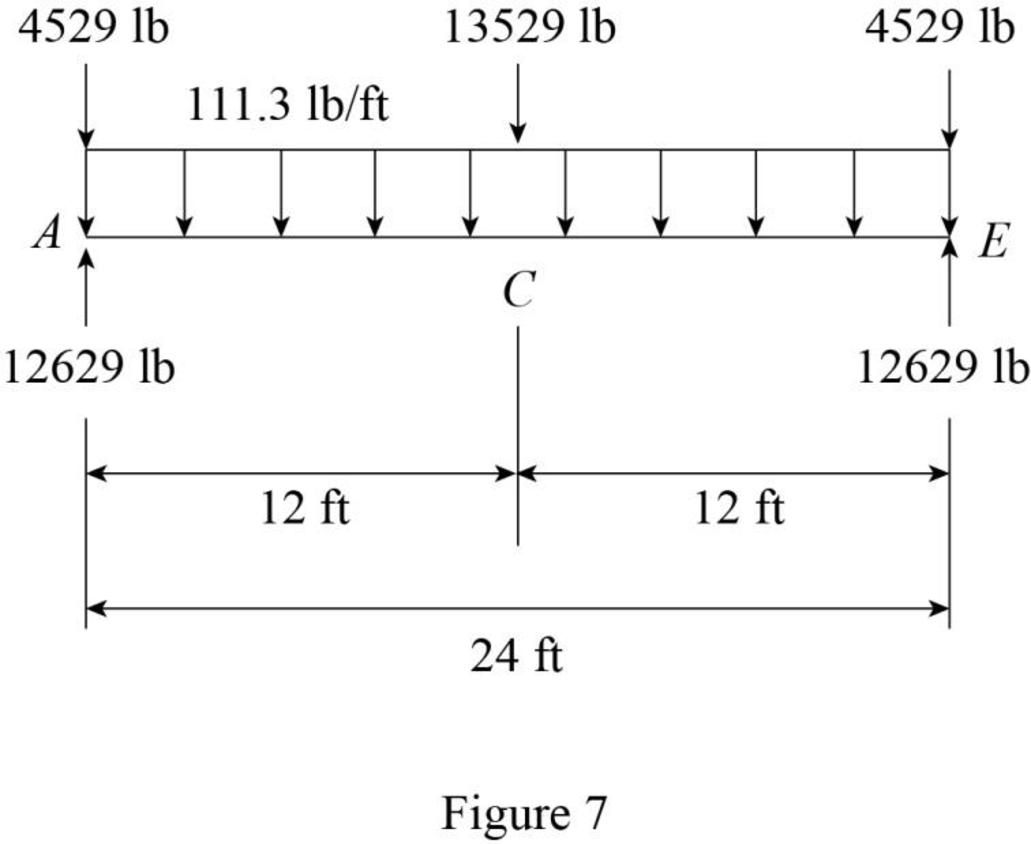
Refer Figure 7.
The dead load at C, A, and E are
The uniformly distributed load in the girder AE is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Structural Analysis, SI Edition
- 6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forwardProblem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forwardProblem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forward
- Problem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forwardUniform Grade of Pipe Station of Point A is 9+50.00. Elevation Point A = 250.75.Station of Point B is 13+75.00. Elevation Point B = 244.10 1) Calculate flowline of pipe elevations at every 50 ft. interval (Half Station). 2) Tabulate station and elevation for each station like shown on example 3) Draw Sketcharrow_forward40m 150N B 40marrow_forward
- Note: Please accurately answer it!. I'll give it a thumbs up or down based on the answer quality and precision. Question: What is the group name of Sample B in problem 3 from the image?. By also using the ASTM flow chart!. This unit is soil mechanics btwarrow_forwardPick the rural location of a project site in Victoria, and its catchment area-not bigger than 25 sqkm, and given the below information, determine the rainfall intensity for ARI = 5, 50, 100 year storm event. Show all the details of the procedure. Each student must propose different length of streams and elevations. Use fig below as a sample only. Pt. E-ht. 95.0 200m 600m PLD-M. 91.0 300m Pt. C-93.0 300m PL.B-ht. 92.0 PL.F-ht. 96.0 500m Pt. A-M. 91.00 To be deemed satisfactory the solution must include: Q.F1.1.Choice of catchment location Q.F1.2. A sketch displaying length of stream and elevation Q.F1.3. Catchment's IFD obtained from the Buro of Metheorology for specified ARI Q.F1.4.Calculation of the time of concentration-this must include a detailed determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.5.Use must be made of the Bransby-Williams method for the determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.6.The graphical display of the estimation of intensities for ARI 5,50, 100 must be shown.arrow_forwardQUANTITY SURVEYINGarrow_forward

 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning





