
Interpretation:
The given table is to be completed for the given neutral elements.
Concept introduction:
The electrons in the atoms revolve around the nucleus in different orbits. The nucleus of the atom has two particles, protons and neutrons. The number of proton is the
Answer to Problem 29P
The complete table is as shown below.
| Element Symbol | Atomic number | Mass Number | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Number of Electrons | |
| a | ||||||
| b | ||||||
| c | ||||||
| d | ||||||
| e | ||||||
| f | ||||||
| g | ||||||
| h |
Explanation of Solution
All the elements are assigned a letter symbol from their name. The symbol is the first or first two letters from the name of the element.
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its atom.
The mass number of the element is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of the atom.
The protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus of the atom and electrons revolve around the nucleus. The number of electrons and protons are equal in a neutral atom as the electrons and protons are charged bodies.
To complete the given table, the points given above are to be considered.
For the case (a), the data given is the
So,
The symbol
The number of neutrons is calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the above formula.
Hence, carbon with element symbol
For the case (b) the data given is its mass number
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. This atom has
The number of neutrons can be calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the formula below.
So, the element is phosphorus as its atomic number is
For the case (c), the data given is its number of neutrons
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. This atom has
Its number of neutrons is
Substitute the given values in the above formula
So, the element is zinc as its atomic number is
For the case (d), the data given is the symbol of element
So, the symbol
The number of neutrons can be calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the above formula.
So, the magnesium element with symbol
For the case (e), the data given is its number of neutrons
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. This atom has
Its atomic number is
Substitute the given values in the above formula
So the element is iodine as its atomic number is
For the case (f), the data given is its atomic number
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. Its atomic number is
The mass number of the element can be calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the formula below.
So the element is beryllium as its atomic number is
protons and 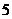 neutrons. Its atomic number is
neutrons. Its atomic number is
and mass number is 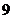
For the case (g) the data given is its atomic number
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. Its atomic number is
The number of neutron of the element can be calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the above formula
So the element is zirconium as its atomic number is
For the case (h), the number of neutrons is
So, the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and electrons in the atom. This atom has
The mass number can be calculated by the formula given below.
Substitute the given values in the formula below.
So the element is sulfur as its atomic number is
The table is completed with the symbols of elements and the information about their atoms and nucleus.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- How many particles does a face-centered cubic (fcc) unit cell contain? Group of answer choices 2 14 8 4arrow_forwardV Highlight all of the carbon atoms that have at least one beta (B) hydrogen, using red for one ẞ hydrogen, blue for two ẞ hydrogens, and green for three ẞ hydrogens. If none of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens, check the box underneath the molecule. ED X None of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens. Explanation esc 2 Check * F1 F2 1 2 80 # 3 Q W tab A caps lock shift fn control F3 N S option O 694 $ F4 F5 F6 005 % E R D F LL 6 olo 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility A DII F7 F8 87 & * 8 T Y U G H 4 F9 F10 ( 9 0 E F11 F12 உ J K L + || X C V B N M H H command option commandarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below and answer the following questions. Part 1 of 4 Br NaOCH2CH3 Identify the mechanisms involved. Check all that apply. SN 1 SN 2 E1 E2 None of the above Part 2 of 4 Skip Part Check esc F1 F2 lock 1 2 Q W A S #3 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 Save For © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ˇˇ % & 4 5 6 89 7 IK A 分 བ F7 F8 F9 F * E R T Y U 8 9 D F G H K V B N M 0 Oarrow_forward
- What kind of holes are not generated when solid-state particles adopt a close packing pattern? Group of answer choices tetrahedral cubic octahedral None of the other choices are correctarrow_forwardFor the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. 田 Major Product: Check ☐ + I Na OH esc F1 F2 2 1 @ 2 Q W tab A caps lock S #3 80 F3 69 4 σ F4 % 95 S Click and drag to sta drawing a structure mm Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use GO DII F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 6 CO 89 & 7 LU E R T Y U 8* 9 0 D F G H J K L Z X C V B N M 36arrow_forwardProblem 7 of 10 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. S' S 1. BuLi 2. ethylene oxide (C2H4O) Select to Draw a Submitarrow_forward
- Feedback (4/10) 30% Retry Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the reactant and missing intermediates involved in this reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 6 attempts remaining :0: Draw the Reactant H H3CO H- HIO: Ö-CH3 CH3OH2* protonation H. a H (+) H Ο CH3OH2 O: H3C protonation CH3OH deprotonation > CH3OH nucleophilic addition H. HO 0:0 Draw Intermediate a Xarrow_forwardCan I please get the blank spaces answered/answers?arrow_forward1. Identify the following alkenes as E or Z NH₂ Br 2. Draw the structures based on the IUPAC names (3R,4R)-3-bromo-4-fluoro- 1-hexene (Z)-4-bromo-2-iodo-3-ethyl- 3-heptene تر 3. For the following, predict all possible elimination product(s) and circle the major product. HO H₂SO4 Heat 80 F4 OH H2SO4 Heat 어요 F5 F6 1 A DII 4 F7 F8 F9 % & 5 6 7 * ∞ 8 BAB 3 E R T Y U 9 F D G H J K O A F11 F10arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. ○ O 1. H₂O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up a N W X 人 Parrow_forward✓ Check the box under each molecule that has a total of five ẞ hydrogens. If none of the molecules fit this description, check the box underneath the table. tab OH CI 0 Br xx Br None of these molecules have a total of five ẞ hydrogens. esc Explanation Check caps lock shift 1 fn control 02 F2 W Q A N #3 S 80 F3 E $ t 01 205 % 5 F5 & 7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility FT * 8 R T Y U כ F6 9 FIG F11 F D G H J K L C X V B < N M H option command P H + F12 commandarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic acid side product. O 1. CHзMgBr (excess) 2. H₂O ✓ W X 人arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





