
Concept explainers
The financial statements for Daniels’ Custom Haircuts for the month of October follow.
Required
Solve for the missing information.
Solve the missing information.
Answer to Problem 5PA
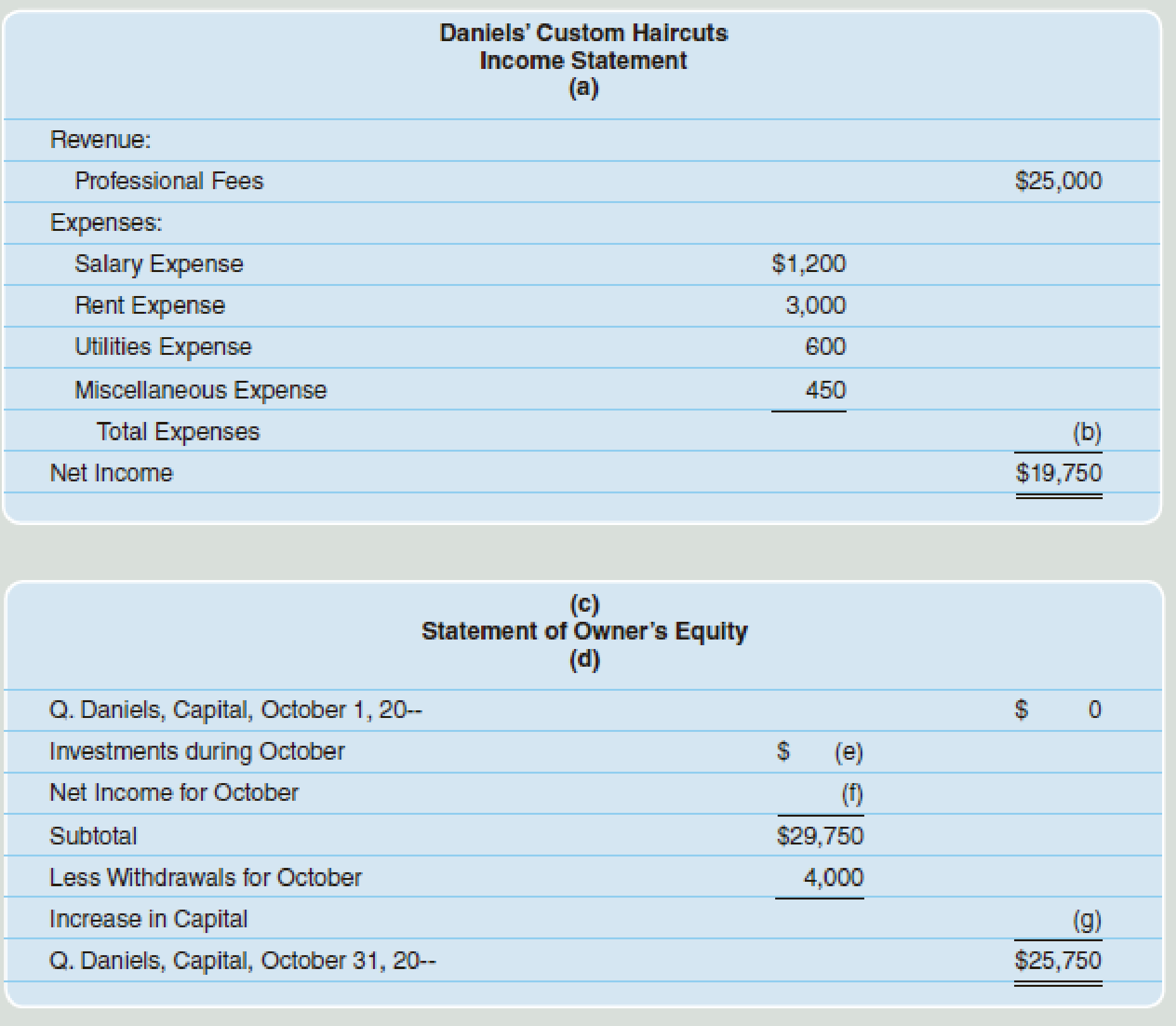
(a) For the year ended October 31
(b) 5,250.
(c) Company D.
(d) For the year ended October 31.
(e) 10,000.
(f) 19,750.
(g) 25,750.
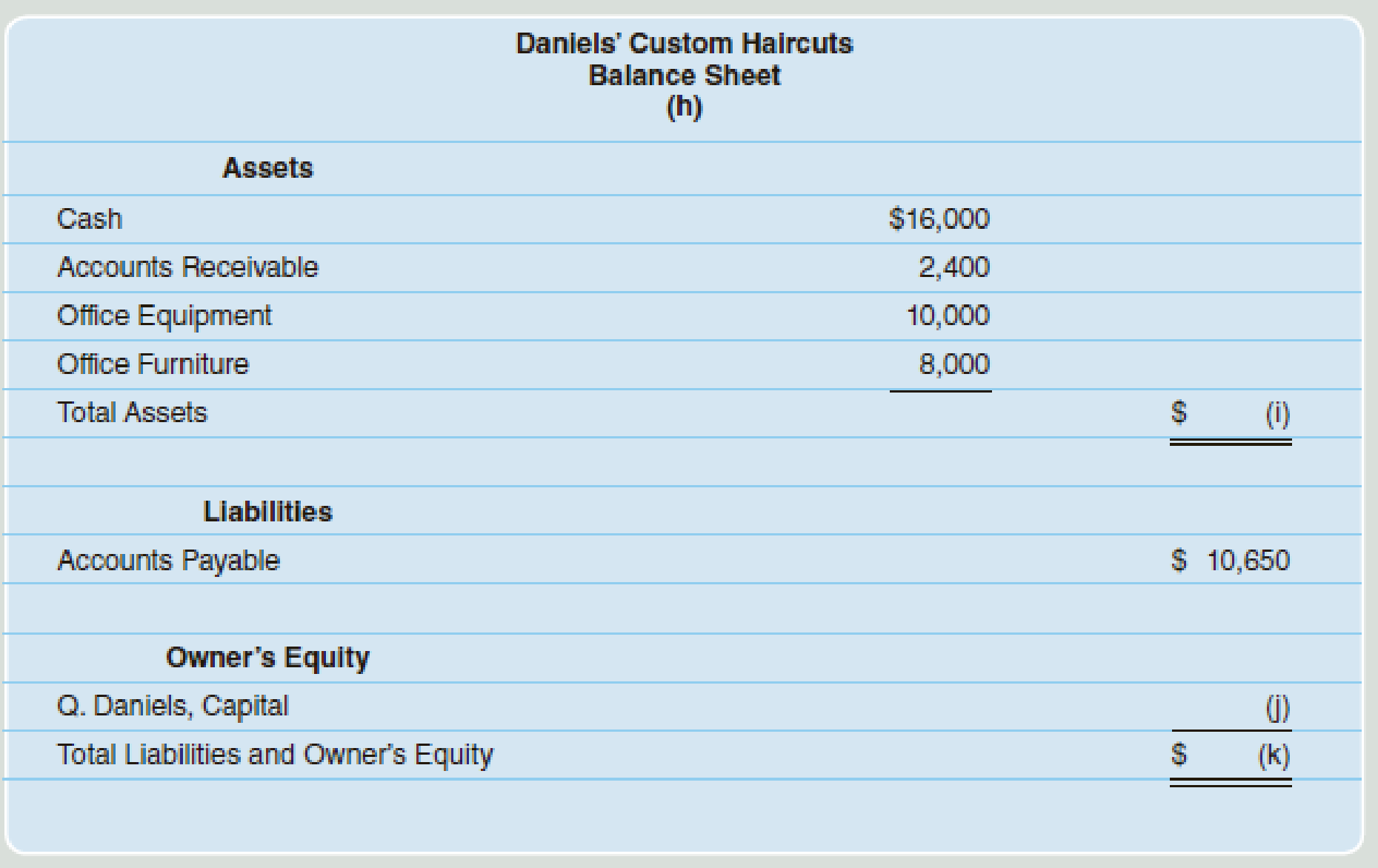
(h) For the year ended October 31.
(i) 36,400.
(j) 25,750.
(k)36,400.
Explanation of Solution
Financial statement:
Financial statements are condensed summary of transactions communicated in the form of reports for the purpose of decision making. The financial statements reports, and shows the financial status of the business. The financial statements consist of the balance sheet, income statement, statement of retained earnings, and the cash flow statement.
Missing information (a):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended October 31) is missing in the income statement.
| Company D |
| Income Statement |
| (a) For the year ended October 31 |
Table (1)
Missing information (b):
The amount of total expense is missing in the income statement and it is calculated by adding all expenses:
| Company D | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| (a) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue: | ||
| Professional Fees | 25,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salary Expense | 1,200 | |
| Rent Expense | 3,000 | |
| Utilities Expense | 600 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 450 | |
| Total Expenses | (b)5,250 | |
| Net income | 19,750 | |
Table (2)
Therefore, the amount of total expenses is (b) 5,250.
Missing information (c):
In this case, “Name of the Company “(Company D) is missing in the statement of owners’ equity.
| (c) Company D |
| Statement of Owners' equity |
| (d) For the year ended October 31 |
Table (3)
Missing information (d):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended October 31) is missing in the statement of owners’ equity.
| (c) Company D |
| Statement of Owners' equity |
| (d) For the year ended October 31 |
Table (4)
Missing information (e):
In this case, the amount of investments made during the month of October is missing and it is calculated as follows:
| (c) Company D | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, October 1 | ||
| Investments during October (1) | (e) 10,000 | |
| Net income for October | (f) 19,750 | |
| Subtotal | 29,750 | |
Table (5)
Therefore, the amount of investments during October is (e) $10,000.
Working note:
(1) Calculate the amount of investment made during October:
Missing information (f):
In this case, the net income mentioned in the income statement is recorded in the statement of owners’ equity. Therefore, amount of net income is $19,750.
| (c) Company D | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, October 1 | ||
| Investments during October (1) | (e) 10,000 | |
| Net income for October | (f) 19,750 | |
| Subtotal | 29,750 | |
Table (6)
Note:
The net income or net loss computed in the income statement is reported in the statement of owners’ equity for ascertaining the amount of ending capital balance. Then, the balance of ending capital is reported in the balance sheet (owners’ equity section). Therefore, any transaction affecting the income statement eventually, affects the balance sheet through the balance of owners’ equity.
Missing information (g):
In this case, the amount of increase in capital is (g) $25,750 and it is same as the Ending capital of Person Q as on October 31, since the amount of beginning capital is given as zero. Suppose, If the amount of beginning capital is given, then the increase in capital is computed by deducting the ending capital from the beginning capital.
| (c ) Company D | ||
| Statement of Owners' equity | ||
| (d) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Person Capital, October 1 | ||
| Investments during October | (e) 10,000 | |
| Net income for October | (f) 19,750 | |
| Subtotal | 29,750 | |
| Less: Withdrawals for October | 4,000 | |
| Increase in capital | (g)25,750 | |
| Person Q, Capital, October 31 | 25,750 | |
Table (7)
Missing information (h):
In this case, information regarding “Period of time” (For the year ended October 31) is missing in the balance sheet.
| Company D |
| Balance Sheet |
| (h) For the year ended October 31 |
Table (8)
Missing information (i):
In this case, the amount of total assets is missing and it is calculated as follows;
| Company D | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 16,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 2,400 | |
| office Equipment | 10,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 8,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 36,400 | |
Table (9)
Therefore, the amount of total assets is (i) 36,400.
Missing information (j):
In this case, the amount of Person Q, Capital is (j) $25,750 and it is the same as the amount of ending capital of Person Q that is calculated in the statement of owners’ equity.
| Company D | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 16,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 2,400 | |
| office Equipment | 10,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 8,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 36,400 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 10,650 | |
| Owners' Equity | ||
| Person Q, Capital | (j) 25,750 | |
Table (10)
Note:
The net income or net loss computed in the income statement is reported in the statement of owners’ equity for ascertaining the amount of ending capital balance. Then, the balance of ending capital is reported in the balance sheet (owners’ equity section). Therefore, any transaction affecting the income statement eventually, affects the balance sheet through the balance of owners’ equity.
Missing information (k):
In this case, the amount of total liabilities and owners’ equity is same as the amount of total assets ($36,400) and it is calculated as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| (h) For the year ended October 31 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 16,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 2,400 | |
| office Equipment | 10,000 | |
| Office Furniture | 8,000 | |
| Total Assets | (i) 36,400 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 10,650 | |
| Owners' Equity | ||
| Person Q, Capital | (j) 25,750 | |
| Total liabilities and owners’ equity (2) | (k)36,400 | |
Table (11)
Therefore, the total amount of liabilities and owners’ equity is (k) $36,400.
Working note:
(2) Calculate the amount of total liabilities and owners’ equity:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
College Accounting: A Career Approach (with Quickbooks Online), Loose-leaf Version
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
- Total equity is 920arrow_forwardOver the past four years, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) delivered annual returns of 12%, -3%, 18%, and 9%. What is the arithmetic average annual return per year? a) 10.25% b) 8.50% c) 9.00% d) 9.75%arrow_forwardMAX's Auto Repair, a proprietorship, started the year with total assets of $72,000 and total liabilities of $48,500. During the year, the business recorded $120,600 in repair revenues, $65,400 in expenses, and MAX Grant, the owner, withdrew $12,500. MAX’s capital balance at the end of the year?arrow_forward
- Peterson Company estimates that overhead costs for the next year will be $3,600,000 for indirect labor and $910,000 for factory utilities. The company uses machine hours as its overhead allocation base. If 110,000 machine hours are planned for this next year, what is the company's plantwide overhead rate? a) $41.00 per machine hour b) $32.30 per machine hour c) $0.03 per machine hour d) $8.27 per machine hour e) $0.12 per machine hourarrow_forwardneed true answer of this General accounting questionarrow_forwardCreston Alloy Works manufactures a single product that sells for $90 per unit. Variable costs are $58 per unit, and fixed costs total $135,000 per month. Calculate the operating income if the selling price is raised to $94 per unit, advertising expenditures are increased by $18,000 per month, and monthly unit sales volume becomes 5,500 units.arrow_forward
- If Ram Nation can give up one unit of future consumption and as a result increase its current consumption by 0.96 units, what must be its real rate of interest. Nonearrow_forwardWhat is the depreciation expense for the scanner ?arrow_forwardAssume Newcome pays no taxes on this project.??arrow_forward
- Give me this question answerarrow_forwardCalculate the Debt to Equity Ratio given that Total Equity is $920 and Total Debt is $780. a. 0.52 b. 0.85 c. 1.10 d. 1.33arrow_forwardIf Ram Nation can give up one unit of future consumption and as a result increase its current consumption by 0.96 units, what must be its real rate of interest. Answer this questionarrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





