
Concept explainers
Draw a “formula” for each of the following molecules using circular symbols of your choice to represent atoms:
a. A diatomic molecule of an element
b. A diatomic molecule of a compound
c. A triatomic molecule of an element
d. A molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element
(a)
Interpretation:
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
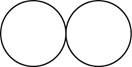
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of an element is a diatomic which means that the compound consists of two atoms with similar identity. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering a diatomic molecule of an element that is chlorine gas. The chemical formula of chlorine gas is
Therefore, the formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.

Figure 1
In the given figure, white circles represent the chlorine atoms.
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
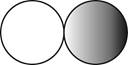
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of a compound is diatomic which means that the compound consists of two different atoms. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is hydrogen fluoride. The chemical formula of hydrogen fluoride is
Therefore, the formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
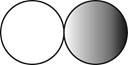
Figure 2
In the given figure, grey circle represent the fluorine atom, whereas white circle represent the hydrogen atoms.
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
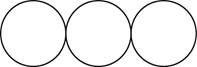
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of an element is a triatomic which means that the compound consists of three atoms with similar identity. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is ozone. The chemical formula of ozone is
Therefore, the formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.

Figure 3
In the given diagram, white circles represent oxygen atoms.
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
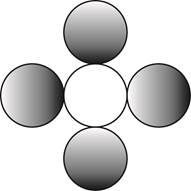
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule contains one atom of one element and four atoms of another element. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is carbon tetrachloride. The chemical formula of carbon tetrachloride is
Therefore, the formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
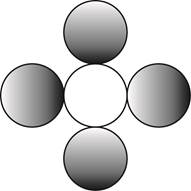
Figure 4
In the given diagram, white circle represent carbon atom, whereas grey circle represent chlorine atoms.
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Physical Science
Organic Chemistry
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
- Drawing of 3-fluro-2methylphenolarrow_forwardWhich compound(s) will be fully deprotonated (>99%) by reaction with one molar equivalent of sodium hydroxide? I, II, III I, || I, III I only II, III SH | H3C-C=C-H || III NH2arrow_forwardWill NBS (and heat or light) work for this reaction, or do we have to use Br2?arrow_forward
- HAND DRAWarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: Some important notes: Δ CN ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. ONO reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardThe following product was made from diethyl ketone and what other reagent(s)? £ HO 10 2-pentyne 1-butyne and NaNH2 ☐ 1-propanol ☐ pyridine butanal ☐ pentanoatearrow_forward
- Which pair of reagents will form the given product? OH X + Y a. CH3 b. CH2CH3 ༧་་ C. CH3- CH2CH3 d.o6.(རི॰ e. CH3 OCH2CH3 -MgBr f. CH3-MgBr g. CH3CH2-MgBr -C-CH3 CH2CH3arrow_forwardQuestion 3 What best describes the product of the following reaction? 1. CH3CH2MgBr (2 eq) 2. H a new stereocenter will not be formed a new stereocenter will be formed an alkyl halide will result an alkane will result an aromatic compound will result 1 ptsarrow_forwardRank the following from most to least reactive toward nucleophilic attack. 1. [Select] [Select] 2. Acyl halide Aldehyde 3. Carboxylate ion 4. Carboxylic acid Ketone 5. [Select]arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





