
Concept explainers
(a)
The frequency
(a)
Answer to Problem 19.14P
The frequency
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The mass
The mass
The spring constant (k) is
The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Show the electromagnet with cable and crane arrangement as in Figure (1).
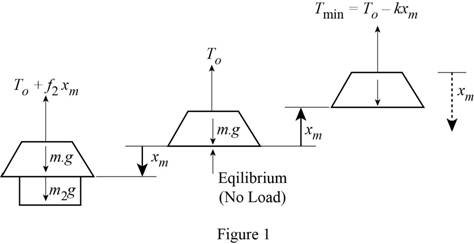
Refer Figure (1), when the electromagnet is off, the tension in the cable is equal to the force due to the mass of the electromagnet.
Express the force balance equation for the first case.
Here,
Calculate the natural circular frequency
Substitute
Calculate the natural frequency
Substitute
By referring the Figure 1, when the electromagnet is on, the tension in the cable is equal to the force due to the mass of the electromagnet and that due to mass of the scrap steel.
Express the force balance equation for the second case.
Here,
Substitute Equation (1) in Equation (2).
Calculate the amplitude
Substitute
Calculate the maximum velocity
Substitute
Therefore, the frequency
(b)
The minimum tension
(b)
Answer to Problem 19.14P
The minimum tension
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The mass
The mass
The spring constant (k) is
The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
The minimum value of tension occurs when the displacement (x) is maximum at upward direction
Express the minimum tension
Substitute Equations (1) and (3) in Equation (4).
Calculate the minimum tension
Substitute 150 kg for
Therefore, the minimum tension
(c)
The velocity
(c)
Answer to Problem 19.14P
The velocity
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The mass
The mass
The spring constant (k) is
The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Express the displacement (x) of the simple harmonic motion at any instant.
Here,
When time (t) is 0, the initial displacement is
Substitute 0 for t and
For the above equation to satisfy the value of
Calculate the velocity
Substitute
Therefore, the velocity
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- **Problem 8-45.** The man has a mass of 60 kg and the crate has a mass of 100 kg. If the coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is \( \mu_s = 0.4 \) and between the crate and the ground is \( \mu_c = 0.3 \), determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. **Diagram Explanation:** The diagram illustrates a scenario where a man is attempting to pull a crate using a rope-and-pulley system. The setup is as follows: - **Crate (C):** Positioned on the ground with a rope attached. - **Rope:** Connects the crate to a pulley system and extends to the man. - **Pulley on Tree:** The rope runs over a pulley mounted on a tree which redirects the rope. - **Angles:** - The rope between the crate and tree forms a \(30^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - The rope between the tree and the man makes a \(45^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - **Man (A):** Pulling on the rope with the intention of moving the crate. This arrangement tests the…arrow_forwardplease solve this problems follow what the question are asking to do please show me step by steparrow_forwardplease first write the line action find the forces and them solve the problem step by steparrow_forward
- please solve this problem what the problem are asking to solve please explain step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forward
- please solve this problem for me the best way that you can explained to solve please show me the step how to solvearrow_forwardplese solbe this problem and give the correct answer solve step by step find the forces and line actionarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problems first write the line of action and them find the forces {fx=0: fy=0: mz=0: and them draw the shear and bending moment diagram. please explain step by steparrow_forward
- please solve this problem step by step like human and give correct answer step by steparrow_forwardPROBLEM 11: Determine the force, P, that must be exerted on the handles of the bolt cutter. (A) 7.5 N (B) 30.0 N (C) 52.5 N (D) 300 N (E) 325 N .B X 3 cm E 40 cm cm F = 1000 N 10 cm 3 cm boltarrow_forwardUsing the moment-area theorems, determine a) the rotation at A, b) the deflection at L/2, c) the deflection at L/4. (Hint: Use symmetry for Part a (θA= - θB, or θC=0), Use the rotation at A for Parts b and c. Note that all deformations in the scope of our topics are small deformation and for small θ, sinθ=θ).arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





