
(a)
Interpretation:
The formulas for ammonium and ammonia are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms. In covalent bonding, there is a mutual attraction between two nuclei and the two electrons that reside between them. The elements that engage in covalent bond formation are present at the rightmost corner of the periodic table. These elements are non-metals. The interaction between two non-metal elements leads to the formation of a covalent bond.
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.96P
The formula for ammonia is
Explanation of Solution
Ammonia is a covalent compound in which three hydrogen atoms are covalently bonded to a nitrogen atom. It is denoted by the molecular formula
The ammonium ion is a molecule of ammonia in which one hydrogen ion
The difference between ammonia and ammonium is, while the former is a neutral molecule, the latter is an ion with
The formula for ammonia is
(b)
Interpretation:
The formulas for magnesium sulfide, magnesium sulfite, and magnesium sulfate are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The general rules for naming ionic compounds are as follows:
1) In ionic compounds, the cations are named before the anions.
2) In binary ionic compounds, the name of the cation is the same as the name of the metal. The name of the anion includes the root name of the non-metal and a suffix
3) In polyatomic ions in which a non-metal is bonded to one or more oxygen atoms. In two oxoanions in the family, the ion with fewer oxygen atoms has the non-metal root name and a suffix
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.96P
The formula for magnesium sulfide is
Explanation of Solution
Magnesium sulfide is a binary ionic compound. It is formed as follows:
The sulfide ion is represented by the formula
Sulfate and sulfite are polyatomic oxoanions. The charge on both sulfate and sulfite is
The formation of magnesium sulfate and magnesium sulfite occur as follows:
The
The formula for magnesium sulfide is
(c)
Interpretation:
The formulas for hydrochloric acid, chloric acid, and chlorous acid are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The general formula for naming binary acids is,
The general rules for naming the members of a family with four oxoanions are as follows:
1) The anion with the most number of oxygen atoms has the refix
2) The anion with one fewer oxygen atom has the non-metal root and the suffix
3) The anion with two fewer oxygen atoms has the non-metal root and the suffix
4) The anion with three fewer oxygen atoms has the prefix
(c)
Answer to Problem 2.96P
The formula for hydrochloric acid is
Explanation of Solution
Hydrochloric acid is a binary acid formed by the association of a hydrogen ion with
Therefore the formula for hydrochloric acid is
The oxoanions of chlorine are
The anion
In the ion chlorate, the root name chlor denotes the non-metal chlorine
The suffix
In the ion chlorite, the root name chlor denotes the non-metal chlorine
The suffix
Therefore the formulas for chloric and chlorous acids are
The formula for hydrochloric acid is
(d)
Interpretation:
The formulas for cuprous bromide and cupric bromide are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The general rules for naming ionic compounds with different charges on the same metal are:
1) The root name of the metal is followed by the suffix
2)The root name of the metal is followed by the suffix
(d)
Answer to Problem 2.96P
The formulas for cuprous bromide and cupric bromide are
Explanation of Solution
The element bromine belongs to the
The two ions formed by the copper element are
To balance the
To balance the 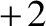 charge on the cupric ion, two bromide ions associate with one cupric ion to form the molecule of cupric bromide as follows:
charge on the cupric ion, two bromide ions associate with one cupric ion to form the molecule of cupric bromide as follows:
The formulas for cuprous bromide and cupric bromide are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
MCGRAW: CHEMISTRY THE MOLECULAR NATURE
- please provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forwardpresented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forwardReaction A 0,0arrow_forward
- presented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forward
- Name the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





