
Interpretation: The pressure difference across a simple U-tube manometer is to be calculated in the appropriate units.
Concept introduction: A simple U-tube Manometer is a device that can measure the pressure difference across a U-tube filled with fluids of different or the same density.
The pressure difference across the Manometer is given as,
In the above formula, the notations used are,
The density of the substance is given as,
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The pressure difference across a U-tube Manometer is 23544 N/m2.
Explanation of Solution
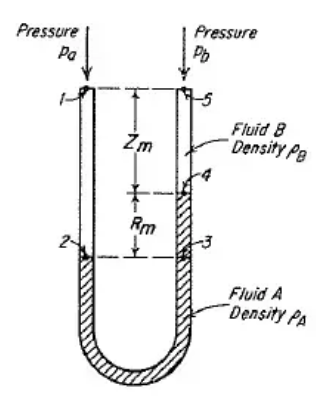
The U-tube Manometer mentioned in the question can be given as:
The fluid A is Mercury and the fluid B is Carbon tetrachloride here.
The given data is,
Substitute these values in equation (1) above,
The pressure difference across a U-tube Manometer for the given readings of density and manometer is 23544 N/m2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
- acetone with these parameters: po:=101325; #Standard atmospheric pressure in PaTfo:=273.15-94.45; #Melting temperature in K Tvo:=273.15+56.15; #Boiling temperature in K Hv:=31270; #Enthalpy of vaporization in J/molR:=8.314; #Gas Constant in J/mol*KNLe:=1.76; #Lewis number for acetoneMw:= 0.05808 ; #kg/mol molecular weight of acetoneW0:= 0.15; Wsp:=0.005;Am:= 0.12; #m^2/kg dry solid for the exposed wet areah:= 11; #W/m^2K for heat transfer coefficienttau__min:= Hv*(W0-Wsp)/Mw/Am/h/(T8-TS); tau__min/60;arrow_forwardchemical engineering Material-energy balance. Only focus on the nitrogen gas, which is H(3)arrow_forward1. The settling chamber, shown schematically in Figure 2E1.1, is used as a primary separation device in the removal of dust particles of density 1500 kg/m³ from a gas of density 0:7 kg/m³ and viscosity 1.90 x 10-5 Pa s. Gas inlet Elevation Gas Gas exit exit H Collection surface -W Section X-X Dimensions: H=3m L = 10 m W=2m Figure 2E1.1 Schematic diagram of settling chamber Assuming Stokes' law applies, show that the efficiency of collection of particles of size x is given by the expression collection efficiency, x = x²8(pp - Pi)L 18μHU where U is the uniform gas velocity through the parallel-sided section of the chamber. State any other assumptions made. (b) What is the upper limit of particle size for which Stokes' law applies? (c) When the volumetric flow rate of gas is 0.9 m³/s, and the dimensions of the chamber are those shown in Figure 2E1.1, determine the collection efficiency for spherical particles of diameter 30 mm.arrow_forward
- Can you answer this sequantially correct like show me the full process. Also, since it is chemical engineering related problem a perry's handbook is used. Thank youarrow_forwardchemical engineering Demonstrate how each specific enthalpy was calculated, from the reference state to the process state. Be thorough to the fullest. This is a material-energy balance. The answers are H(1) = 35.7 KJ/kmol, H(2) = 32.0 KJ/kmol, and H(3) = -1.26 KJ/kmol.arrow_forwardheat and mass transfer:arrow_forward
- Chemical Engineering. Be thorough to the fullest for the three enthalpies. H(1) = 35.7 kj/kmol H(2) =32.0 Kj/kmol H(3)= -1.26 Kj/kmolarrow_forwardchemical engineering Only solve the specific enthalpies. Be thorough to the fullest for each calculationarrow_forwardDo question 9 please! Question 7 Is just there for reference!!arrow_forward
- 7) You are tasked with separating two proteins by ion exchange chromatography on a 30 cm long column with an inner diameter of 2 cm. The resin has a diameter of 100 μm and a void fraction of 0.3, and your mobile phase flows through the column at a rate of Q = 5 cm³/min. The Van Deemter coefficients A, B, and C have been determined to be 0.0228 cm, 0.0036 cm²/min, and 0.00053 min, respectively, for both proteins. Protein A elutes from the column with an average retention time of 27 min and standard deviation of 0.8 min. Protein B elutes from the column. with an average retention time of 33.8 min and standard deviation of 1.0. a) How many theoretical plates does the column contain? b) What flow rate (Q) will give you the maximum resolution? c) What is the minimum height of a theoretical plate for the system?arrow_forward4) A fixed bed adsorption unit contains rigid (incompressible) silica particles with a diameter of 120 um and porosity of 0.3. The resin bed is 200 cm long and has a diameter of 15 cm. A protein solution is pumped into the column at a rate of 50 L/min, and the mobile phase has a viscosity of 1.2 CP. a) What is the pressure drop for this system (in bar)? b) What would be the pressure drop if the particle diameter were decreased to 30 μm?arrow_forwardYou are part of a team constructing a pipeline to transfer shale gas produced at the oceanfloor to the coastline. The temperature of the pipeline is nearly constant at 2 oC. The pipelineis made of smooth stainless steel and is 0.3 m in diameter and 100 m long. The averagevelocity of shale gas is 10 m/s and the inlet temperature is 20 oC ** Useful shale gas properties at 20 oC (Table A-12 for propane gas):(use these values for calculations and validate them later)• Density (ρ) = 18.13 kg/m3• Cp = 1974 J/kg-K• Viscosity (μ) = 8.54*10-6 kg/m-s• Pr = 0.918• k = 0.01836 W/m-Ka) Is the flow laminar or turbulent? Is the flow hydrodynamically and thermally fully developed?(circle your answer below and provide justification. • Laminar vs. Turbulent• Hydrodynamically developing vs. developed• Thermally developing vs. fully developedJustification: b) Calculate convective heat transfer coefficient (h). c) Calculate the exit temperature of the shale gas. d) Are the shale gas properties…arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





