
Biology
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260487947
Author: BROOKER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 19.4, Problem 1CS
Genetic Properties of Bacteria
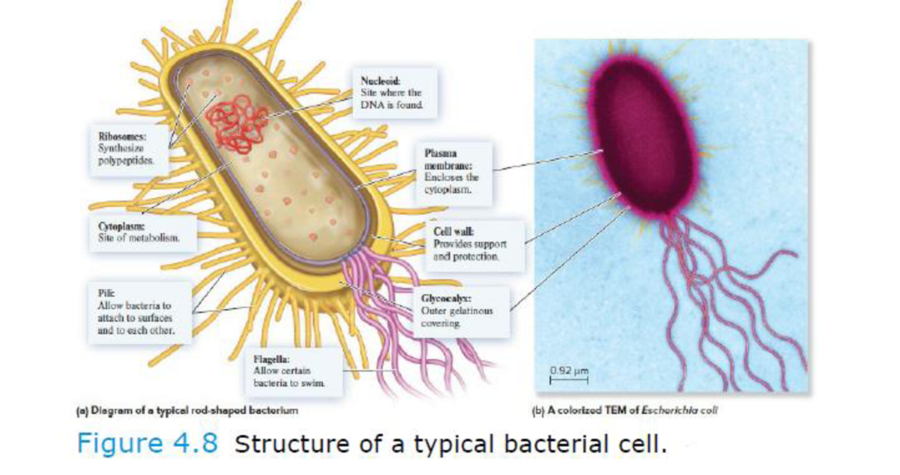
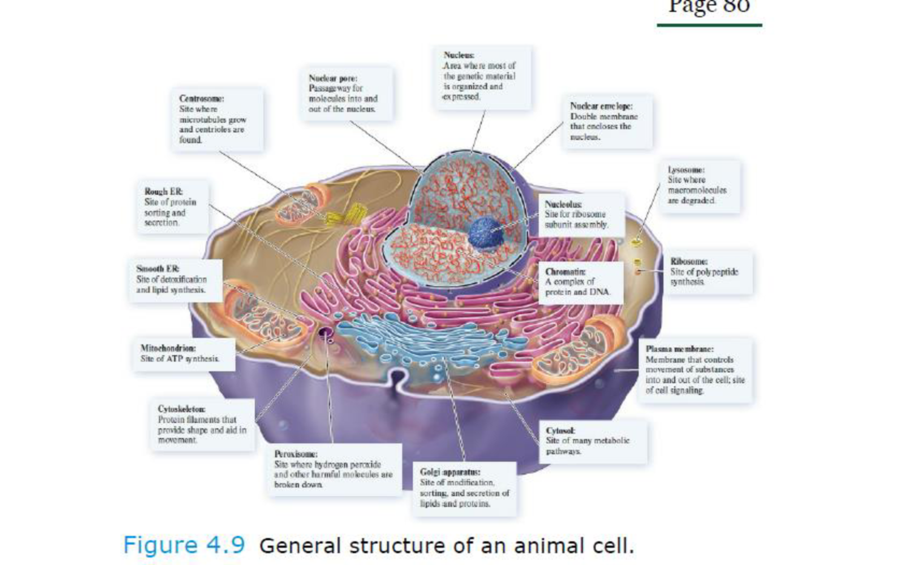
Core Skill: Connections Look back at Figures 4.8 and 4.9. How is a nucleoid different from a nucleus found in a eukaryotic cell?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Hi,
Please type the whole transcript correctly using comma and periods and as needed. The picture of a video on YouTube has been uploaded down.
HSCI701_D04_202520
Quizzes
Quiz: References, Quotations, and Formatting
Quiz: References, Quotations, and Formatting
If you transplant trunk neural crest into the cranial neural crest region of a developing embryo, will you see the donor tissue form cartilage?
Does the neural crest only give rise to two cells in the developing embryo, and is essential for lamprey to develop their jaw structure?
Does a multipotent neural crest cell that is receiving Wnt signals become a Chromaffin cell?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Biology
Ch. 19.1 - Prob. 1CSCh. 19.2 - Prob. 1CSCh. 19.2 - Viral Reproductive Cycles Concept Check: From the...Ch. 19.4 - Genetic Properties of Bacteria Core Skill:...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 1CCCh. 19.4 - Genetic Properties of Bacteria Concept Check:...Ch. 19.4 - Prob. 3CCCh. 19.5 - Prob. 1CCCh. 19.5 - Prob. 1EQCh. 19.5 - Prob. 2EQ
Ch. 19.5 - Gene Transfer Between Bacteria CoreSKILL The gene...Ch. 19.5 - Prob. 2CCCh. 19.5 - Gene Transfer Between Bacteria Core Skill:...Ch. 19.5 - Gene Transfer Between Bacteria Concept Check: Is...Ch. 19 - Prob. 1TYCh. 19 - The characteristics of viral genomes show many...Ch. 19 - During viral infection, attachment is usually...Ch. 19 - Prob. 4TYCh. 19 - Prob. 5TYCh. 19 - Prob. 6TYCh. 19 - Prob. 7TYCh. 19 - Prob. 8TYCh. 19 - Prob. 9TYCh. 19 - Prob. 10TYCh. 19 - How are viruses similar to living cells, and how...Ch. 19 - Prob. 2CQCh. 19 - Prob. 3CQCh. 19 - Prob. 1COQCh. 19 - Prob. 2COQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using quail and chick embryos, quail-specific antibody and fluorescent tissue-specific antibodies, design an experiment where you investigate the tissues the cranial neural crest can give rise to. What are four derivatives of the cranial neural crest that you expect to see in the resulting chimeric embryos?arrow_forwardDoes the neural crest have to undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition prior to migration through the developing embryo? Does the neural crest differentiate into different cell types based on their axial position along the anterior and posterior axis?arrow_forwardUsing quail and chicken embryos, what kind of experiment would you conduct to test if rib forming somites have their axial identity specified before segmentation? How do we know this phenotype is due to axial identity being specified before segmentation and not due to our experimental method?arrow_forward
- 8. Aerobic respiration of a 5 mM solution of tripeptide that is composed of the following three amino acids; alanine, leucine and isoleucine. Alanine breaks down to pyruvate, leucine breaks down to Acetyl-CoA and isoleucine breaks down to succinyl-CoA. Alanine NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Leucine Isoleucine Totals Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 4arrow_forward9. Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. fatty acids glycerol 18 carbons 12 carbons 0=arrow_forwardinfluences of environment on the phenotype.arrow_forward
- What is the difference between codominance and phenotypic plasticity?arrow_forwardExplain the differences between polygeny and pleiotropy,arrow_forwardIf using animals in medical experiments could save human lives, is it ethical to do so? In your answer, apply at least one ethical theory in support of your position.arrow_forward
- You aim to test the hypothesis that the Tbx4 and Tbx5 genes inhibit each other's expression during limb development. With access to chicken embryos and viruses capable of overexpressing Tbx4 and Tbx5, describe an experiment to investigate whether these genes suppress each other's expression in the limb buds. What results would you expect if they do repress each other? What results would you expect if they do not repress each other?arrow_forwardYou decide to delete Fgf4 and Fgf8 specifically in the limb bud. Explain why you would not knock out these genes in the entire embryo instead.arrow_forwardYou implant an FGF10-coated bead into the anterior flank of a chicken embryo, directly below the level of the wing bud. What is the phenotype of the resulting ectopic limb? Briefly describe the expected expression domains of 1) Shh, 2) Tbx4, and 3) Tbx5 in the resulting ectopic limb bud.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning


QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY