
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285190907
Author: James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 17PC
Interpreting Income Tax Disclosures. The financial statements of ABC Corporation, a retail chain, reveal the information for income taxes shown in Exhibit 2.15.
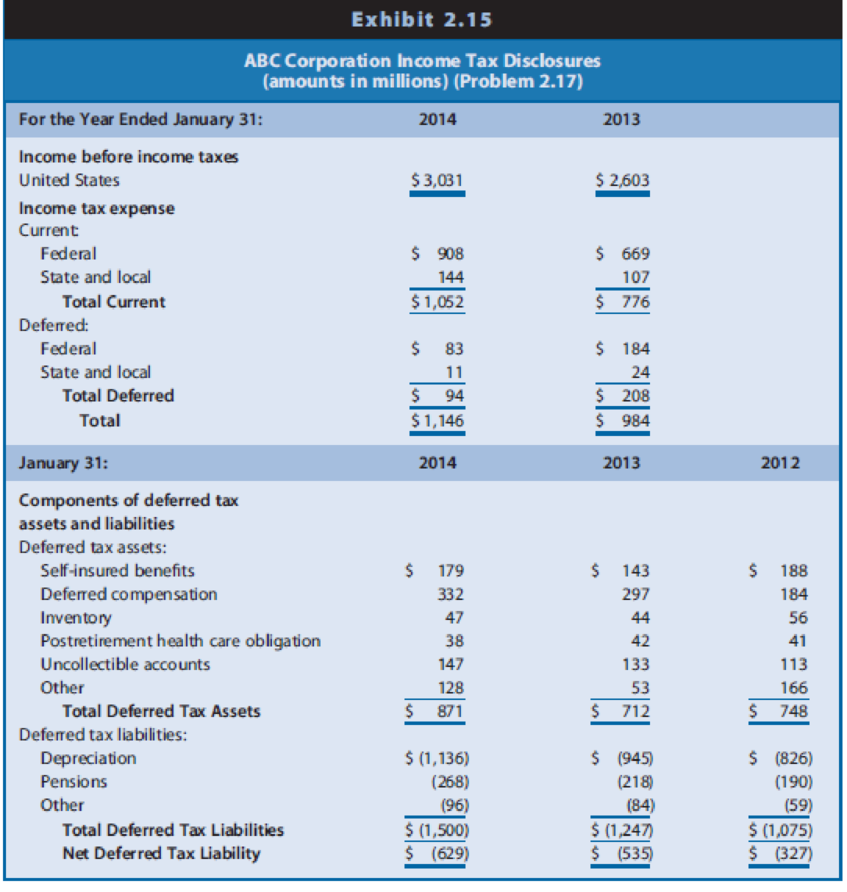
REQUIRED
- a. Assuming that ABC had no significant permanent differences between book income and taxable income, did income before taxes for financial reporting exceed or fall short of taxable income for 2013? Explain.
- b. Did income before taxes for financial reporting exceed or fall short of taxable income for 2014? Explain.
- c. Will the adjustment to net income for
deferred taxes to compute cash flow from operations in the statement of cash flows result in an addition or a subtraction for 2013? For 2014? - d. ABC does not contract with an insurance agency for property and liability insurance; instead, it self-insures. ABC recognizes an expense and a liability each year for financial reporting to reflect its average expected long-term property and liability losses. When it experiences an actual loss, it charges that loss against the liability. The income tax law permits self-insured firms to deduct such losses only in the year sustained. Why are deferred taxes related to self-insurance disclosed as a
deferred tax asset instead of adeferred tax liability ? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014. - e. ABC treats certain storage and other inventory costs as expenses in the year incurred for financial reporting but must include these in Inventory for tax reporting. Why are deferred taxes related to inventory disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014.
- f. Firms must recognize expenses related to postretirement health care and pension obligations as employees provide services, but claim an income tax deduction only when they make cash payments under the benefit plan. Why are deferred taxes related to health care obligation disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Why are deferred taxes related to pensions disclosed as a deferred tax liability? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for these deferred tax items between 2012 and 2014.
- g. Firms must recognize expenses related to uncollectible accounts when they recognize sales revenues, but claim an income tax deduction when they deem a particular customer’s accounts uncollectible. Why are deferred taxes related to this item disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014.
- h. ABC uses the straight-line
depreciation method for financial reporting and accelerated depredation methods for income tax purposes. Why are deferred taxes related to depreciation disclosed as a deferred tax liability? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax liability between 2012 and 2014.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Could you please help explain the follow-up interviews in a data collecting method?
How is to use the follow-up interviews in qualitative data collection methods?
Could the qualitative data collection methods can be used in the thematic analysis?
We often hear about the importance of financial statement analysis. Given the various statements prepared and all the information included therein, the question becomes which of the financial statements should get a closer review and why?
Explain what the basic financial statements are and what is the purpose of each statement.
Within the different statements, in your opinion what is/are the key areas of information to focus on and why? Be specific as to the importance of your selection.
Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
Ch. 2 - Prob. 1QECh. 2 - Asset Valuation and Income Recognition. Asset...Ch. 2 - Trade-Offs among Acceptable Accounting...Ch. 2 - Income Flows versus Cash Flows. The text states,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5QECh. 2 - Prob. 6QECh. 2 - Prob. 7QECh. 2 - Prob. 8QECh. 2 - Computation of Income Tax Expense. A firms income...Ch. 2 - Computation of Income Tax Expense. A firms income...
Ch. 2 - Costs to Be Included in Historical Cost Valuation....Ch. 2 - Effect of Valuation Method for Nonmonetary Asset...Ch. 2 - Prob. 13PCCh. 2 - Prob. 14PCCh. 2 - Prob. 15PCCh. 2 - Deferred Tax Assets. Components of the deferred...Ch. 2 - Interpreting Income Tax Disclosures. The financial...Ch. 2 - Interpreting Income Tax Disclosures. Prepaid Legal...Ch. 2 - Interpreting Income Tax Disclosures. The financial...Ch. 2 - Analyzing Transactions. Using the analytical...Ch. 2 - Prob. 21PCCh. 2 - Starbucks The financial statements of Starbucks...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1BICCh. 2 - Prob. 1CICCh. 2 - Prob. 1DICCh. 2 - Prob. 1EICCh. 2 - Prob. 1FICCh. 2 - Starbucks The financial statements of Starbucks...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Revision Questions for This Week Suppose you see the following regression table: earnings Coef. Std. Err. married 7737.006 265.0139 _cons 9058.677 210.3906 1. What are the 95 confidence intervals for (i) the intercept, (ii). the slope, rounded to the second decimal place? 2. Are any of the coefficients statistically significant at the 5% level of significance? Explain. 3. Return to the t-statistic example from earlier (below). Do either of the 95% confidence intervals contain zero? Should they? log(wage) = .284.092 educ· (.104) (.007)arrow_forwardKenji’s Tax Scenario Kenji is a young professional with taxable income of $138,000 as an advertising account executive. What is Kenji’s total tax liability? (Note: Round your answer to the nearest cent, if necessary.) What is Kenji’s top marginal tax rate? What is Kenji's average tax rate?arrow_forward1. A project manager is using the payback method to make the final decision on which project to undertake. The company has a 9% required rate of return and expects a 5% rate of inflation for the following five years. i. ii. What is the non-discounted payback of a project that has cash flows as shown in the table? What is the rate of return? (use equation given in class) Cash Outflow Cash inflow Net Flow Year 10 $500,000 0 1 12. * 0 $75,000 & $50,000 $150,000 3 $200,000 $350,000 4 0 $150,000 5 0 $750,000arrow_forward
- Problem 4. Consider the following balance sheet for Watchover Savings Incorporated (in millions): Assets Liabilities and Equity Floating-rate mortgages (currently 12% per annum) Now deposits (currently 8% per $ 82 annum) $ 116 30-year fixed-rate loans (currently 9% per annum) 5-year time deposits (currently 8% per 101 annum) 29 Equity 38 $ 183 Total $ 183 Total a. What is Watchover's expected net interest income at year-end? b. What will be the net interest income at year-end if interest rates rise by 3 percent? c. Using the one-year cumulative repricing gap model, what is the change in the expected net interest income for a 3 percent increase in interest rates?arrow_forwardYou are given the following information for Frankenson Pizza Company: Sales = $72,000; Costs = $32,300; Addition to retained earnings = $6,500; Dividends paid = $2,220; Interest expense = $5,200; Tax rate = 23 percent. Calculate the depreciation expense. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.arrow_forwardAssume coupons are paid annually. Here are the prices of three bonds with 10-year maturities. Assume face value is $100. Bond Coupon (%) Price (%) 2 4 8 81.62 98.39 133.42 a. What is the yield to maturity of each bond? b. What is the duration of each bond? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B What is the yield to maturity of each bond? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Bond Coupon (%) YTM 2 % 4 8 % % Required A Required R Required B What is the duration of each bond? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Bond Coupon (%) Duration 2 years 4 years 8 yearsarrow_forward
- Two building owners - Alice and Bob - each own a building worth $1,000,000. They are considering forming a mutual insurance pool. Based on historical data, there are three possible fire damage scenarios for each building in a given year: No damage: 85% probability Partial damage: 12% probability, with repair costs of $200,000 Total loss: 3% probability, with a cost of $1,000,000 Calculate the standard deviation of the loss of each owner with pooling (2 buildings together)arrow_forwardCritically evaluate the usefulness of Net Present Value as an investment appraisal.arrow_forwardSales are $2.90 million, cost of goods sold is $590,000, depreciation expense is $148,000, other operating expenses are $298,000, addition to retained earnings is $1,126,625, dividends per share are $1, tax rate is 21 percent, and number of shares of common stock outstanding is 88,000. LaTonya's Flop Shops has no preferred stock outstanding. Use the above information to calculate the times interest earned ratio for LaTonya's Flop Shops, Incorporated. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Interest earned timesarrow_forward
- Two building owners - Alice and Bob - each own a building worth $1,000,000. They are considering forming a mutual insurance pool. Based on historical data, there are three possible fire damage scenarios for each building in a given year: No damage: 85% probability Partial damage: 12% probability, with repair costs of $200,000 Total loss: 3% probability, with a cost of $1,000,000 Calculate the standard deviationarrow_forwardWhat is the role of the researcher, population and sampling, and data collection, could you help explain each one of them? How to start working on the population structures essential to research? What are the structured ways in which to present key research elements?arrow_forwardCould you please help explain the Qualitative Research Data Analysis? What is the Coding, and Interrater Reliability? How do they work and when we use them?What are the description of populations and Samples, please help to explain them.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...
Finance
ISBN:9781285190907
Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chapter 19 Accounting for Income Taxes Part 1; Author: Vicki Stewart;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FMjwcdZhLoE;License: Standard Youtube License