
Concept explainers
(a)
To show:The speed of a sky diver, whose acceleration is given by the equation
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equation for the acceleration
The expressions for the terminal speed
The speed of the sky diver at time
Calculation:
Rewrite equation (1) using the expression for acceleration
Rearrange the above equation as follows:
Integrate both sides of the equation.
Therefore,
Evaluate the integral
Let
Therefore,
Rewrite equation (5) as shown:
The expression
Therefore, equation (7) takes the form,
Use the identity,
Hence write equation (8) as,
Therefore, equation (4) can be written as ,
Substitute the value of
Apply the initial conditions of the sky diver
Therefore, equation (10) can be written as,
Therefore,
From equations (2)
Therefore, equation (12) can be written as,
Hence,
Conclusion:
Thus, it is proved that the speed of a sky diver, whose acceleration is given by the equation
(b)
To Find:The fraction of the terminal speed is the speed of the sky diver at time
(b)
Answer to Problem 119P
At time
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equation for the speed of the sky diver
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, at time
(c)
To graph:
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equation for the speed of the sky diver
Calculation:
In a spread sheet, calculate the values of
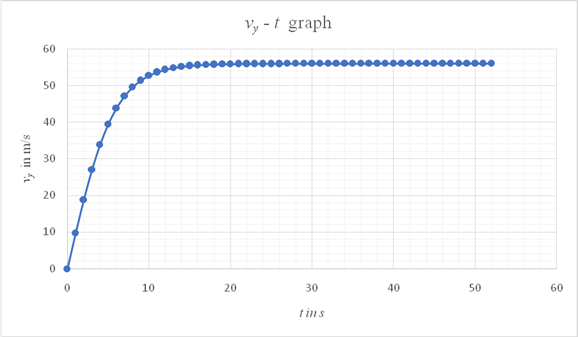
Conclusion:
Thus, it can be seen from the graph that the sky diver attains the terminal velocity at around 20 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





