
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic (IUPAC) name of each group substituent in the given organic molecules should be draw and identified.
Concept introduction:
The several organic compounds can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).
The IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix: Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
For example the saturated hydrocarbons not only from only carbon-hydrogen bonds rather than the carbon-carbon bonds that have added hydrogen atoms. These
Suffix: Denotes the presence of
Root word: It represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
To identify: The systematic (stereo chemical) name for the given molecule (a).
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
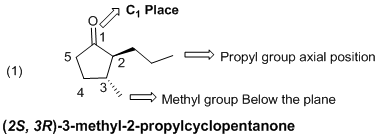
The given molecule (a) is drawn as above, in the case the carbonyl group is part of carbonyl group of a five membered ring, so the given molecule is cyclopentane-1-one. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is cyclic in nature which contains of 5 carbons one keto group (-C=O). Hence root name of the molecule is ‘cyclopentane-1-one’. Since it is an alkane with five carbons, one keto then ‘1-pentanone’ will be the functional carbon chain name.
Further the molecule (a) one cyclic
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (a) is (2S, 3R)-3-methyl-2-propylcyclopentanone.
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic (IUPAC) name of each group substituent in the given organic molecules should be draw and identified.
Concept introduction:
The several organic compounds can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).
The IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix: Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
For example the saturated hydrocarbons not only from only carbon-hydrogen bonds rather than the carbon-carbon bonds that have added hydrogen atoms. These alkanes have to prefix ‘cyclo’ due to the configuration of rings of carbon atoms.
Suffix: Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. For example alkene molecules, suffix will be ‘ene’. (Or) If the presence of completely saturated alkane molecules, suffix will be ‘ane’.
Root word: It represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
To identify: The systematic (stereo chemical) name for the given molecule (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
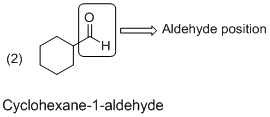
The given molecule (b) is drawn; the parent carbon skeleton is cyclic nature which contains 6 carbons one keto group. Hence root name of the molecule is cyclohexane-1-carbaldehyde. Here given compound with six carbon atoms, one keto groups then cyclohexane
The cyclic compound containing a one aldehyde (
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (b) is ‘Cyclohexane-1-aldehyde’ (aldehyde group is connected to a six membered ring at C1 place).
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic (IUPAC) name of each group substituent in the given organic molecules should be draw and identified.
Concept introduction:
The several organic compounds can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).
The IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix: Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
For example the saturated hydrocarbons not only from only carbon-hydrogen bonds rather than the carbon-carbon bonds that have added hydrogen atoms. These alkanes have to prefix ‘cyclo’ due to the configuration of rings of carbon atoms.
Suffix: Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. For example alkene molecules, suffix will be ‘ene’. (Or) If the presence of completely saturated alkane molecules, suffix will be ‘ane’.
Root word: It represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
To identify: The systematic (stereo chemical) name for the given molecule (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
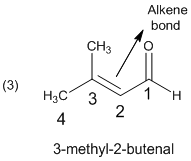
The given molecule is drawn as shown above. This compound (c) is an one aldehyde group with a parent of four carbon, so the parent should be butanol. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is contains 4 carbons one double bond, which indicated by changing ‘an’ to ‘en’ as in propane into propene.
In molecule (c) parent (or) functional group is numbered so that the
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (c) is 3-methyl-2-butenal.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic (IUPAC) name of each group substituent in the given organic molecules should be draw and identified.
Concept introduction:
The several organic compounds can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).
The IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix: Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
For example the saturated hydrocarbons not only from only carbon-hydrogen bonds rather than the carbon-carbon bonds that have added hydrogen atoms. These alkanes have to prefix ‘cyclo’ due to the configuration of rings of carbon atoms.
Suffix: Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. For example alkene molecules, suffix will be ‘ene’. (Or) If the presence of completely saturated alkane molecules, suffix will be ‘ane’.
Root word: It represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
To identify: The systematic (stereo chemical) name for the given molecule (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
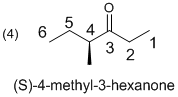
The given linear molecule is drawn as shown above. The parent is a chain of six carbon atoms, with the carbonyl group at C3, so the parent is 3-hexanone. Further the identified number of substituents, above the compound is only one methyl group at C4 position.
Hence the assign a configuration to the chirality center for the molecule (d) is (S)-4-methyl-3-hexanone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- Consider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forward
- What is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





