
(a)
The equation for Total cost and total revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
P = -0.25D + 250
P = unit sales
D = annual quantity demanded for the product.
Total Cost (TC) = Fixed Cost+ Variable cost
Total Revenue (TR) − Quantity demanded X Price
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
The cost and revenue details of the company are given below:
The variable costs per unit are $20.00 and the fixed costs are $10.875.00
The price-
Here,
P = unit sales price
D = annual quantity demanded for the product.
The following three formulas were also provided to assist you with the problem as wll.
Total Cost (TC) = Fixed Cost+ Variable cost
Total Revenue (TR) − Quantity demanded× Price
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
To determine the total cost of the problem, it should be noted that TC is equal to the combination of both fixed costs and variable costs.
Total Costs (TC) - $10,875.00+20.00D
Where, D is the quantity demanded or sold.
Total Revenue can be calculated by the multiplying price with quantity
Total Revenue = Price × Quantity Demanded
=(-0.25D+250)×D
= -0.25D2 + 250D
Total Revenue = -0.25D2 + 250D.
(b)
Breakeven quantity.
Explanation of Solution
Breakeven point for units is that one would need to produce inorder to achieve no profit or loss. In this case, set the formula,
Total Cost = Total Revenue
$10,875+20.00D = -0.25D2 +250D
0.25D2 -250D+20.00D+$10,875.00=0
0.25D2 -230D+$10,875.00=0
The standard formula that assists in getting the correct answer.
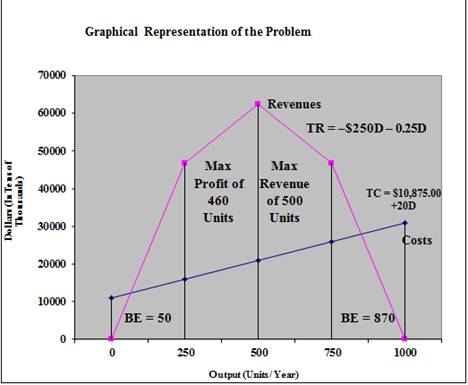
Thus, the break even points for this situation are both 50 units and 870 units respectively. It can be said that anything above 870 units and below 50 units could constitute a loss whereas anything between would be profitable to profitable.
(c)
Number of units the company would want to produce if they wanted to maximize the revenues.
Explanation of Solution
Total Revenue = -0.25D2 +250D
Revenue maximization:
Revenue is maximized when MR equals to zero.
Revenue maximization;
Thus to maximize revenue, the company must produce 500 units.
(d)
Total Profit at revenue maximization point of 500 units:
Explanation of Solution
Total Profit = Total Revenue- Total Costs
Thus, the total profit at revenue maximization point of 500 units is $41,625.
The company’s maximum profit is obtained when marginal revenue equals to marginal cost.
Marginal Cost (MC) is calculated as shown below:
Profit maximization is at MR = MC
Thus, maximum profit is obtained at 460 units.
Total Profit = Total Revenue − Total Costs
Maximum possible profit is $42,025.
(e)
Graphical Representation:
Explanation of Solution
Graphical Representation:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ENGINEERING ECO ANALYSIS W/STUDY GUIDE
- Answerarrow_forwardM” method Given the following model, solve by the method of “M”. (see image)arrow_forwardAs indicated in the attached image, U.S. earnings for high- and low-skill workers as measured by educational attainment began diverging in the 1980s. The remaining questions in this problem set use the model for the labor market developed in class to walk through potential explanations for this trend. 1. Assume that there are just two types of workers, low- and high-skill. As a result, there are two labor markets: supply and demand for low-skill workers and supply and demand for high-skill workers. Using two carefully drawn labor-market figures, show that an increase in the demand for high skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers. 2. Using the same assumptions as in the previous question, use two carefully drawn labor-market figures to show that an increase in the supply of low-skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers.arrow_forward
- Published in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curves facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. a. Calculate the values of profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss, and illustrate these on the graph. b. Repeat the calculations in part a, but now assume the monopoly is able to practice perfect price discrimination.arrow_forwardThe projects under the 'Build, Build, Build' program: how these projects improve connectivity and ease of doing business in the Philippines?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





