
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100581557
Author: Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.1OQ
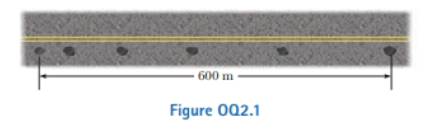
One drop of oil falls straight down onto the road from the engine of a moving car every 5 s. Figure OQ2.1 shows the pattern of the drops left behind on the pavement. What is the average speed of the car over tins section of its motion? (a) 20 m/s (b) 24 m/s (c) .30 m/s (d) 100 m/s (e) 120 m/s
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Amel goes for a walk with a speed of 3kph. After 30 minutes of walk, his wife follows him. Walking 3.25 km for the first hour, 3.75 km for the second hour, 4 km for the third hour and so on maintaining a speed of .25 km per hour. How many hours does the wife take to catch up to her husband?
The velocity of a particle is given by the function v(t)=t^2-7t+1027 , where the velocity is measured in meters per second. Determine the total displacement of the particle and the total distance travelled by the particle in the first ten seconds of its travel. Give exact answers, and provide units on your final answer.
A Honda Civic drives for 1000 meters at a speed of 5.0 m/s. It then speeds up and travels another 1000 meters at 100 m/s.
What is the average speed of the car?
O 9.5 m/s
O 53 m/s^2
O 210 s
O 0 m/s
Question ?
10
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 2 - Are officers in the highway patrol more interested...Ch. 2 - Make a velocitytime graph for the car in Figure...Ch. 2 - If a car is traveling eastward and slowing down,...Ch. 2 - Which one of the following statements is true? (a)...Ch. 2 - In Figure 2.12, match each vxt graph on the top...Ch. 2 - Consider the following choices: (a) increases, (b)...Ch. 2 - One drop of oil falls straight down onto the road...Ch. 2 - A racing car starts from rest at t = 0 and reaches...Ch. 2 - A juggler throws a bowling pin straight up in the...Ch. 2 - When applying the equations of kinematics for an...
Ch. 2 - A cannon shell is fired straight up from the...Ch. 2 - An arrow is shot straight up in the air at an...Ch. 2 - When the pilot reverses the propeller in a boat...Ch. 2 - A rock is thrown downward from the top of a...Ch. 2 - A skateboarder starts from rest and moves down a...Ch. 2 - Oil another planet, a marble is released from rest...Ch. 2 - As an object moves along the .v axis, many...Ch. 2 - A pebble is dropped from rest from the lop of a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - Von drop a ball from a window located on an upper...Ch. 2 - A pebble is released from rest at a certain height...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which...Ch. 2 - A hard rubber ball, not affected by air resistance...Ch. 2 - Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b). and (c)...Ch. 2 - If the average velocity of an object is zero in...Ch. 2 - Try the following experiment away from traffic:...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.3CQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.4CQCh. 2 - Prob. 2.5CQCh. 2 - You throw a ball vertically upward so that it...Ch. 2 - (a) Can (he equations of kinematics (Eqs....Ch. 2 - (a) Can the velocity of an object at an instant of...Ch. 2 - Two cars are moving in the same direction in...Ch. 2 - Section 2.1 Position, Velocity, and Speed The...Ch. 2 - The speed of a nerve impulse in the human body is...Ch. 2 - A prison walks first al a constant speed of 5.00...Ch. 2 - A particle moves according to the equation x =...Ch. 2 - The position of a pinewood derby car was observed...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along the x axis...Ch. 2 - A positiontime graph for a particle moving along...Ch. 2 - An athlete leaves one end of a pool of length L at...Ch. 2 - Find the instantaneous velocity of the particle...Ch. 2 - Review. The North American and European plates of...Ch. 2 - A hare and a tortoise compete in a race over a...Ch. 2 - A car travels along a straight line at a constant...Ch. 2 - A person takes a trip, driving with a constant...Ch. 2 - Review. A 50.0-g Super Ball traveling al 25.0 m/s...Ch. 2 - A velocity-time graph for an object moving along...Ch. 2 - A child rolls a marble on a bent track that is 100...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.9 shows a graph of vx versus t for the...Ch. 2 - (a) Use the data in Problem 3 to construct a...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from rest and accelerates as...Ch. 2 - An object moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A panicle mows along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - Draw motion diagrams for (a) an object moving to...Ch. 2 - Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b), and (c)...Ch. 2 - The minimum distance required to stop a car moving...Ch. 2 - An electron in a cathode-ray tube accelerates...Ch. 2 - A speedboat moving at 30.0 m/s approaches a...Ch. 2 - A parcel of air moving in a straight tube with a...Ch. 2 - A truck covers 40.0 m in 8.50 s while smoothly...Ch. 2 - An object moving with uniform acceleration has a...Ch. 2 - In Example 2.7, we investigated a jet landing on...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.31PCh. 2 - Solve Example 2.8 by a graphical method. On the...Ch. 2 - A truck on a straight road starts from rest,...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 2 - The driver of a car slants on the brakes when he...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.36PCh. 2 - A speedboat travels in a straight line and...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the x axis. Its position is...Ch. 2 - A glider of length moves through a stationary...Ch. 2 - A glider of length 12.4 cm moves on an air track...Ch. 2 - An object moves with constant acceleration 4.00...Ch. 2 - At t = 0, one toy car is set rolling on a straight...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.43 represents part of the performance...Ch. 2 - A hockey player is standing on his skates on a...Ch. 2 - In Chapter 9, we will define the center of mass of...Ch. 2 - An attacker at the base of a castle wall 3.65 m...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? Emily...Ch. 2 - A baseball is hit so that it travels straight...Ch. 2 - It is possible to shoot an arrow at a speed as...Ch. 2 - The height of a helicopter above the ground is...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.51PCh. 2 - A ball is thrown upward from the ground with an...Ch. 2 - A student throws a set of keys vertically upward...Ch. 2 - At time t = 0, a student throws a set of keys...Ch. 2 - A daring ranch hand sitting on a tree limb wishes...Ch. 2 - A package is dropped at time t = 0 from a...Ch. 2 - Automotive engineers refer to the time rate of...Ch. 2 - A student drives a moped along a straight road as...Ch. 2 - The speed of a bullet as it travels down the...Ch. 2 - A certain automobile manufacturer claims that its...Ch. 2 - The froghopper Philaenus spumarius is supposedly...Ch. 2 - An object is at x = 0 at t = 0 and moves along the...Ch. 2 - Ail inquisitive physics student and mountain...Ch. 2 - In Figure 2.11b, the area under the velocitytime...Ch. 2 - A ball starts from rest and accelerates at 0.5(H)...Ch. 2 - A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the...Ch. 2 - An elevator moves downward in a tall building at a...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 2 - The Acela is an electric train on the...Ch. 2 - Two objects move with initial velocity 8.00 m/s,...Ch. 2 - At t = 0, one athlete in a race running on a long,...Ch. 2 - A catapult launches a test rocket vertically...Ch. 2 - Kathy tests her new sports car by racing with...Ch. 2 - Two students are on a balcony a distance h above...Ch. 2 - Two objects, A and B, are connected by hinges to a...Ch. 2 - Astronauts on a distant planet toss a rock into...Ch. 2 - A motorist drives along a straight road at a...Ch. 2 - A commuter train travels between two downtown...Ch. 2 - Lisa rushes down onto a subway platform to find...Ch. 2 - A hard rubber ball, released at chest height,...Ch. 2 - A blue car of length 4.52 m is moving north on a...Ch. 2 - Review. As soon as a traffic light turns green, a...Ch. 2 - In a womens 100-m race, accelerating uniformly,...Ch. 2 - Two thin rods are fastened to the inside of a...Ch. 2 - A man drops a rock into a well, (a) The man hears...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
5.106 A 70-kg person rides in a 30-kg cart moving at 12 m/s at the top of a hill that is in the shape of an arc...
University Physics (14th Edition)
Can the observer shown see a star when it is located below the horizon? Why or why not?
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
7. (II) (a) What is the current in the element of an electric clothes dryer with a resistance of 8.6 ?when it i...
Physics: Principles with Applications
Is Earths inner core solid and the outer core liquid because the inner core is cooler than the outer core? Expl...
Conceptual Integrated Science
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- height h (cm) Time t1 (s) Time t2 (s) Mean time t (s) t² (s?) h/t? (m/s?) g (m/s²) 45 0.3021 0.3029 55 0.3351 0.3357 65 0.3640 0.3650 The average value 'g' from the above table is m/s2arrow_forwardQ1. a). A ball is thrown upwards into the air. Total time for the ball to move upwards to the peak and then return to the ground is (251.85) seconds. Find the height to which the ball rises before it reaches its peak. b). You drive a beat up truck along a straight road for 11 km at 60 km/h, at which point the truck runs out of gasoline and stops. Over the next (251.85) min, you walk another 5 km farther. What is your overall displacement from the beginning of drive to your arrival at the station? What is the time interval from the beginning of your drive to your travel at the station? What is your average velocity from beginning of your drive to your arrival at the station?arrow_forwardA student witnesses a flash of lightning and then t = 1.5 s later the student hears the associated clap of thunder.Sound travels at 343 m/s in the air. What distance from the student is the lightning strike, in meters? Light travels at 3.0 × 108 m/s in the air. How long, t1, in seconds did it take the light to reach the student's eyes after the lightning strike?arrow_forward
- A pumpkin is shot straight up with an initial speed of 5.9 m/s. What is the maximum height it can reach, in meters? Use g = 10 m/s2.Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forwardMario rides his motorcycle in going to school. He drives at an average speed of 30 kilometers per hour. The distance between his house and the school is 15 kilometers. Every time he sees his best friend Jessica walking on the road, he invites her for a ride and lowers his speed. On the other hand, he increases his speed when he wakes up late for school. a) If x represents the time it takes Mario to drive to school with the given distance of 15 kilometers, how will you represent the relationship of his speed (y) versus the time (x)?arrow_forwardAn object has an initial velocity v = 2.4i + 4.5j m/s. Over a period of time t = 2.9 s, its velocity becames v2 = 2.4i +35 m/s. The magnitude of the object's acceleration (in m/s?) is: a. 1.73 b. 0.52 с. 2.59 d. 3.07 e. 0.26arrow_forward
- Crash acceleration. A car crashes head on into a wall and stops, with the front collapsing by 0.500 m. The driver is firmly held to the seat by a seat belt and thus moves forward by 0.500 m during the crash. Assume that the acceleration is constant during the crash. What is the magnitude of the driver’s acceleration in g units if the initial speed of the car is (a) 35 mi/h and (b) 70 mi/h?arrow_forwardThe acceleration of an object (in m/s?) is given by the function a(t) = 4 sin(t). The initial velocity of the object is v(0) = - 5 m/s. Round your answers to four decimal places. a) Find an equation v(t) for the object velocity. v(t) = b) Find the object's displacement (in meters) from time 0 to time 3. meters c) Find the total distance traveled by the object from time 0 to time 3. metersarrow_forwardThe velocity of a rat traveling on a straight line is v(s)=1/(s+1), where the velocity is in meters per second and s is in meters. the rat travels 10 meters from s=0 to s=10m. Assume s=0 when t=0. 1. The total time it took for the rat to reach s=10m is ____s. 2. The expression for the position as a function of time is s(t)=_____. 3. The absolute maximum (maximum of absolute values) acceleration of the rat during the 10-meter trip is ____ m/s^2. Please help solve these questions, the solutions are given below I'm just not sure how to solve it. (Use paper sheet ,Not Typewritten) The solutions are: 1) 110 2)(sqrt(t+0.25))-0.5 3)1.00arrow_forward
- A runner is moving with a speed of 2.68[m/s]. How long will it take the runner to complete a 5.0[km] race? Express your answer in seconds. Ignore the time it takes to reach this speed, and assume the runner is always at this speed.arrow_forward-L.1971+38.67 Time (in seconds) The driver of a vehicle applies the brakes, softly at first, then harder, coming to a complete stop after 7 sec. The velocity as a function of time is modeled by the function v(t) = -1.197t² + 58.67,. where v is in feet per second, t is in seconds and 0sis 7. How far did the vehicle travel while the driver was braking? Velocity (in feet per second)arrow_forwardSlowing Down: The speed of an object moving through a viscous fluid is given byU(1) = A. c-br(a) If the numerical value of A (in SI units) is 5.20 and the numerical value of b (in SIunits) is 1.19, then what is the initial acceleration of the particle, at time / = 0?(b) How far does the particle move in the first 3.00 s?You may ignore gravity. The particle has the same density as the fluid.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY