
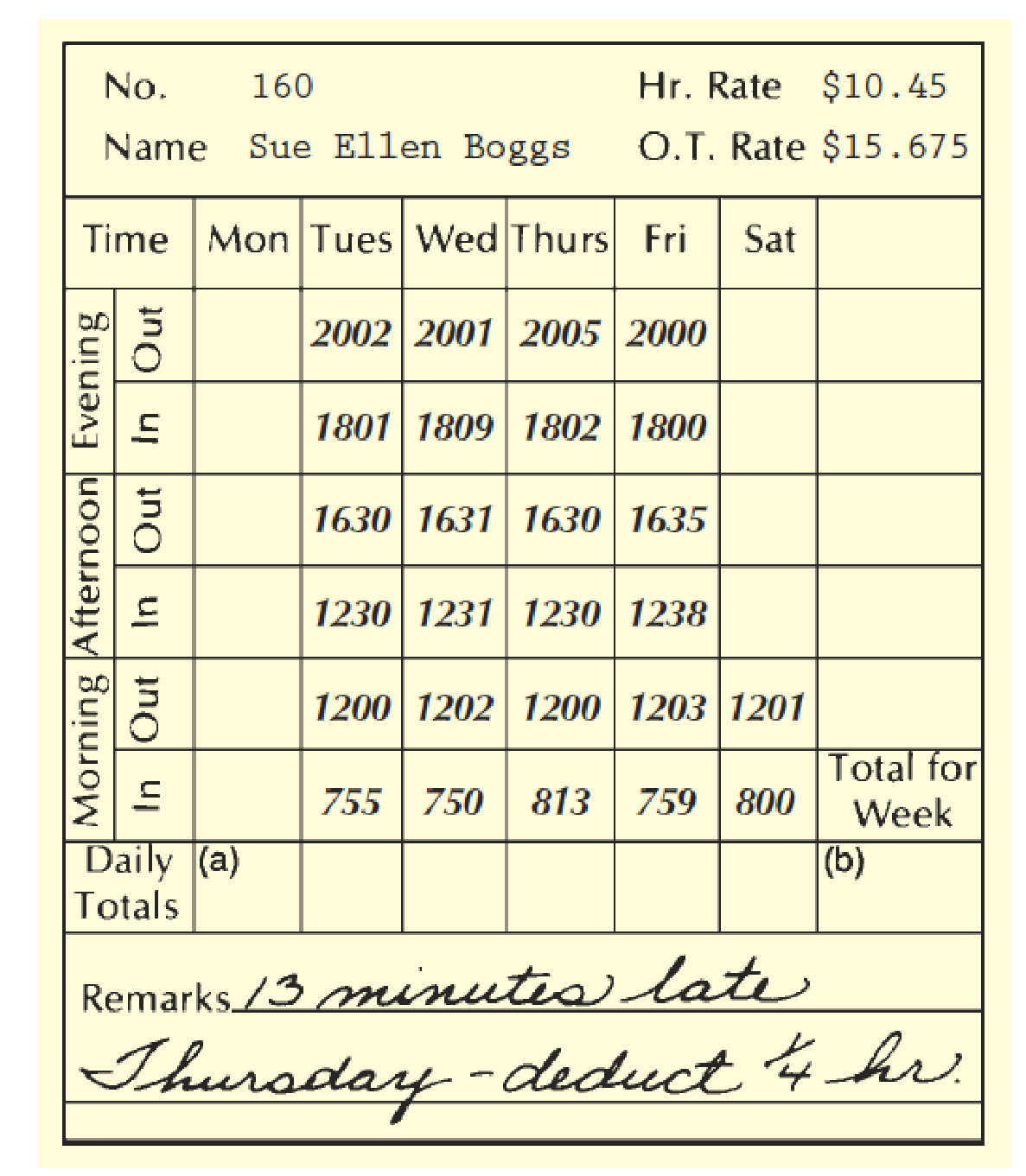
Potts, Inc., recently converted from a 5-day, 40-hour workweek to a 4-day, 40-hour workweek, with overtime continuing to be paid at one and one-half times the regular hourly rate for all hours worked beyond 40 in the week. In this company, time is recorded under the continental system, as shown on the time card on the following page.
Sue Ellen Boggs is part of the Group B employees whose regular workweek is Tuesday through Friday. The working hours each day are 800 to 1200; 1230 to 1630; and 1800 to 2000. The company disregards any time before 800, between 1200 and 1230, and between 1630 and 1800, and permits employees to ring in up to 10 minutes late before any deduction is made for tardiness. Deductions are made to the nearest ¼ of an hour for workers who are more than 10 minutes late in ringing in.
Refer to the time card and compute:
- a. The daily total hours .......................................................................... ___________
- b. The total hours for the week ............................................................... ___________
- c. The regular weekly earnings ................................................................ $___________
- d. The overtime earnings (company rounds O.T. rate to 3 decimal places) ___________
- e. The total weekly earnings ..................................................................... $__________
a.
Calculate the daily total hours for Employee S.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the daily total hours for Employee S.
| Tuesday | ||
| Session | Time | Hours worked |
| Morning | 755 to 1200 (see Note 1) | 4hours |
| Afternoon | 1230 to 1630 | 4 hours |
| Evening | 1801 to 2002 | 2hours, 1 minute |
| Total hours worked | 10 hours, 1 minute (rounded to 10 hours) | |
Table (1)
Note 1: In the morning session, Employee S worked from 755 to 1200. The 5 minutes he worked before 800 are forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
| Wednesday | ||
| Session | Time | Hours worked |
| Morning | 750 to 1202 (see Note 1) | 4hours |
| Afternoon | 1231 to 1631 (Note 2) | 3hours, 59 minutes |
| Evening | 1809 to 2001 | 1hour, 52 minutes |
| Total hours worked | 9 hours, 53 minutes (rounded to 10 hours) | |
Table (2)
Note 1: In the morning session, Employee S worked from 750 to 1202. He worked for 10 minutes before 800, and 2 minutes after 1200. The time before 800 and the time after 1200 are forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
Note 2: In the afternoon session, he worked from 1231 to 1631. He worked for 1 minute after 1630 which is forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
| Thursday | ||
| Session | Time | Hours worked |
| Morning | 813 to 1200 (see Note 1) | 3 hours, 32 minutes |
| Afternoon | 1230 to 1630 | 4 hours |
| Evening | 1802 to 2005 | 2 hours, 3 minutes |
| Total hours worked | 9 hours 35 minutes (rounded to 9.45 hours) | |
Table (3)
Note 1: In the morning session, Employee S worked from 813 to 1200. That means, he came 13 minutes late. So, as per the provisions, the company will deduct
| Friday | ||
| Session | Time | Hours worked |
| Morning | 759 to 1203 (see Note 1) | 3 hours, 59 minutes |
| Afternoon | 1238 to 1635 (see Note 2) | 3 hours, 52 minutes |
| Evening | 1800 to 2000 | 2 hours |
| Total hours worked | 9 hours, 51 minutes (rounded to 10 hours) | |
Table (4)
Note 1: In the morning session, Employee S worked from 759 to 1203. He worked for 1 minute before 800 and 3 minutes after 1200. The time before 800 and the time after 1200 are forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
Note 2: In the afternoon session, he worked from 1238 to 1635. He worked for 5 minutes after 1630. The time after 1630 is considered as forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
| Saturday | ||
| Session | Time | Hours worked |
| Morning | 800 to 1201 (see Note 1) | 4 hours |
| Afternoon | ||
| Evening | ||
| Total hours worked | 4 hours | |
Table (5)
Note 1: In the morning session, Employee S worked from 800 to 1201. He worked for 1 minute after 1200 which is forbidden time, and will not be considered as working hour.
b.
Calculate the total number of hours worked for the week by Employee S.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total number of hours worked for the week by Employee S.
Hence, the total number of hours worked for the week by Employee S is 43 hours 45 minutes.
c.
Calculate the regular weekly earnings for Employee S.
Explanation of Solution
Regular earnings: Generally, employees in a firm work in pre-determined hours (40 hours) and get paid accordingly. The amount of earnings that is calculated based predetermined hours is called as regular earnings of an employee.
Calculate the regular weekly earnings for Employee S.
Hence, the regular weekly earnings for Employee S is $418.
d.
Calculate the overtime earnings for Employee S.
Explanation of Solution
Overtime Earnings: If an employee works more than the stipulated working hours (more than 40 hours) of the employment then, the employee is mandated to get paid one and a half times more than the normal working pay. This one and half times can be termed as overtime premium or earnings.
Calculate the overtime earnings for Employee S.
Step 1: Calculate the number of overtime hours worked.
Step 2: Calculate the overtime earnings:
Hence, the overtime earnings for Employee S is $58.78.
e.
Calculate the total weekly earnings for Employee S.
Explanation of Solution
Total Earnings: It is the amount of employee’s gross earnings during a period. It includes regular earnings plus overtime earnings or any bonus or commission if applicable.
Calculate the total weekly earnings for Employee S.
Hence, the total weekly earnings for Employee S is $476.78.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
PAYROLL ACCT.,2019 ED.(LL)-TEXT
- Please My problem with accountingarrow_forwardRick Industries reported beginning total assets of $18,500,000 and ending total assets of $21,700,000 for the year 2023. The company's asset turnover ratio was 2.1 times. Based on this information, what was the net sales for the year 2023?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forward

 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning

