
(a)
The equation for Total cost and total revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
P = -0.25D + 250
P = unit sales price
D = annual quantity demanded for the product.
Total Cost (TC) = Fixed Cost+ Variable cost
Total Revenue (TR) − Quantity demanded X Price
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
The cost and revenue details of the company are given below:
The variable costs per unit are $20.00 and the fixed costs are $10.875.00
The price-demand relationship is P = -0.25D+250 .......(1)
Here,
P = unit sales price
D = annual quantity demanded for the product.
The following three formulas were also provided to assist you with the problem as wll.
Total Cost (TC) = Fixed Cost+ Variable cost
Total Revenue (TR) − Quantity demanded× Price
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
To determine the total cost of the problem, it should be noted that TC is equal to the combination of both fixed costs and variable costs.
Total Costs (TC) - $10,875.00+20.00D
Where, D is the quantity demanded or sold.
Total Revenue can be calculated by the multiplying price with quantity
Total Revenue = Price × Quantity Demanded
=(-0.25D+250)×D
= -0.25D2 + 250D
Total Revenue = -0.25D2 + 250D.
(b)
Breakeven quantity.
Explanation of Solution
Breakeven point for units is that one would need to produce inorder to achieve no profit or loss. In this case, set the formula,
Total Cost = Total Revenue
$10,875+20.00D = -0.25D2 +250D
0.25D2 -250D+20.00D+$10,875.00=0
0.25D2 -230D+$10,875.00=0
The standard formula that assists in getting the correct answer.
Thus, the break even points for this situation are both 50 units and 870 units respectively. It can be said that anything above 870 units and below 50 units could constitute a loss whereas anything between would be profitable to profitable.
(c)
Number of units the company would want to produce if they wanted to maximize the revenues.
Explanation of Solution
Total Revenue = -0.25D2 +250D
Revenue maximization:
Revenue is maximized when MR equals to zero.
Revenue maximization;
Thus to maximize revenue, the company must produce 500 units.
(d)
Total Profit at revenue maximization point of 500 units:
Explanation of Solution
Total Profit = Total Revenue- Total Costs
Thus, the total profit at revenue maximization point of 500 units is $41,625.
The company’s maximum profit is obtained when marginal revenue equals to marginal cost.
Marginal Cost (MC) is calculated as shown below:
Profit maximization is at MR = MC
Thus, maximum profit is obtained at 460 units.
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
Maximum possible profit is $42,025.
(e)
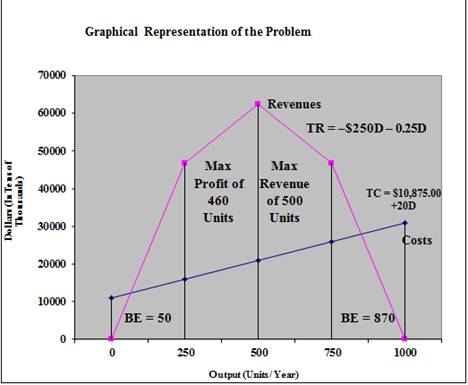
Graphical Representation:
Explanation of Solution
Graphical Representation:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ENGINEERING ECONOMIC ENHANCED EBOOK
- If food is produced in the U.S., sold in the U.S. and consumed in the U.S., a reduction in its price will have which of the following effects ______? Two of the answers are correct. The consumer price index will decrease. None of the answers are correct. The GDP deflator will decrease.arrow_forwardhow to caculate verible cost?arrow_forwardWhat is the deficit?arrow_forward
- Identify the two curves shown on the graph, and explain their upward and downward slopes. Why does curve Aintersect the horizontal axis? What is the significance of quantity d? What does erepresent? How would the optimal quantity of information change if the marginal benefit of information increased—that is, if the marginal benefit curve shifted upward?arrow_forward6. Rent seeking The following graph shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves for a single-price monopolist that produces a drug that helps relieve arthritis pain. Place the grey point (star symbol) in the appropriate location on the graph to indicate the monopoly outcome such that the dashed lines reveal the profit-maximizing price and quantity of a single-price monopolist. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to show the profits earned by the monopolist. 18 200 20 16 16 14 PRICE (Dollars per dose) 12 10 10 8 4 2 MC = ATC MR Demand 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Millions of doses per year) Monopoly Outcome Monopoly Profits Suppose that should the patent on this particular drug expire, the market would become perfectly competitive, with new firms immediately entering the market with essentially identical products. Further suppose that in this case the original firm will hire lobbyists and make donations to several key politicians to extend its…arrow_forwardConsider a call option on a stock that does not pay dividends. The stock price is $100 per share, and the risk-free interest rate is 10%. The call strike is $100 (at the money). The stock moves randomly with u=2 and d=0.5. 1. Write the system of equations to replicate the option using A shares and B bonds. 2. Solve the system of equations and determine the number of shares and the number of bonds needed to replicate the option. Show your answer with 4 decimal places (x.xxxx); do not round intermediate calculations. This is easy to do in Excel. A = B = 3. Use A shares and B bonds from the prior question to calculate the premium on the option. Again, do not round intermediate calculations and show your answer with 4 decimal places. Call premium =arrow_forward
- Answer these questions using replication or the risk neutral probability. Both methods will produce the same answer. Show your work to receive credit. 6. What is the premium of a call with a higher strike. Show your work to receive credit; do not round intermediate calculations. S0 = $100, u=2, d=0.5, r=10%, strike=$150arrow_forwardAnswer these questions using replication or the risk neutral probability. Both methods will produce the same answer.arrow_forwardProblem 2: At a raffle, 2000 tickets are sold at $5 each for five prizes of $2000, $1000, $500, $250, and $100. You buy one ticket. What is the expected value of your gain? 1. Find the gain for each prize. 2. Write a probability distribution for the possible gains. 3. Find the expected value. 4. Interpret the results.arrow_forward
- This activity focuses on developing direct and supported opinions using various sources of information on the importance of the following topics: non-renewable and renewable energies, economic factors and obstacles that can affect the relationship between international trade and economic growth, devaluation of the currency in countries, and the imbalance of economic equity. In this context, it is essential that, when studying and developing these topics, students understand the concepts of the value of currencies and that leads to devaluation, non-renewable and renewable energy resources, economic development and obstacles, distribution of wealth, economic growth and external and internal constraints, and about international trade as a growth factor. Thus, the objectives that are intended to be achieved are the following: Acquire knowledge about the concepts mentioned above. Determine relationships between economic growth and international trade. Understand what some limitations that…arrow_forwardConsider a firm facing conventional production technology. The short run Production Function has a small range of increasing marginal product (increasing marginal returns) and then is subject to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Product (diminishing marginal returns). A. Putting quantity on the horizontal axis and dollars on the vertical axis, depict three important curves: Fixed Cost (FC), Variable Cost (VC), and Total Cost (TC). (Note that we are not asking you to depict average cost functions!) B. Please clearly indicate on this graph the range of quantities where the firm is experiencing (1) increasing marginal product and (2) diminishing marginal product. C. In a few sentences, please justify why you've made this specific classification of increasing/diminishing marginal product in part (b).arrow_forwardplease answer the following questions: What is money, and why does anyone want it? Explain the concept of the opportunity cost of holding money . Explain why an increase in U.S. interest rates relative to UK interest rates would affect the U.S.-UK exchange rate. Suppose that a person’s wealth is $50,000 and that her yearlyincome is $60,000. Also suppose that her money demand functionis given by Md = $Y10.35 - i2Derive the demand for bonds. Suppose the interest rate increases by 10 percentage points. What is the effect on her demand for bonds?b. What are the effects of an increase in income on her demand for money and her demand for bonds? Explain in wordsarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





