
Concept explainers
a. Which compounds are Bronsted-Lowry acids:
b. Which compounds are Bronsted-Lowry bases:
c. Classify each compound as an acid, a base, or both:
(a)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acids are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry acids are those species which donate proton. They are also known as proton donor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry acids can be zero or negative or positive.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acid is
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-Lowry acids donate proton.
Hydrogen bromide contain hydrogen atom. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Ammonia contains a lone pair of electrons which can be easily donated to form a new bond. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry base.
No hydrogen is present in the
In the given set of compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acid is
(b)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-Lowry bases are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which can accept a proton. The Base must contain a lone pair or pi bond that could be easily donated to an acid to form a new bond. Bronsted-Lowry base are proton acceptor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry base can be zero and negative.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-lowry bases contain lone pair of electrons or pi bond. In
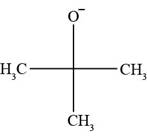
Figure 1
The molecule
![]()
Figure 2
There is neither a pi bond nor a negative charge present in
In the given set of compounds, Bronsted-Lowry acids are
(c)
Interpretation: Among the given compounds, Bronsted-lowry bases are to be identified.
Concept introduction: Bronsted-Lowry bases are those species which can accept a proton. The Base must contain a lone pair or pi bond that could be easily donated to an acid to form a new bond. Bronsted-Lowry base are proton acceptor. The net charge on Bronsted-Lowry base can be zero and negative.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Explanation of Solution
All Bronsted-Lowry bases contain lone pairs of electrons or pi bond. Bronsted-Lowry acids contain proton.
Ethanol contains hydrogen atom and lone pairs on oxygen atom. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry base as well as a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
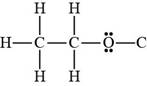
Figure 3
Propane contains only hydrogen atoms. Hence, it is a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
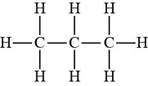
Figure 4
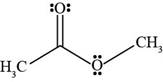
Figure 5
The Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The electrons flow from the electron-rich atoms of the nucleophile to the electrons poor atoms of the alkyl halide. Identify the electron rich in the nucleophile. Enter the element symbol only, do not include any changes.arrow_forwardHello, I am doing a court case analysis in my Analytical Chemistry course. The case is about a dog napping and my role is prosecution of the defendant. I am tasked in the Area of Expertise in Neutron Activation and Isotopic Analysis. Attached is the following case study reading of my area of expertise! The landscaping stone was not particularly distinctive in its decoration but matched both the color and pattern of the Fluential’s landscaping stone as well as the stone in the back of the recovered vehicle. Further analysis of the stone was done using a technique called instrumental neutron activation analysis. (Proceed to Neutron Activation data) Photo Notes: Landscaping stone recovered in vehicle. Stone at Fluential’s home is similar inappearance. Finally, the white paint on the brick was analyzed using stable isotope analysis. The brick recovered at the scene had smeared white paint on it. A couple of pieces of brick in the back of the car had white paint on them. They…arrow_forwardCite the stability criteria of an enamine..arrow_forward
- What would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forward
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





