
BIO Effect of
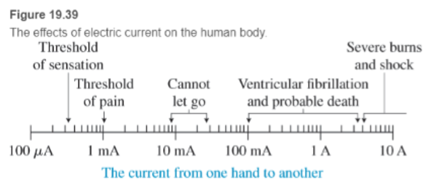
A potential difference across two parts of the body (for example, the 120-V potential difference from a wall socket from one hand to the other or from the hands to the feet) can initiate an electric current in the body that stimulates nerve endings and triggers nerve signals that cause muscular contraction. Even worse, the current in the body can upset the rhythmic electrical operation of the heart. The heart muscles might be stimulated randomly in what is called ventricular fibrillation—a random contraction of the ventricles, which can be deadly. A rough guide to the effects of electric current on the body at different current levels is provided in Figure 19.39. Under dry conditions, human skin has high electrical resistance. Wet skin dramatically lowers the body’s resistance and makes electrocution more likely to occur.
Why is it dangerous to place a hair dryer, radio, or other electric appliance that is plugged into a wall socket near a bathtub?
a. The water provides a
b. If the appliance is accidentally knocked into the tub while a person is bathing, large currents could pass through the person’s low-resistance body because of the 120-V potential difference that powers the appliance.
c. There is no potential for danger, because electric appliances are grounded.
d. a and b
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK COLLEGE PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Example Two charges, one with +10 μC of charge, and another with - 7.0 μC of charge are placed in line with each other and held at a fixed distance of 0.45 m. Where can you put a 3rd charge of +5 μC, so that the net force on the 3rd charge is zero?arrow_forward* Coulomb's Law Example Three charges are positioned as seen below. Charge 1 is +2.0 μC and charge 2 is +8.0μC, and charge 3 is - 6.0MC. What is the magnitude and the direction of the force on charge 2 due to charges 1 and 3? 93 kq92 F == 2 r13 = 0.090m 91 r12 = 0.12m 92 Coulomb's Constant: k = 8.99x10+9 Nm²/C² ✓arrow_forwardMake sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as wellarrow_forward

 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





