
Interpretation: The structure of three salts formed needs to be determined if 0.27 g of octahedral complex of Cr reacts with strong dehydrating agent and lost mass of 0.036 g. Reaction of 270 mg of second salt with same dehydrating agent show mass loss of 18 mg. The 3rd salt did not lose any mass while treating with dehydrating agent.
Given:
Concept Introduction:
Crystal field theory is the theory given to explain the bonding in the coordination complexes. As ligand approaches towards the metal ion, the d-orbital of metal ion divide according to the energy of metal ion. On the basis of energy and degeneracy, the d-orbital can be classified as
In octahedral complex, the
Answer to Problem 84AE
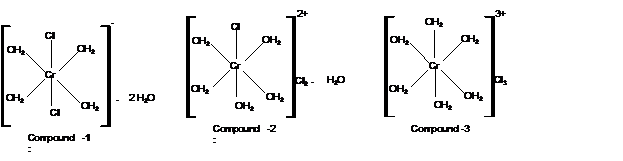
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Addition of excess of aqueous silver nitrate to 100.0 mL portion of 0.100 M solution of each salt forms silver chloride,
- 1st solution= 1430 mg AgCl
- 2nd solution = 2870 mg AgCl
- 3rd solution = 4300 mg AgCl
Two salts are green and one is violet here.
Compound 1:
Calculate moles of water of hydration:
With 2 moles of water; the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 1430 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Calculate moles of water of hydration:
With 1 moles of water; the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 2870 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Compound 3:
Moles of water of hydration is 0 as no water lose is there. Thus the formula must be
Mass of AgCl = 4300 mg
Check the mass of Cl in
Hence the structure of complexes should be:
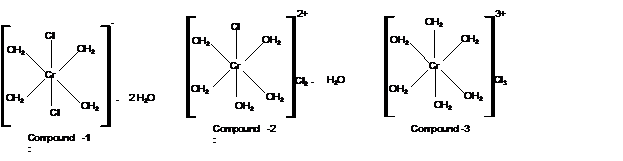
Thus,
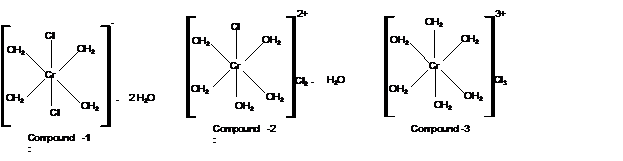
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- Calculate the ionization energy of He+ and Li²+ ions in their ground states. Thannnxxxxx sirrr Ahehehehehejh27278283-4;*; shebehebbw $+$;$-;$-28283773838 hahhehdvaarrow_forwardPlleeaasseee solllveeee question 3 andd thankss sirr, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee don't use AIarrow_forwardCalculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forward
- 4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward
- 3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning


