
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The names, three-letter abbreviations and one-letter abbreviations for the given structure of amino acids are needed to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing amino as well as a carboxylic group. The general molecular formula of an amino acid is as follows:
Here, R refers to different groups for different amino acids. If there is more than one amino group present in amino acid, it is considered as basic amino acid and if there is more than one carboxylic group present, then it is considered as an acidic amino acid.
Answer to Problem 1P
A: Proline, the three-letter abbreviation is Pro and a one-letter abbreviation is P.
B: Tyrosine, the three-letter abbreviation is Tyr and a one-letter abbreviation is Y.
C: Leucine, the three-letter abbreviation is Leu and a one-letter abbreviation is L.
D: Lysine, the three-letter abbreviation is Lys and a one-letter abbreviation is K.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of amino acids (A-D) are:
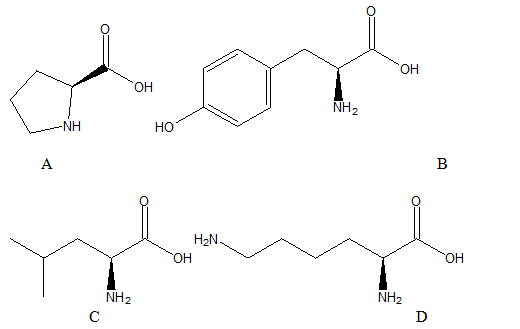
The amino acid in structure A is proline. It is one of the a-amino acids that is used by living organisms as the building blocks of the proteins. Its three-letter abbreviation is Pro, and one letter abbreviation is P.
Structure B represents a non-essential amino acid, tyrosine. In animals, it is synthesized from phenylalanine. It is also the precursor of epinephrine, thyroid hormones and melanin. Its three-letter abbreviation is Tyr, and one letter abbreviation is Y.
The structure C represents the amino acid Leucine which is obtained from the hydrolysis of most common proteins. It was discovered in 1819in muscle fiber and wool. Its three-letter abbreviation is Leu and the one-letter abbreviation is L.
The structure D represents the amino acid Lysine which is an essential amino acid for the nutrition of humans. Its three-letter abbreviation is Lys, and one letter abbreviation is K.
A: Proline, the three-letter abbreviation is Pro and a one-letter abbreviation is P.
B: Tyrosine, the three-letter abbreviation is Tyr and a one-letter abbreviation is Y.
C: Leucine, the three-letter abbreviation is Leu and a one-letter abbreviation is L.
D: Lysine, the three-letter abbreviation is Lys and a one-letter abbreviation is K.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
BIOCHEM-ACHIEVE(FIRST DAY DISCOUNTED)
- Calculate the standard change in Gibbs free energy, AGrxn, for the given reaction at 25.0 °C. Consult the table of thermodynamic properties for standard Gibbs free energy of formation values. NH,Cl(s) →NH; (aq) + C1 (aq) AGrxn -7.67 Correct Answer Determine the concentration of NH+ (aq) if the change in Gibbs free energy, AGrxn, for the reaction is -9.27 kJ/mol. 6.49 [NH+] Incorrect Answer kJ/mol Marrow_forwardWhat are some topics of interest that neurotoxicologists study? For example, toxin-induced seizures, brain death, and such along those lines?arrow_forwardCould you help me with the explanation of the answer to exercise 15, chapter 1 of Lehinger Question Nombramiento de estereoisómeros con dos carbonos quirales utilizando el sistema RS(R,R)El isómero del metilfenidato (Ritalin) se utiliza para tratar el trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad (TDAH).(S,S)El isómero es un antidepresivo. Identifique los dos carbonos quirales en la siguiente estructura. ¿Es este el(R,R)o el(S,S)¿isómero? Dibuja el otro isómero. Nombramiento de estereoisómeros con dos carbonos quirales utilizando el sistema RS(R,R)El isómero del metilfenidato (Ritalin) se utiliza para tratar el trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad (TDAH).(S,S)El isómero es un antidepresivo.arrow_forward
- The reaction A+B → C + D AG°' = -7.3 kcal/mol can be coupled with which of the following unfavorable reactions to drive it forward? A. EFG+HAG° = 5.6 kcal/mol. B. J+KZ+A AG° = 2.3 kcal/mol. C. P+RY+DAG° = 8.2 kcal/mol. D. C + T → V + W AG°' = -5.9 kcal/mol. E. AN→ Q+KAG°' = 4.3 kcal/mol.arrow_forwardWhat would be the toxicological endpoints for neurotoxicity?arrow_forwardWhat are "endpoints" in toxicology exactly? Please give an intuitive easy explanationarrow_forward
- Fura-2 Fluorescence (Arbitrary Unit) 4500 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 [Ca2+]=2970nM, 25°C [Ca2+] 2970nM, 4°C [Ca2+]=0.9nM, 25°C [Ca2+] = 0.9nM, 4°C 0 260 280 300 340 360 380 400 420 440 Wavelength (nm) ← < The figure on the LHS shows the excitation spectra of Fura-2 (Em = 510 nm) in 2 solutions with two different Ca2+ ion concentration as indicated. Except for temperature, the setting for excitation & signal acquisition was identical.< ப a) The unit in Y-axis is arbitrary (unspecified). Why? < < b) Compare & contrast the excitation wavelength of the Isosbestic Point of Fura-2 at 25 °C & 4 °C. Give a possible reason for the discrepancy. < c) The fluorescence intensity at 25 °C & 4 °C are different. Explain why with the concept of electronic configuration. <arrow_forwarddraw in the structure of each amino acid (as L-amino acids) using the Fischer projection style. an example has been included. Draw the structure for glycine, alanine, valine, isoleucine, methionine, proline, phenylalanine, tryptophan, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, lysine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine, tyrosine, cysteinearrow_forwarddraw in the structure of each amino acid (as L-amino acids) using the Fischer projection style. an example has been includedarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





