
(a)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of tungsten should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Answer to Problem 2.10P
Electronic configuration of tungsten is:
Explanation of Solution
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the sub-shell. The specific region of space in which the movements of electrons are confined is said to be shells which are divided into sub-shells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these sub-shells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these sub-shells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, sub-shell is:
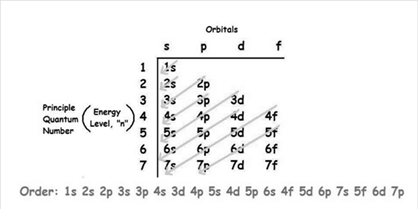
As the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom so,
The atomic number of tungsten is = 74
The electronic configuration of tungsten is:
(b)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of cobalt should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Answer to Problem 2.10P
Electronic configuration of cobalt is:
Explanation of Solution
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the sub-shell. The specific region of space in which the movements of electrons are confined is said to be shells which are divided into sub-shells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these sub-shells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these sub-shells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, sub-shell is:
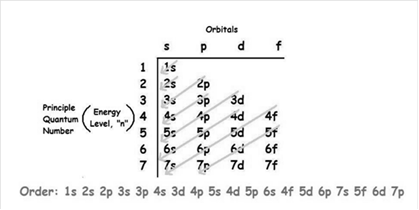
As the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom so,
The atomic number of cobalt is = 27
The electronic configuration of cobalt is:
(c)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of zirconium should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Answer to Problem 2.10P
The electronic configuration of zirconium is:
Explanation of Solution
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the sub-shell. The specific region of space in which the movements of electrons are confined is said to be shells which are divided into sub-shells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these sub-shells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these sub-shells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, sub-shell is:
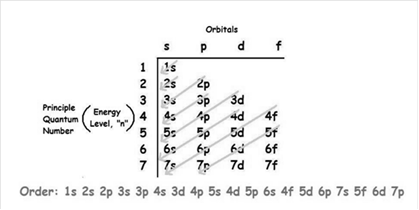
As the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom so,
The atomic number of zirconium is = 40
The electronic configuration of zirconium is;
(d)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of uranium should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Answer to Problem 2.10P
Electronic configuration of uranium is:
Explanation of Solution
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the sub-shell. The specific region of space in which the movements of electrons are confined is said to be shells which are divided into sub-shells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these sub-shells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these sub-shells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, sub-shell is:
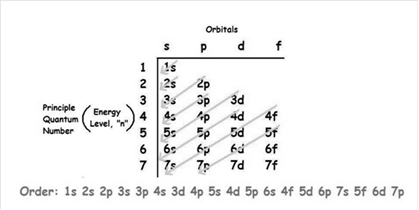
As the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom so,
The electronic configuration of uranium is:
(e)
The electronic configuration of aluminum should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom in an increasing order of energy levels and this description of orbitals of atom occupied by electrons is known as electronic configuration.
Answer to Problem 2.10P
Electronic configuration of aluminum is:
Explanation of Solution
Electrons are distributed in the orbitals of the sub-shell. The specific region of space in which the movements of electrons are confined is said to be shells which are divided into sub-shells and are s-, p-, d-, and f-. Among these sub-shells, the electrons are grouped as orbitals.
The numbers of electrons that these sub-shells can hold are:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, sub-shell is:
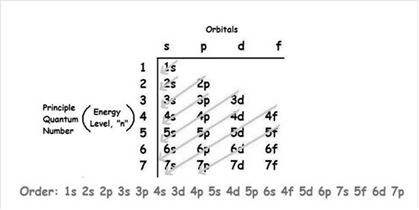
As the number of electrons for a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of an atom so,
The atomic number of aluminum is = 13
The electronic configuration of aluminum is:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- 1. The figure shows a car jack to support 400kg (W=400kg). In the drawing, the angle (0) varies between 15 and 70 °. The links are machined from AISI 1020 hot-rolled steel bars with a minimum yield strength of 380MPa. Each link consists of two bars, one on each side of the central bearings. The bars are 300mm in length (/) and 25 mm in width (w). The pinned ends have the buckling constant (C) of 1.4 for out of plane buckling. The design factor (nd) is 2.5. (1) Find the thickness (t) of the bars and the factor of safety (n). (2) Check if the bar is an Euler beam. Darrow_forwardcan you do specific control loop for dc including reboiler and condenserarrow_forward- A 3-phase, 4-wire distributor supplies a balanced voltage of 400/230 V to a load consisting of 8 A at p.f. 0.7 lagging for R-phase, 10 A at p.f. 0-8 leading for Y phase and 12 A at unity p.f. for B phase. The resistance of each line conductor is 0.4 2. The reactance of neutral is 0.2 2. Calculate the neutral current, the supply voltage for R phase and draw the phasor diagram. The phase sequence is RYB.arrow_forward
- No AI WILL REJECTarrow_forwardCan you please do with hand calcs and answer the following: a Determine the global stiffness matrix (K) of the beam including indicating correct degrees-of freedom (dof) b i) Calculate vectors D and Q ii) Show partition and solve KD=Q for D iii) Calculate all reactions c BMD & max BM, deflected shape d i) Solve the problem using Strand7 (model) ii) Display the deflected shape and BMD e Comparisons of reactions + Max BM including commentsarrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forward
- I want to solve 13.2 using matlab please helparrow_forwarda) Show a possible trace of the OSPF algorithm for computing the routing table in Router 2 forthis network.b) Show the messages used by RIP to compute routing tables.arrow_forwardUNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE SAN ANTONIO ABAD DEL CUSCO PRIMER EXAMEN PARCIAL DE MECÁNICA DE FLUIDOS I ............ Cusco, 23 de setiembre de 2024 AP. Y NOMBRES: ........ 1.- Para el tanque de la figura: a) Calcule la profundidad de la hidrolina si la profundidad del agua es de 2.8 m y el medidor del fondo del tanque da una lectura de 52.3kPa. b) Calcule la profundidad del agua si la profundidad de la hidrolina es 6.90 m y el medidor de la parte inferior del tanque registra una lectura de 125.3 kPa. Hidrolina Sp=0.90 Abertura Agua sup suge to but amulor quit y 2.- Calcule la magnitud de la fuerza resultante sobre el área A-B y la ubicación del centro de presión. Señale la fuerza resultante sobre el área y dimensione su ubicación con claridad. 3.5 ft 12 in: Oil (38-0.93) 14 in 8 inarrow_forward
- using r language to answer question 4 Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forwardplease solve this problem and give me the correct answer step by steparrow_forwardplease solve this problem step by step and show the best way that can be explainedarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





