
While shopping online for AA batteries, Masoud found that he could order a pack of 8 batteries for
What is the domain and range of the relation?
Express the relation as a set of ordered pairs.
Express the relation as a mapping.
Express the relation as a graph.
(a)
The range and domain of a relation, where the relation is defined using number of batteries as input and price as output, with the data Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Answer to Problem 1RE
Solution:
The domain of the relation is
The range of the relation is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Explanation:
The relation is defined as the number of batteries as input and price as output.
The domain is a set of inputs for relation.
Here, the number of batteries is an input for relation.
Therefore, the domain is
The range is a set of outputs for relation.
Here, price is an output for relation.
Therefore, the range is
(b)
The relation as a set of order pairs, where the relation is defined using the number of batteries as input and price as output, with the data Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Answer to Problem 1RE
Solution:
The relation as set of order pairs is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Explanation:
A set of order pairs consists of input, number of batteries, as first coordinate and output, price, as second coordinate.
In the relation
Therefore, the relation as a set of order pairs is
(c)
The relation as mapping, where the relation is defined using the number of batteries as input and price as output, with the data Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Answer to Problem 1RE
Solution:
The mapping is given by
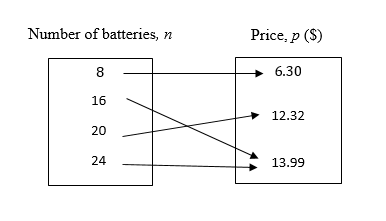
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Explanation:
For mapping, consider
Thus, the mapping is:

(d)
To graph: A scatter plot of a relation, where the relation is defined using the number of batteries as input and price as output, with the data Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Masoud could order a pack of 8 batteries at
Graph:
The scatter plot of given data is:
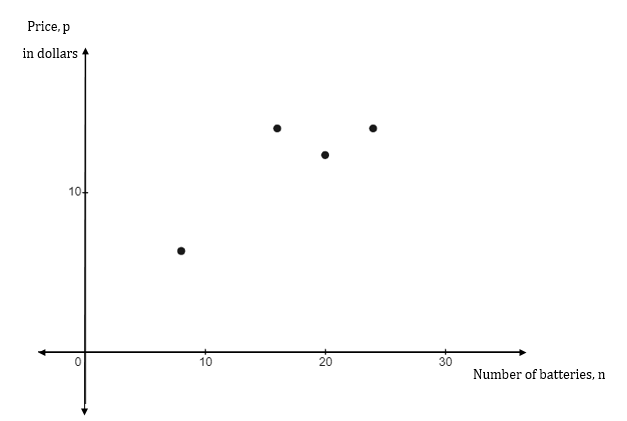
Interpretation:
The scatter plot represents thenumber of batteries as the independent variable and price in dollars as the dependent variable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mylab Math With Pearson Etext -- Standalone Access Card -- For Precalculus (11th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Mathematics for the Trades: A Guided Approach (11th Edition) (What's New in Trade Math)
Precalculus
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- A 20 foot ladder rests on level ground; its head (top) is against a vertical wall. The bottom of the ladder begins by being 12 feet from the wall but begins moving away at the rate of 0.1 feet per second. At what rate is the top of the ladder slipping down the wall? You may use a calculator.arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.4.1(root test) and 12.4.2(ratio test)arrow_forwarduse Integration by Parts to derive 12.6.1arrow_forward
- Explain the relationship between 12.3.6, (case A of 12.3.6) and 12.3.7arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forward
- use Corollary 12.6.2 and 12.6.3 to derive 12.6.4,12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.1(lim(n->infinite) and sigma of k=0 to n)arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.3 about alternating series. and explain the reason why (sigma k=1 to infinite)(-1)k+1/k = 1/1 - 1/2 + 1/3 - 1/4 + .... converges.arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt





