
Requirement – 1
To analyze: The given transaction, and explain their effect on the
Requirement – 1
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
Accounting equation for each transaction is as follows:
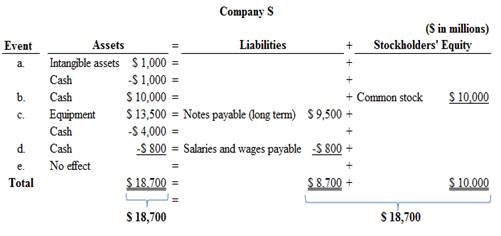
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
Requirement – 2
To record: The
Requirement – 2
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journal entries of Company S are as follows ($ in millions):
a. Intangible assets purchased in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Intangible assets(+A) | 1,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 1,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of supplies in cash) |
Table (1)
- Inventories are an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $1,000. Hence, debit the inventories account for $1,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $1,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $1,000.
b. Issuance of common stock:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 10,000 | |||
| Common stock (+SE) | 10,000 | |||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $10,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $10,000.
- Common stock is a component of stockholder’s equity and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity by $10,000, Hence, credit the common stock for $10,000.
c. Equipment purchased on account and in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Equipment (+A) | 13,500 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 4,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 9,500 | |||
| (To record purchase of equipment on account and in cash) |
Table (3)
- Equipment is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $13,500. Hence, debit the equipment account for $13,500.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $4,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $4,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $9,500. Hence, credit the notes payable for $9,500.
d. Salaries paid to employees
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Salaries and wages payable (+L) | 800 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 800 | |||
| (To recordcash paid to employees) |
Table (4)
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it decreased the value of liabilities by $800. Hence, debit the notes payable for $800.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $800. Hence, credit the cash account for $800.
e. Conducted negotiations to purchase a coffee form:
In this case, no entry required, because it is not a business transaction.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: T-account for each account listed in the requirement 2.
Requirement – 3
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of Company S are as follows ($ in millions):
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. | 2,560 | ||
| (b) | 10,000 | 1,000 | (a) |
| 4,000 | (c) | ||
| 800 | (d) | ||
| End. | 6,760 | ||
| Accounts receivable (A) | |||
| Beg. | 560 | ||
| End. | 560 | ||
| Inventory (A) | |||
| Beg. | 1,110 | ||
| End. | 1,110 | ||
| Prepaid rent (A) | |||
| Beg. | 570 | ||
| End. | 570 | ||
| Short-term investment (A) | |||
| Beg. | 660 | ||
| End. | 660 | ||
| Intangible assets (A) | |||
| Beg. | 2,850 | ||
| (a) | 1,000 | ||
| End. | 3,850 | ||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg. | 3,220 | ||
| (c) | 13,500 | ||
| End. | 16,720 | ||
| Accounts payable (L) | |||
| 4,110 | Beg. | ||
| 4,110 | End. | ||
| Salaries and wages payable (L) | |||
| 1,270 | Beg. | ||
| (d) | 800 | ||
| 470 | End. | ||
| Notes payable (long-term) (L) | |||
| 1,660 | Beg. | ||
| 9,500 | (c) | ||
| 11,160 | End. | ||
| Common Stock (SE) | |||
| 350 | Beg. | ||
| 10,000 | (b) | ||
| 10,350 | End. | ||
| 4,140 | Beg. | ||
| 4140 | End. | ||
Requirement – 4
To explain: The response for event (e).
Requirement – 4
Explanation of Solution
Business transaction:
Business transaction is a record of any economic activity, resulting in the change in the value of the assets, the liabilities, and the stockholder’s equities, of a business. Business transaction is also referred to as financial transaction.
In this case, conducting negotiation to purchase a coffee form is not creating any impact on assets, liabilities and stockholder’s equity of the business, because it is not a business transaction.
Requirement – 5
To prepare: The classified
Requirement – 5
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Classified balance sheet of Company S is as follows ($ in millions):
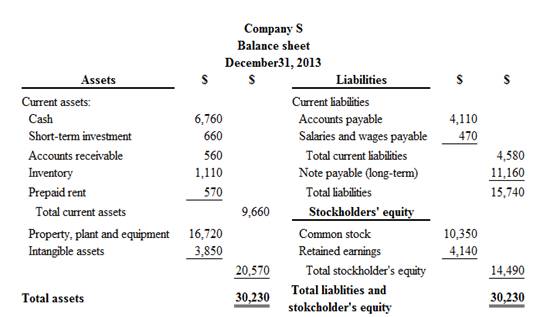
Figure (2)
Therefore, the total assets of Company S are$30,230 million, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity is$30,230 million.
Requirement – 6
Whether the assets amount of Company S is primarily come from liabilities or stockholders’ equity.
Requirement – 6
Explanation of Solution
The invested amount of assets are primarily come from liabilities (current and non-current) of Company S, because liabilities financed $15,740 million of the Company S’s total assets, and stockholder’s equity (common stock) financed $14,490 million.
Requirement – 7
The current ratio of Company S and compare with Company L’s current ratio.
Requirement – 7
Explanation of Solution
Current Ratio:
A part of
Calculate the current ratio of Company S as follows:
Here,
Current assets = $5,460million (1)
Current liabilities= $5,380 million(2)
Therefore, the current ratio of Company S is 1.01.
Current ratio of Company S is 1.01 and Company A is 1.68, so Company S has less current ratio than Company A and it indicates Company A has better position to repay the liabilities.
Working note:
Calculate the value of current assets before given error transaction:
Calculate the value of current liabilities before given error transaction:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose-leaf for Fundamentals of Financial Accounting with Connect
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





