
Concept explainers
a) Bromoacetone
Interpretation:
The structure for bromoacetone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To show:
The structure for bromoacetone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of bromoacetone is
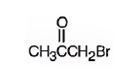
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with three carbon straight chain with a bromine atom attached to C1.
The structure of bromoacetone is

b) (S)-2-Hydroxypropanal
Interpretation:
The structure for (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To show:
The structure for (S)-2-hydroxypropanal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is
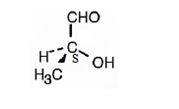
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is an aldehyde with three carbon straight chain with a hydroxyl group attached to C2. The molecule is chiral. The three groups, -OH(first highest priority), -CHO (second highest priority) and -CH3(third highest priority) are arranged anticlockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has S stereochemistry.
The structure of (S)-2-hydroxypropanal is

c) 2-Methyl-3-heptanone
Interpretation:
The structure for 2-methyl-3-heptanone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 2-methyl-3-heptanone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 2-methyl-3-heptanone is
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with seven carbon straight chain having the keto group at position three and a methyl group attached to C2.
The structure of 2-methyl-3-heptanone is
d) (2S,3R)-2,3,4-Trihydroxybutanal
Interpretation:
The structure for (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is
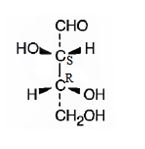
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is an aldehyde with four carbon straight chain and has three hydroxyl groups attached to C2, C3 and C4.
The molecule is chiral. The C2 is attached to the three groups, -OH(first highest priority), -CHO (second highest priority) and –C3 (third highest priority) arranged anticlockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has S stereochemistry.
The C3 is attached to the three groups, -OH(first highest priority), –C2 (second highest priority) and –CH2OH--(third highest priority) arranged clockwise when viewed from the side away from H (fourth highest priority). Hence it has R stereochemistry.
The structure of (2S,3R)-2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is

e) 2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-3-pentanone
Interpretation:
The structure for 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-3-pentanone is
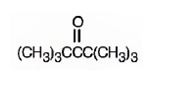
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone with five carbon straight chain with a keto group at position three attached to four methyl groups, two on C2 and other two on C4.
The structure of 2,2,4,4-Tetramethyl-3-pentanone is
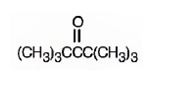
f) 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one
Interpretation:
The structure for 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is
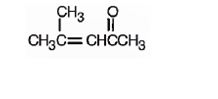
Explanation of Solution
The name indicates that the compound is a ketone containing a five carbon straight chain, having a keto group at position two and a double bond between C3 and C4 with a methyl group on C4.
The structure of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one is

g) Butanedial
Interpretation:
The structure for butanedial is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for butanedial.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of butanedial is
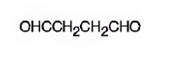
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it has a four carbon straight chain with two aldehyde groups at both ends.
The structure of butanedial is

h) 3-Phenyl-2-propenal
Interpretation:
The structure for 3-phenyl-2-propenal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –al. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the -CHO group and the –CHO group is numbered as carbon 1. For cyclic alcohols in which the –CHO group is directly attached to the ring, the suffix –carbaldehyde is used.
To show:
The structure for 3-phenyl-2-propenal.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 3-phenyl-2-propenal is
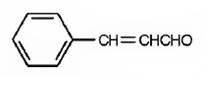
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that the compound is a three carbon aldehyde with a double bond between C2 & C3 and has a phenyl group attached to C3.
The structure of 3-phenyl-2-propenal is

i) 6,6-Dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone
Interpretation:
The structure for 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo.
To show:
The structure for 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is
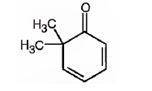
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it is a cyclic ketone with a cyclohexadiene ring containing two double bonds, one between C2 & C3 and other between C4 & C5. It also has two methyl groups on C6.
The structure of 6,6-dimethyl-2,4-cyclohexadienone is

j) p-Nitroacetophenone
Interpretation:
The structure for p-nitroacetophenone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ketones are named by replacing the terminal –e of the parent alkane with –one. The parent chain is the longest one that includes the ketone group and the numbering begins at the end nearer to the carbonyl carbon. If other functional groups are present the double bonded oxygen is considered as a substituent on the parent chain with the prefix –oxo. Some common names like acetophenone are retained by IUPAC.
To show:
The structure for p-nitroacetophenone.
Answer to Problem 54AP
The structure of p-nitroacetophenone is
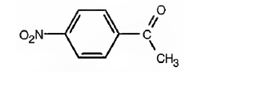
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound indicates that it contains an actyl and nitro groups attached to a benzene ring in para relationship.
The structure of p-nitroacetophenone is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- Correct each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the skeletal ("line") structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO Explanation Check NH, 2 W O :□ G ©2025 M unter Accessibilityarrow_forwardAn expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forward
- One liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forward
- Benzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


